Summary
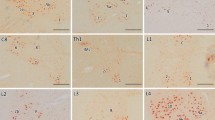
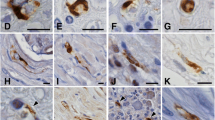
Lower motor neurons of the spinal cord of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Werdnig-Hoffmann's disease (WH), X-linked recessive bulbospinal neuronopathy (X-BSNP) and multiple system atrophy (MSA), all of which were known to involve the lower motor neurons, were immunohistochemically examined by using a monoclonal antibody (Ta-51) specific to phosphorylated epitopes of high molecular weight subunits of neurofilaments. The incidence of Ta-51-positive neurons was significantly increased in ALS, WH and MSA, but not in X-BSNP. Ta-51-positive neurons showed a wide variety of morphological appearances, including neurons with normal appearance, central chromatolysis, simple atrophy and neurons containing massive neurofilamentous accumulation. In aged-control cases, similar Ta-51-positive neurons were observed, although to a much lesser extent. In ALS, spheroids and globules, which were strongly positive for Ta-51, were also significantly increased. Ta-51-positive motor neurons, spheroids and globules appeared in proportional to the number of remaining large motor neurons in ALS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Binet S, Maininger V (1988) Modifications of microtubule proteins in ALS nerve procede detectable histologic and ultrastructural changes. Neurology 38:1596–1600
Bizzi A, Gambetti P (1986) Phosphorylation of neurofilaments is altered in aluminium intoxication. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 71:154–158
Breuer AC, Lynn MP, Atkinson MB, Chou SM, Wilbourn AJ, Marks KE, Culver JE, Fleegler EJ (1987) Fast axonal transport in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: an intra-axonal organelle traffic analysis. Neurology 37:738–748
Carden MJ, Sehlaepfer WW, Lee VM-Y (1985) The structure, biochemical properities and immunogenicity of neurofilament peripheral regions are determined by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 260:9805–9817
Carden MJ, Trojanowski JQ, Schlaepfer WW, Lee VM-Y (1987) Two-stage expression of neurofilament polypeptide during rat neurogenesis with early establishment of adult phosphorylation patterns. J Neurosci 7:3489–3504
Carpenter S (1968) Proximal axonal enlargement in motor neuron disease. Neurology 18:841–851
Chou SM, Fakadej AV (1971) Ultrastructure of chromatolytic motoneurons and anterior spinal roots in a case of Werdnig-Hoffman disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 30:368–379
Clark AW, Parhad IM, Griffin JW, Price DL (1984) Neurofilamentous axonal swellings as a normal finding in the spinal anterior horn of man and other primates. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 43:253–262
Cork LC, Sternberger NH, Sternberger LA, Casanova MF, Struble RG, Price DL (1986) Phosphorylated neurofilament antigens in neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 45:56–64
Cork LC, Troncoso JC, Klavano GG, Johnson ES, Sternberger LA, Sternberger NH, Price DL (1988) Neurofilamentous abnormalities in motor neurons in spontaneously occurring animals disorders. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47:420–431
Delisle MB, Carpenter S (1984) Neurofibrillary axonal swellings and mayorophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 63:241–250
Dickson DW, Yen SH, Suzuki KI, Davies P, Carcia JH, Hirano A (1986) Ballooned neurons in select neurodegenerative diseases contain phosphorylated neurofilament epitopes. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 71:216–223
Forno LS, Sternberger LA, Sternberger NH, Strefling AM, Swanson K, Eng LF (1986) Reaction of Lewy bodies with antibodies to phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated neurofilaments. Neurosci Lett 64:253–258
Gold BG, Price DL, Griffin JW, Rosenfeld J, Hoffmen PN, Sternberger NH, Sternberger LA (1988) Neurofilament antigens in acrylamide neuropathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47:145–157
Hirano A (1982) Aspects of the ultrastructure of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. In: Rowland LP (ed) Human motor neuron disease. Raven Press, New York, pp 75–88
Hirano A, Donnenfeld H, Sasaki S, Nakano I (1984) Fine structural observations of neurofilamentous changes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 43:461–470
Konno H, Yamamoto T, Iwasaki Y, Iizuka H (1986) Shy-Drager syndrome and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: cytoarchitectonic and morphometric studies of sacral autonomic neurons. J Neurol Sci 73:193–204
Kumagai T, Hashizume Y (1982) Morphological and morphometric studies on the spinal cord lesion in Werdnig-Hoffmann disease. Brain Develop 4:87–96
Lee VM-Y, Wu H-L, Schlaepfer WW (1982) Monoclonal antibodies recognize individual neurofilament triplet proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:6089–6092
Lee VM-Y, Carden MJ, Schaepfer WW (1986) Structural similarities and differences between neurofilament proteins from five different species as revealed using monoclonal antibodies. J Neurosci 6:179–188
Lee VM-Y, Carden MJ, Schlaepfer WW, Trojanowski JQ (1987) Monoclonal antibodies distinguish several differentially phosphorylated states of the two largest rat neurofilament subunits (NF-H and NF-M) and demonstrate their existence in the normal nervous system of adult rats. J Neurosci 7:3474–3488
Leigh PN, Dodson A, Swash M, Brion J-P, Anderton BH (1989) Cytoskeletal abnormalities in motor neuron disease, and immunocytochemical study. Brain 112:521–535
Lippa CF, Smith TW (1988) Chromatolytic neurons in Werdnig-Hoffmann disease contain phosphorylated neurofilaments. Acta Neuropathol 77:91–94
Manetto V, Sternberger NH, Perry G, Sternberger LA, Gambetti P (1988) Phosphorylation of neurofilaments is altered in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47:642–653
Moss TH, Lewkowicz SJ (1983) The axon reaction in motor and sensory neurons of mice studied by a monoclonal antibody marker of neurofilament protein. J Neurol Sci 61:267–280
Munoz DG, Greene C, Perl DP, Selkoe DJ (1988) Accumulation of phosphorylated neurofilaments in anterior horn motoneurons of amyotrophic lateral scerlosis patients. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47:9–18
Rasool CG, Selkoe DJ (1985) Sharing of specific antigens by degenerating neurons in Pick's disease and Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med 312:700–705
Rosenfeld J, Dorman ME, Griffin JW, Sternberger LA, Sternberger NH, Price DL (1987) Distribution of neurofilament antigens after axonal injury. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 46:269–282
Sasaki S, Kamei H, Yamane Y, Maruyama S (1988) Swelling of neuronal processes in motor neuron disease. Neurology 38:1114–1118
Schlaepfer WW (1987) Neurofilaments: structure, metabolism and implication in disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 46:117–129
Schmidt ML, Carden MJ, Lee VMY, Trojanowski JQ (1987) Phosphate dependent and independent neurofilament epitopes in the axonal swellings of patients with motor neuron disease and controls. Lab Invest 56:282–294
Sobue G, Sahashi K, Takahashi A, Matsuoka Y, Muroga T, Sobue I (1983) Degenerating compartment and functioning compartment of motor neurons in ALS: possible process of motor neuron loss. Neurology 33:654–657
Sobue G, Hashizume Y, Ohya M, Takahashi A (1986) Shy-Drager syndrome: Neuronal loss depends on size, function and topography in ventral spinal outflow. Neurology 36:404–407
Sobue G, Yasuda T, Mitsuma T, Ross A, Pleasure D (1988) Expression of nerve growth factor receptors in human peripheral neuropathies. Ann Neurol 24:64–72
Sobue G, Hashizume Y, Mukai E, Hirayama M, Mitsuma T, Takahashi A (1989) X-linked recessive bulbospinal neuronopathy, a clinicopathological study. Brain 112:209–232
Sternberger LA, Sternberger NH (1983) Monoclonal antibodies phosphorylated forms of neurofilaments in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:6126–6130
Sternberger LA, Sternberger NH, Ulrich J (1985) Aberant neurofilament phosphorylation in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4274–4276
Terao S, Sobue G, Takeda A, Mitsuma T, Takahashi A (1988) Three-dimensional distribution of spinal anterior horn cells in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Shy Drager syndrome — A study of cytoarchitectonic feature. Clin Neurol (Tokyo) 28:1178–1187
Toroncoso JC, Sternberger NH, Sternberger LA, Hoffmann PN (1986) Immunocytochemical studies of neurofilament antigens in the neurofibrillary pathology induced by aluminium. Brain Res 364:295–300
Toyoshima I, Yamamoto A, Masamune O, Satake M (1989) Phosphorylation of neurofilament proteins and localization of axonal swellings in motor neuron disease. J Neurol Sci 89:269–277
Trojanowski JQ, Walkenstein N, Lee VMY (1986) Expression of neurofilament subunits in neurons of the central and peripheral nervous system: an immunohistochemical study with monoclonal antibodies. J Neurosci 6:650–662
Wiley CA, Love S, Skoglund RR, Lampert PW (1987) Infantile neurodegenerative disease with neuronal accumulation of phosphorylated neurofilaments. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 72:369–376
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants from the Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare, and the National Center for Nervous and Mental Health (NCNMH) of Japan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sobue, G., Hashizume, Y., Yasuda, T. et al. Phosphorylated high molecular weight neurofilament protein in lower motor neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other neurodegenerative diseases involving ventral horn cells. Acta Neuropathol 79, 402–408 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00308716
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00308716