Abstract
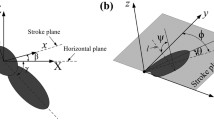
The movement of the halteres during fixed flight was video recorded under stroboscopic illumination phase coupled to the wing beat. The halteres swing in a rounded triangular manner through an angle of almost 80° in vertical planes tilted backwards from the transverse plane by ca. 30° (Figs. 1, 2).
The physics of the halteres are described in terms of a general formula for the force acting onto the endknob of the moving haltere during rotations and linear accelerations of the fly (Eq. 1). On the basis of the experimentally determined kinematics of the haltere, the primary forces and the forces dependent on angular velocity and on angular acceleration are calculated (Figs. 3, 4).
Three distinct types of angular velocity dependent (Coriolis) forces are generated by rotations about 3 orthogonal axes. Thus, in principle one haltere could detect all rotations in space (Fig. 6).
The angular acceleration dependent forces have the same direction and frequency as the Coriolis forces, but they are shifted in phase by 90°. Thus, they could be evaluated in parallel and independently from the Coriolis forces. They are, however, much smaller than the Coriolis forces for oscillation frequencies of the fly up to 20 Hz (Fig. 5). From these considerations it is concluded that Coriolis forces play the major role in detecting body rotations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Demoll R (1918) Der Flug der Insekten und der Vögel. Gustav Fischer, Jena
Derham W (1711) Physico-Theology. London 1711–1712
Faust R (1952) Untersuchungen zum Halterenproblem. Zool Jahrb Physiol 63:325–366
Fraenkel G (1939) The function of the halteres of flies. Proc Zool Soc Lond A 109:69–78
Fraenkel G, Pringle JWS (1938) Halteres of flies as gyroscopic organs of equilibrium. Nature 141:919–921
Giliomee JH (1967) Morphology and taxonomy of adult males of the family Coccidae (Homoptera: Coccidae). Bull Brit Mus Entomol Suppl 7
Gnatzy W, Grünert U, Bender M (1987) Campaniform sensilla of Calliphora vicina (Inserta, Diptera). I. Topography. Zoomorphology 106:312–319
Hengstenberg R (1984) Roll-stabilization during flight of the blowfly's head and body by mechanical and visual cues. In: Varjú D, Schnitzler HU (eds) Localization and orientation in biology and engineering. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 121–134
Hengstenberg R (1988) Mechanosensory control of compensatory head roll during flight in the blowfly Calliphora erythrocephala Meig. J Comp Physiol A 163:151–165
Hengstenberg R, Sandeman DC, Hengstenberg B (1986) Compensatory head roll in the blowfly Calliphora during flight. Proc R Soc Lond B 227:455–482
Hirth C (1981) Elektrophysiologische Untersuchungen über die Bildung der Impulsmuster in den neuromotorischen Systemen nicht-fibrillärer Flugmuskeln von Schmeißfliegen (Calliphora). Dissertation, Universität Düsseldorf
Miller PL (1971) The possible stabilizing function of the elytra of Atractocerus brevicornis (L.) (Lymexylidae: Coleoptera) in flight. The Entomologist 104:105–110
Nalbach G (1985) Die Haltere als Drehsinnesorgan. Zulassungsarbeit für das Staatsexamen, Universität Tübingen
Nalbach G (1988) Linear oscillations elicit haltere mediated turning illusions and entrainment in the blowfly Calliphora. Proc Göttingen Neurobiol Conf 16:131
Nalbach G (1989) The gear change mechanism of the blowfly (Calliphora erythrocephala) in tethered flight. J Comp Physiol A 165:321–331
Nalbach G (1991) Verhaltensuntersuchungen zur Funktion der Halteren bei der Schmeißfliege Calliphora erythrocephala mit echten und simulierten Drehreizen. Dissertation, Universität Tübingen
Nalbach G, Hengstenberg R (1986) Die Halteren von Calliphora als Drehsinnesorgan. Verh Dtsch Zool Ges 79:229
Pflugstaedt H (1912) Die Halteren der Dipteren. Z Wiss Zool 100:1–59
Pix W, Nalbach G, Zeil J (1992) The forewings of male Strepsiptera are haltere-like organs of equilibrium. Proc 20th Göttingen Neurobiol Conf, 175
Pringle JWS (1948) The gyroscopic mechanism of the halteres of Diptera. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 233:347–384
Pringle JWS (1957) Insect flight. Cambridge University Press, London
Sandeman DC (1980) Angular acceleration, compensatory head movements and the halteres of flies (Lucilia sericata). J Comp Physiol 136:361–367
Schneider G (1953) Die Halteren der Schmeißfliege (Calliphora) als Sinnesorgane und als mechanische Flugstabilisatoren. Z Vergl Physiol 35:416–458
Thurm U, Stedtler A, Foelix R (1974) Reizwirksame Verformungen der Terminalstrukturen eines Mechanorezeptors. Verh Dtsch Zool Ges 67:37–41
Tracey D (1975) Head movements mediated by halteres in the fly (Musca domestica). Experientia 31:44–45
Ulrich W (1930) Die Strepsipteren-Männchen als Insekten mit Halteren anstelle der Vorderflügel. Z Morphol Ökol Tiere 17:552–624
Varjú D (1977) Systemtheorie für Biologen und Mediziner. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Weinland E (1891) Über die Schwinger (Halteren) der Dipteren. Z Wiss Zool 51:55–166
Weismann A (1864) Die nachembryonale Entwicklung der Musciden nach Beobachtungen an Musca vomitoria und Sarcophaga carnaria. Z Wiss Zool 14:187–336
Wigglesworth VB (1946) Organs of equilibrium in flying insects. Nature 157:655
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nalbach, G. The halteres of the blowfly Calliphora . J Comp Physiol A 173, 293–300 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212693
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212693