Summary
-
1.
Binaurally time-shifted and intensityunbalanced noise, delivered through earphones, induced owls to respond with a head-orienting behavior similar to that which occurs to free field auditory stimuli.
-
2.
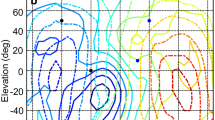
Owls derived the azimuthal and elevational coordinates of a sound from a combination of interaural time difference (ITD) and interaural intensity difference (IID).
-
3.
IID and ITD each contained information about the azimuth and elevation of the signal. Thus, IID and ITD formed a coordinate system in which the axes were non-orthogonal.
-
4.
ITD was a strong determinant of azimuth, and IID was a strong determinant of elevation, of elicited head turn.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IID :
-
Interaural intensity difference
- ITD :
-
Interaural time difference
References
Blauert J (1983) Spatial hearing. The MIT Press, Cambridge (Mass) London
Brown CH, Schessler T, Moody D, Stebbins W (1982) Vertical and horizontal sound localization in primates. J Acoust Soc Am 72:1804–1811
Durlach NI, Colburn HS (1978) Binaural phenomena. In: Carterette EC, Friedman MP (eds) Handbook of perception, vol IV. Academic Press, New York San Francisco London, pp 365–466
Esterly S, Knudsen EI (1987) Tuning for interaural difference cues varies with frequency for space-specific neurons in the owl's optic tectum. Neurosci Abstr 13:1468
Hafter ER, Dye RH, Grilkey RH (1979) Lateralization of tonal signals which have neither onsets nor offsets. J Acoust Soc Am 65:471–477
Houben D, Gourevitch G (1979) Auditory lateralization in monkeys: an examination of two cues serving directional hearing. J Acoust Soc Am 66:1057–1063
Knudsen EI (1980) Sound localization in birds. In: Popper AN, Fay RR (eds) Comparative studies of hearing in vertebrates. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 289–322
Knudsen EI, Blasdel GG, Konishi M (1979) Sound localization by the barn owl (Tyto alba) measured with the search coil technique. J Comp Physiol 133:1–11
Knudsen EI, Konishi M (1979) Mechanisms of sound localization in the barn owl (Tyto alba). J Comp Physiol 133:13–21
Knudsen EI, Konishi M (1980) Monaural occlusion shifts receptive-field locations of auditory midbrain units in the owl. J Neurophysiol 44:687–695
Levy ET, Butler RA (1978) Stimulus factors which influence the perceived externalization of sound presented through headphones. J Auditory Res 18:41–50
Mills AW (1972) Auditory localization. In: Tobias JV (ed) Foundations of modern auditory theory, vol II Academic Press, New York London, pp 303–348
Moiseff A, Konishi M (1981) Neuronal and behavioral sensitivity to binaural time differences in the owl. J Neurosci 1:40–48
Moiseff A, Konishi M (1983) Binaural characteristics of units in the owl's brainstem auditory pathways: precursors of restricted spatial receptive fields. J Neurosci 3:2553–2562
Moiseff A (1989) Binaural disparity cues available to the barn owl for sound localization. J Comp Physiol A 164:629–636
Moushegian G, Jeffress LA (1959) Role of interaural time and intensity differences in the lateralization of low-frequency tones. J Acoust Soc Am 31:1441–1445
Payne RS (1971) Acoustic location of prey by barn owls (Tyto alba). J Exp Biol 54:535–573
Sayers BM, Cherry EC (1957) Mechanism of binaural fusion in the hearing of speech. J Acoust Soc Am 29:973–987
Stern RMJ, Colburn HS (1978) Theory of binaural interaction based on auditory-nerve data. IV. A model for subjective lateral position. J Acoust Soc Am 64:127–140
Sullivan WE, Konishi M (1984) Segregation of stimulus phase and intensity coding in the cochlear nucleus of the barn owl. J Neurosci 4:1787–1799
Takahashi T, Konishi M (1985) Parallel pathways in the owl's brainstem auditory system. Anat Rec 211:191A
Takahashi T, Moiseff A, Konishi M (1984) Time and intensity cues are processed independently in the auditory system of the owl. J Neurosci 4:1781–1786
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moiseff, A. Bi-coordinate sound localization by the barn owl. J. Comp. Physiol. 164, 637–644 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00614506
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00614506