Summary
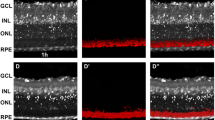
Cellular retinol-, retinaldehyde- and retinoic acid-binding proteins were localized in rat retina during pre- and postnatal development by indirect immunofluorescence. Cryostat tissue sections were prepared daily from embryonic day 11 until the day of birth (E11–22) and from postnatal days 1–32 (P1–32). Cellular retinaldehyde- and retinol-binding proteins were first detected in retinal pigment epithelium on E13 and E18, respectively, and in Müller cells at P1 and P15. Parallel studies showed that in adult retina cellular retinoic acid-binding protein is present in a subpopulation of GABAergic amacrine cells. During retinal differentiation, cellular retinoic acid-binding protein was first detected at E18 in cells sclerad to the developing inner plexiform layer, suggesting that this binding protein is expressed in amacrine cells very early during differentiation. During early ocular morphogenesis, cellular retinoic acid-binding protein was present in mesenchymal cells enveloping the eye (E12–15), in the neuroblastic layer of the retina (E13–15), in the nerve fibre layer (E14–15), and the developing optic nerve (E15). Our results suggest that retinoic acid, the natural ligand of cellular retinoic acid-binding protein, may be involved in neuronal differentiation in the inner retina. The studies further support a role for cellular retinoic acid-binding protein in mediating the effects of retinoic acid on developing neural crest cells and raise new questions about the role of cellular retinaldehyde-binding protein in the visual cycle and during development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blaner, W. S., Das, K., Mertz, J. R., Das, S. R. &Goodman, D. S. (1986) Effects of dietary retinoic acid on cellular retinol- and retinoic acid-binding protein levels in various rat tissues.Journal of Lipid Research 27, 1084–8.
Bok, D., Ong, D. E. &Chytil, F. (1984) Immunocytochemical localization of cellular retinol-binding proteins in the rat retina.Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 25, 877–83.
Bunt-Milam, A. H. &Saari, J. C. (1983) Immunocytochemical localization of two retinoid-binding proteins in vertebrate retina,Journal of Cell Biology 97, 703–12.
Carter-Dawson, L., Alvarez, R. A., Fong, S.-L., Liou, G. I., Sperling, H. G. &Bridges, C. D. B. (1986) Rhodopsin, 11-cis vitamin A, and interstitial retinolbinding protein (IRBP) during retinal development in normal andrd mutant mice.Developmental Biology 116, 431–8.
Chytil, F. &Ong, D. E. (1984) Cellular retinoid-binding proteins. InThe Retinoids (edited bySporn, M. B., Roberts, A. B. &Goodman, D. S.), Vol. 2, pp. 90–123. San Diego: Academic Press.
Chytil, F. &Ong, D. E. (1987) Intracellular vitamin Abinding. proteins.Annual Review of Nutrition 7, 321–35.
Cullum, M. E., Johnson, B. C. &Zile, M. H. (1984) Comparison of fetal and adult retinol and retinoic acid binding proteins in bovine serum and pigment epithelium.International Journal of Vitamin and Nutrition Research 54, 297–305.
Dencker, L., D'Argy, R., Danielsson, B. R. G., Ghantous, H. &Sperber, G. O. (1987) Saturable accumulation of retinoic acid in neural and neural crest derived cells in early embryonic development.Developmental Pharmacology and Therapeutics 10, 212–23.
Dowling, J. E. &Wald, G. (1960) The biological action of vitamin A acid.Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (USA) 46, 587–608.
Eisenfeld, A. J., Bunt-Milam, A. H. &Saari, J. C. (1985) Localization of retinoid-binding proteins in developing rat retina.Experimental Eye Research 41, 299–304.
Floyd, E. E. &Jetten, A. M. (1988) Editorial. Retinoids, growth factors, and the tracheobronchial epithelium.Laboratory Investigation 59, 1–4.
Fuchs, E. (1988) Keratins as biochemical markers of epithelial differentiation.Trends in Genetics 4, 277–81.
Gaur, V. P., De Leeuw, A. M., Milam, A. H. &Saari, J. C. (1990) Localization of cellular retinoic acid-binding protein to amacrine cells of rat retina.Experimental Eye Research (in press).
Gaur, V. P., Saari, J. C., Bunt-Milam, A. H. &Garwin, G. G. (1986) Monoclonal antibodies against bovine cellular retinaldehyde-binding protein. Characterization and use in immunocytochemistry.Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science (Supplement) 27, 191.
Giguere, V., Ong, E. S., Segui, P. &Evans, R. M. (1987) Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid.Nature 330, 624–9.
Giguere, V., Ong, E. S., Evans, R. M. &Tabin, C. J. (1989) Spatial and temporal expression of the retinoic acid receptor in the regenerating amphibian limb.Nature 337, 566–9.
Goodman, D. S. (1984) Vitamin A and retinoids in health and disease.New England Journal of Medicine 310, 1023–31.
Grün, G. (1982) The development of the vertebrate retina: a comparative survey.Advances in Anatomy, Embryology and Cell Biology 78, 1–83.
Lund, R. D. &Bunt, A. H. (1976) Prenatal development of central optic pathways in albino rats.Journal of Comparative Neurology 165, 247–64.
Maden, M., Ong, D. E., Summerbell, D. &Chytil, F. (1988) Spatial distribution of cellular protein binding to retinoic acid in the chick limb bud.Nature 335, 733–5.
Milam, A. H., de Leeuw, A. M., Gaur, V. P. &Saari, J. C. (1990) Immunolocalization of cellular retinoic acidbinding protein to Müller cells and/or a subpopulation of GABA positive amacrine cells in retinas of different species.Journal of Comparative Neurology (in press).
Momoi, T., Kitamoto, T., Kasuya-Sato, J., Seno, H. &Momoi, M. (1989) Developmental changes in the expression of cellular retinoic acid binding protein (CRABP) in the central nervous system of the chick embryo.Biomedical Research 10, 43–8.
Ong, D. E., Crow, J. A. &Chytil, F. (1982) Radioimmunochemical determination of cellular retinol- and retinoic acid-binding proteins in cytosols of rat tissues.Journal of Biological Chemistry 257, 13385–9.
Petkovich, M., Brand, N. J., Krust, A. &Chambon, P. (1987) A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors.Nature 330, 444–50.
Pratt, R. M., Goulding, E. H. &Abbott, B. D. (1987) Retinoic acid inhibits migration of cranial neural crest cells in the cultured mouse embryo.Journal of Craniofacial Genetics and Developmental Biology 7, 205–17.
Roberts, A. B. &Sporn, M. B. (1984) Cellular biology and biochemistry of the retinoids. InThe Retinoids (edited bySporn, M. B., Roberts, A. B. &Goodman, D. S.), Vol. 2, pp. 210–86. San Diego: Academic Press.
Saari, J. C. (1989) Enzymes and proteins of the visual cycle. InProgress in Retinal Research (edited byOsborne, N. N. &Chader, G. J.), Vol. 8 (in press). Oxford: Pergamon Press.
Saari, J. C. &Bredberg, D. L. (1982) Enzymatic reduction of 11-cis-retinal bound to cellular retinal-binding protein.Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 716, 266–72.
Saari, J. C., Bredberg, L. &Garwin, G. G. (1982) Identification of the endogenous retinoids associated with three cellular retinoid-binding proteins from bovine retina and retinal pigment epithelium.Journal of Biological Chemistry 257, 13329–33.
Saari, J. C., Bunt-Milam, A. H., Bredberg, L. &Garwin, G. G. (1984) Properties and immunocytochemical localization of three retinoid-binding proteins from bovine retina.Vision Research 24, 1595–1603.
Saari, J. C. &Futterman, S. (1976) Separable binding proteins for retinoic acid and retinol in bovine retina.Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 444, 789–93.
Saari, J. C., Futterman, S. &Bredberg, L. (1978) Cellular retinol- and retinoic acid-binding proteins of bovine retina.Journal of Biological Chemistry 253, 6432–6.
Thaller, C. &Eichele, G. (1987) Identification and spatial distribution of retinoids in the developing chick limb bud.Nature 327, 625–8.
Wald, G. (1968) The molecular basis of visual excitation.Nature 219, 800–7.
Wiggert, B., Bergsma, D. R., Helmsen, R. &Chader, G. J. (1978) Vitamin A receptors. Retinoic acid binding in ocular tissues.Biochemical Journal 169, 87–94.
Wiley, M. J., Cauwenbergs, P. &Taylor, I. M. (1983) Effects of retinoic acid on the development of the facial skeleton in hamsters: early changes involving cranial neural crest cells.Acta Anatomica 116, 180–92.
Wolbach, S. B. &Howe, P. R. (1925) Tissue changes following deprivation of fat soluble A vitamin.Journal of Experimental Medicine 42, 753–77.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Leeuw, A.M., Gaur, V.P., Saari, J.C. et al. Immunolocalization of cellular retinol-, retinaldehyde- and retinoic acid-binding proteins in rat retina during pre- and postnatal development. J Neurocytol 19, 253–264 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01217303
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01217303