Summary
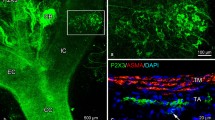
An analysis of the morphology of the carotid sinus nerve in 39 rats revealed that the nerve emerged from the glossopharyngeal nerve (nerve IX) 0.6–1.0 mm beyond the distal extent of the petrosal ganglion. In 68% of cases the nerve consisted of a single bundle of axons; two bundles were present in the other nerves. Near the rostral pole of the carotid body, the nerve divided into multiple bundles of axons. Most axon bundles entered the carotid body, but some instead joined sympathetic nerves from the superior cervical ganglion. Some of the latter group of sinus nerve axons innervated the wall of the carotid sinus. Other presumptive baroreceptor axons reached the carotid sinus from the sinus nerve by first traversing the carotid body.
The sinus nerve had an average length of 2.0 ± 0.13 mm (mean ± S.E.M., range=1.3–2.9 mm,N=15) and was elliptical in cross-section (major axis=77 μm, minor axis=46 μm). The nerve contained an average of 625 axons, 86% of which were unmyelinated. The perineurial sheath that enveloped the circumference of the nerve was comprised of 3 or 4 layers of cells interconnected by gap junctions and tight junctions. Near the carotid body, the perineurium extended into the nerve where it compartmentalized fascicles of axons. The endoneurium consisted mainly of collagenous fibres (mean diameter 40 nm) that were only half the size of those outside the perineurium. Endoneurial connective tissue cells were sparse, being only 5% as numerous as Schwann cells. The one blood vessel in the nerve (mean luminal diameter 12.4 ± 1.2 μm) usually arose from vessels in nerve IX and terminated in a venule at the rostral surface of the carotid body.
Ganglion cells were located in nerve IX near the origin of the sinus nerve and along the length of the sinus nerve itself. All ganglion cells examined were postsynaptic to vesicle-containing nerve terminals, and therefore were presumed to be autonomie rather than sensory. Ganglion cells were more numerous in terminal branches of the sinus nerve on the ventral surface of the carotid body. Most other ganglion cells in the carotid body were located among axons of the ganglioglomerular nerve, although some were associated with a small branch of the vagus nerve. Paraganglia were located within the sinus nerve in 15% of cases, and in another 10% of cases they were found nearby in nerve IX. The paraganglia, which measured approximately 50 × 50 × 100 μm, were innervated by axons that resembled sensory nerves of the carotid body.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, W. E. (1958)The Comparative Morphology of the Carotid Body and Carotid Sinus. Springfield: Thomas.
Ask-Upmark, E. &Hillarp, N.-A. (1961) The fibre size in the carotid sinus nerve of the cat.Acte Anatomica 46, 25–9.
Biscoe, T. J. &Sampson, S. R. (1968) Rhythmical and nonrhythmical spontaneous activity recorded from the central cut end of the sinus nerve.Journal of Physiology 196, 327–38.
Bolter, C. P. &Ledsome, J. R. (1980) Influence of cervical sympathetic nerve stimulation on carotid sinus baroreceptor afferents.Experientia 36, 1301–2.
Boyd, J. D. (1937) The development of the human carotid body.Contributions to Embryology 152, 1–31.
Chiarini, C. N. (1965) Ricerche anatomiche sull'innervazione delle zone pressorecettive seno-carotidee, aortiche e polmonari nel ratto.Archivio Italiano di Anatomia e di Embriologia (Firenze) 70, 237–52.
Clarke, J. A. &Daly, M. D. B. (1981) A comparative study of the distribution of carotid body type-I cells and periadventitial type-I cells in the carotid bifurcation regions of the rabbit, rat, guinea-pig and mouse.Cell and Tissue Research 220, 753–72.
De Castro, F. (1926) Sur la structure et l'innervation de la glande intercarotidienne (glomus caroticum) de l'homme et des mammifères, et sur un nouveau système d'innervation autonome du nerf glossopharyngien.Travaux du Laboratoire de Recherches Biologiques de l'Université de Madrid 24, 365–432.
De Castro, F. (1928) Sur la structure et l'innervation du sinus carotidien de l'homme et des mammifères. Nouveaux faits sur l'innervation et la fonction du glomus caroticum.Travaux du Laboratoire de Recherches Biologiques de l'Université de Madrid 25, 330–80.
De Castro, F. (1951) Sur la structure de la synapse dans les chemorecepteurs: Leur mécanisme d'excitation et rôle dans la circulation sanguine locale.Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 22, 14–43.
De Castro, F. (1962) Sur la vascularisation et l'innervation des corpuscules carotidiens aberrants.Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Thérapie 139, 212–24.
Eyzaguirre, C. &Levin, J. (1961) The effect of sympathetic stimulation on carotid nerve activity.Journal of Physiology 159, 251–67.
Eyzaguirre, C. &Uchizono, K. (1961) Observations on the fibre content of nerves reaching the carotid body of the cat.Journal of Physiology 159, 268–81.
Fidone, S. J. &Sato, A. (1969) A study of chemoreceptor and baroreceptor A and C-fibres in the cat carotid nerve.Journal of Physiology 205, 527–48.
Gerard, M. W. &Billingsley, P. R. (1923) The innervation of the carotid body.Anatomical Record 25, 391–400.
Grillo, M. A. (1978) Ultrastructural evidence for a sensory innervation of some SIF cells in rat superior cervical ganglia.Anatomical Record 190, 407.
Hering, H. E. (1924) Der Sinus caroticus an der Ursprungsstelle der Carotis interna als Ausgangsort eines hemmenden Herzreflexes und eines depressorischen Gefässreflexes. II. Mitteilung uber den Karotisdruckversuch.Medizinische Wochenschrift 71, 3–6.
Heymans, C., Bouckaert, J. J. &Dautrebande, L. (1930) Sinus carotidien et réflexes respiratoires, IL Influences respiratoires réflexes de l'acidose de l'alcalose, de l'anhydride carbonique, de l'ion hydrogène et de l'anoxémie. Sinus carotidiens et échanges respiratoirs dans les poumons et au dela des poumons.Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Thérapie 39, 400–48.
Kezdi, P. (1954) Control by the superior cervical ganglion of the state of contraction and pulsatile expansion of the carotid sinus arterial wall.Circulation Research 11, 367–71.
Koizumi, K. &Sato, A. (1969) Influence of sympathetic innervation on carotid sinus baroreceptor activity.American Journal of Physiology 216, 321–9.
Kondo, H. (1977) Innervation of SIF cells in the superior cervical and nodose ganglia: An ultrastructural study with serial sections.Biologie Cellulaire 30, 253–64.
Majcherczyk, S., Coleridge, J. C. G., Coleridge, H. M., Kaufman, M. P. &Baker, D. G. (1980) Carotid sinus nerve efferents: properties and physiological significance.Federation Proceedings 39, 2662–7.
Matthews, M. R. (1976) Synaptic and other relationships of small granule-containing cells (SIF cells) in sympathetic ganglia. InChromaffin, Enterochromaffin and Related Cells (edited byCoupland, R. E. andFujita, T.), pp. 131–46. Amsterdam: Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company.
McDonald, D. M. (1981) Peripheral chemoreceptors: structure-function relationships of the carotid body. InReguation of Breathing, Part I (edited byHornbein, T. F.), pp. 105–319. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc.
McDonald, D. M. (1983) Morphology of the rat carotid sinus nerve: II. Number and size of axons.Journal of Neurocytology 12, 373–92.
McDonald, D. M. &Blewett, R. W. (1981) Location and size of carotid body-like organs (paraganglia) revealed in rats by the permeability of blood vessels to Evans blue dye.Journal of Neurocytology 10, 607–43.
McDonald, D. M. &Larue, D. T. (1983) Ultrastructure and connections of blood vessels supplying the rat carotid body and carotid sinus.Journal of Neurocytology 12, 117–53.
McDonald, D. M. &Mitchell, R. A. (1975) The innervation of glomus cells, ganglion cells and blood vessels in the rat carotid body: a quantitative ultrastructural analysis.Journal of Neurocytology 4, 177–230.
McDonald, D. M. &Mitchell, R. A. (1981) The neural pathway involved in ‘efferent inhibition’ of chemoreceptors in the cat carotid body.Journal of Comparative Neurology 201, 457–76.
McEwen, L. M. (1956) The effect on the isolated rabbit heart of vagal stimulation and its modification by cocaine, hexamethonium and ouabain.Journal of Physiology 131, 678–89.
Mishra, J. &Hess, A. (1978) Fiber size content and origin in the rat carotid sinus nerve.Neuroscience Abstracts 4, 516.
Neil, E. &O'regan, R. G. (1971) The effects of electrical stimulation of the distal end of the cut sinus and aortic nerves on peripheral arterial chemoreceptor activity in the cat.Journal of Physiology 215, 15–32.
Rees, P. M. (1967a) Observations on the fine structure and distribution of presumptive baroreceptor nerves at the carotid sinus.Journal of Comparative Neurology 131, 517–48.
Rees, P. M. (1967b) The distribution of biogenic amines in the carotid bifurcation region.Journal of Physiology 193, 245–53.
Reis, D. J. &Fuxe, K. (1968) Adrenergic innervation of the carotid sinus.American Journal of Physiology 215, 1054–7.
Richardson, K. C. (1969) The fine structure of autonomie nerves after vital staining with methylene blue.Anatomical Record 164, 359–78.
Sampson, S. R. &Mills, E. (1970) Effects of sympathetic stimulation on discharges of carotid sinus baroreceptors.American Journal of Physiology 218, 1650–3.
Sapru, H. N. &Krieger, A. J. (1977) Carotid and aortic chemoreceptor function in the rat.Journal of Applied Physiology: Respiration, Environment, Exercise Physiology 42, 344–8.
Smith, C. (1924) The origin and development of the carotid body.American Journal of Anatomy 34, 87–131.
Stanton, P. D. &Hinrichsen, C. F. L. (1980) Monoaminergic innervation of the carotid sinus in mammals: a histochemical study.Acta Anatomica 108, 34–44.
Thomas, P. K. (1963) The connective tissue of peripheral nerve: an electron microscope study.Journal of Anatomy 97, 35–44.
Tuttle, R. S. &Mccleary, M. (1982) Sinusal afferents supplying superior cervical ganglion.American Journal of Physiology 242, H168-H171.
Winter, B. (1972) Bilateral carotid body resection for asthma and emphysema.International Surgery 57, 458–66.
Wurster, R. D. &Trobiani, S. (1973) Effects of cervical sympathetic stimulation on carotid occlusion reflexes in cats.American Journal of Physiology 225, 978–81.
Yates, R. D. &Chen, I. (1980) An electron microscopic study of the baroreceptors in the internal carotid artery of the spontaneously hypertensive rat.Cell and Tissue Research 205, 473–83.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McDonald, D.M. Morphology of the rat carotid sinus nerve. I. Course, connections, dimensions and ultrastructure. J Neurocytol 12, 345–372 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01159380
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01159380