Summary
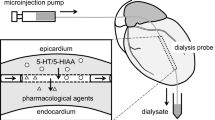
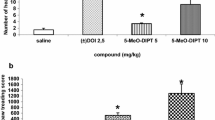
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) synthesis was determined in vivo by measuring the accumulation of 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) in rat frontal cortex after inhibition of aromatic amino acid decarboxylase by administration of m-hydroxybenzylhydrazine (NSD 1015) (100 mg/kg, i.p.). The selective 5-HT reuptake inhibitor, citalopram, the 5-HT1a agonists, (±)8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)-tetralin (8-OH-DPAT), ipsapirone, gepirone and the 5-HT1a/b agonist, 7-trifluoromethyl-4(4-methyl-1-piperazinylpyrolo[1,2-a]-quinoxaline (CGS 12066B), the 5-HT1a/b ligands and β-adrenoceptor antagonists, (±)pindolol and (±)alprenolol, and the non-selective 5-HT ligands, m-chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) and metergoline, all inhibited the synthesis of 5-HT. The 5-HT1a /5-HT2 antagonist, spiperone, alone, had no effect on basal 5-HT synthesis, however it attenuated the effect of 8-OH-DPAT by 56% and CGS 12066B by 39% but only barely that of citalopram by 17%. The selective 5-HT1a antagonist, WAY 100635, which did not modify by itself 5-HT synthesis, had no effect on citalopram-induced reduction of 5-HT synthesis. Neither the 5-HT2 agonist, (±)1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-indophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI) nor the 5-HT2 antagonist, ritanserin, had any effect on the synthesis of 5-HT. In addition, ritanserin did not modify the inhibitory effect of citalopram. Methiothepin was the only compound to increase 5-HT synthesis. These results suggest that the effect of citalopram on the synthesis of 5-HT is not mediated by 5-HT1a or 5-HT2 receptors and that other receptors may be involved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arborelius L, Backhand Höök B, Hacksell U, Svensson TH (1994) The 5-HT1a receptor antagonist (S)-UH-301 blocks the (R)-8-OH-DPAT-induced inhibition of serotonergic dorsal raphe cell firing in the rat. J Neural Transm 96: 179–186
Artigas F (1993) 5-HT and antidepressants: new views from microdialysis studies. Trends Pharmacol Sci 14: 262
Artigas F, Perez V, Alvarez E (1994) Pindolol induces a rapid improvement of depressed patients treated with serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51: 248–251
Briley M, Moret C (1988) Modulation of 5-HT autoreceptors probably contributes to the antidepressant action of 5-HT uptake blockers. In: Briley M, Fillion G (eds) New concepts in depression. Macmillan Press, London, pp 15–24
Briley M, Moret C (1993) Neurobiological mechanisms involved in antidepressant therapies. Clin Neuropharmacol 16: 387–400
Briley M, Chopin P, Marien M, Moret C (1996) Functional neuropharmacology of compounds acting at 5-HT1b/d receptors. In: Baumgarten HG, Göthert M (eds) Handbook of experimental pharmacology. Serotoninergic neurons and 5-HT receptors in the CNS. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo
Carlsson A (1977) Effects of antidepressant agents on monoamine synthesis. In: 13th Symposium Medicum Hoechst, Depressive Disorders. Rome, pp 8–12
Carlsson A, Lindqvist M (1978) Effects of antidepressant agents on the synthesis of brain monoamines. J Neural Transm 43: 73–91
Chaput Y, De Montigny C, Blier P (1986) Effects of a selective 5-HT reuptake blocker, citalopram, on the sensitivity of 5-HT autoreceptors: electrophysiological studies in the rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 333: 342–348
Chopin P, Moret C, Briley M (1994) Neuropharmacology of 5-hydroxytryptamine1b/d receptor ligands. Pharmacol Ther 62: 385–405
Corrodi H, Fuxe K (1969) Decreased turnover in central 5-HT nerve terminals induced by antidepressant drugs of the imipramine type. Eur J Pharmacol 7: 56–59
Davidson C, Stamford JA (1995) Evidence that 5-hydroxytryptamine release in rat dorsal raphe nucleus is controlled by 5-HT1a , 5-HT1b and 5-HT1d autoreceptors. Br J Pharmacol 114: 1107–1109
Fernstrom MH, Massoudi MS, Fernstrom JD (1990) Effect of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)-tetralin on the tryptophan-induced increase in 5-hydroxytryptophan accumulation in rat brain. Life Sci 47: 283–289
Fletcher A, Forster EA, Bill DJ, Brown G, Cliffe IA, Hartley JE, Jones DE, McLenachan A, Stanhope KJ, Critchley DJP, Childs KJ, Middlefell VC, Lanfumey L, Corradetti R, Laporte A-M, Gozlan H, Hamon M, Dourish CT (1996) Electrophysiological, biochemical, neurohormonal and behavioural studies with WAY-100635, a potent, selective and silent 5-HT1a receptor antagonist. Behav Brain Res 73: 337–353
Göthert M (1980) Serotonin-receptor-mediated modulation of Ca2+-dependent 5-hydroxytryptamine release from neurones of the rat brain cortex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 314: 223–230
Göthert M (1982) Modulation of serotonin release in the brain via presynaptic receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 3: 437–440
Hamon M, Cossery JM, Spampinato U, Gozlan H (1986) Are there selective ligands for 5-HT1a and 5-HT1b receptor binding sites in brain? Trends Pharmacol Sci 7: 336–338
Hamon M, Fattaccini C-M, Adrien J, Gallissot M-C, Martin P, Gozlan H (1988) Alterations of central serotonin and doparnine turnover in rats treated with ipsapirone and other 5-hydroxytryptamine1a agonists with potential anxiolytic properties. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246: 745–752
Hamon M, Lanfumey L, El-Mestikawy S, Boni C, Miquel M-C, Bolanos F, Schechter L, Gozlan H (1990) The main features of central 5-HT, receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 3: 349–360
Hjorth S (1993) Serotonin 5-HT1a autoreceptor blockade potentiates the ability of the 5-HT reuptake inhibitor citalopram to increase nerve terminal output of 5-HT in vivo: a microdialysis study. J Neurochem 60: 776–779
Hjorth S, Carlsson A (1985) (−)Pindolol stereospecifically inhibits rat brain serotonin (5-HT) synthesis. Neuropharmacology 24: 1143–1146
Hjorth S, Magnusson T (1988) The 5-HT1a receptor agonist, 8-OH-DPAT, preferentially activates cell body 5-HT autoreceptors in rat brain in vivo. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 338: 463–471
Hjorth S, Carlsson A, Lindberg P, Sanchez D, Wikström H, Arvidsson L-E, Hacksell U, Nilsson JLG (1982) 8-Hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)-tetralin, 8-OH-DPAT, a potent and selective simplified ergot congener with central 5-HT-receptor stimulating activity. J Neural Transm 55: 169–188
Hjorth S, Bengtsson HJ, Milano S, Lundberg JF, Sharp T (1995a) Studies on the role of 5-HT1a autoreceptors and α1-adrenoceptors in the inhibition of 5-HT release. I. BMY7378 and prazosin. Neuropharmacology 34: 615–620
Hjorth S, Suchowski CS, Galloway MP (1995b) Evidence for 5-HT autoreceptormediated, nerve impulse-independent, control of 5-HT synthesis in the rat brain. Synapse 19: 170–176
Hoyer D, Clarke DE, Fozard JR, Hartig PR, Martin GR, Mylecharane EJ, Saxena PR, Humphrey PPA (1994) International union of pharmacology classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Pharmacol Rev 46: 157–203
Humphrey PPA, Feniuk W, Perren MJ, Beresford UM, Skingle M (1990) Serotonin and migraine. Ann NY Acad Sci 600: 587–600
Hutson PH, Sarna GS, O'Connell MT, Curzon G (1989) Hippocampal 5-HT synthesis and release in vivo is decreased by infusion of 8-OH-DPAT into the nucleus raphe dorsalis. Neurosci Lett 100: 276–280
Invernizzi R, Carli M, Di Clemente A, Samanin R (1991) Administration of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin in raphe nuclei dorsalis and medianus reduces serotonin synthesis in the rat brain: differences in potency and regional sensitivity. J Neurochem 56: 243–247
Jolas T, Haj-Dahmane S, Lanfumey L, Fattaccini C-M, Kidd EJ, Adrien J, Gozlan H, Guardiola-Lemaitre B, Hamon M (1993) (−)Tertatolol is a potent antagonist at pre- and postsynaptic serotonin 5-HT1a receptors in the rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 347: 453–463
Middlemiss DN (1988) Autoreceptors regulating serotonin release. In: Sanders-Bush E (ed) The serotonin receptors. Humana Press, Clifton, pp 201–224
Middlemiss DN, Fozard JR (1983) 8-Hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin discriminates between subtypes of the 5-HT, recognition site. Eur J Pharmacol 90: 151–155
Moore NA, Rees G, Sanger G, Perrett L (1993) 5-HT1a -mediated lower lip retraction: effects of 5-HT1a agonists and antagonists. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 46: 141–143
Moret C (1985) Pharmacology of the serotonin autoreceptor. In: Green AR (ed) Neuropharmacology of serotonin. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 21–49
Moret C, Briley M (1988) Sensitivity of the response of 5-HT autoreceptors to drugs modifying synaptic availability of 5-HT. Neuropharmacology 27: 43–49
Moret C, Briley M (1992) Effect of antidepressant drugs on monoamine synthesis in brain in vivo. Neuropharmacology 31: 679–684
Moret C, Briley M (1993a) Which 5-HT receptors are involved in the modulation of 5-HT synthesis by the 5-HT uptake blocker, citalopram? Br J Pharmacol 108: 96P
Moret C, Briley M (1993b) The unique effect of methiothepin on the terminal serotonin autoreceptor in the rat hypothalamus could be an example of inverse agonism. J Psychopharmacol 7: 331–337
Moret C, Briley M (1996) Effects of acute and repeated administration of citalopram on extracellular levels of serotonin in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 295: 189–197
Moret C, Charvéron M, Finberg JPM, Couzinier J-P, Briley M (1985) Biochemical profile of midalcipran (F 2207), 1-phenyl-1-diethyl-aminocarbonyl-2-aminornethylcyclopropane (Z) hydrochloride, a potential fourth generation antidepressant drug. Neuropharmacology 24: 1211–1219
Neale RF, Fallen SL, Boyar WC, Wasley JWF, Martin LL, Stone GA, Glaeser BS, Sinton CM, Williams M (1987) Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of CGS 12066B, a selective serotonin-lB agonist. Eur J Pharmacol 136: 1–9
Nybäck HV, Walters JR, Aghajanian GK, Roth RH (1975) Tricyclic antidepressants: effects on the firing rate of brain noradrenergic neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 32: 302–312
Pauwels PJ, Colpaert FC (1995) The 5-HT1d receptor antagonist GR 127,935 is an agonist at cloned human 5-HT1dα receptor sites. Neuropharmacology 34: 235–237
Pettibone DJ, Pfleuger AB (1984) Effects of methiothepin and lysergic acid diethylamide on serotonin release in vitro and serotonin synthesis in vivo: possible relation to serotonin autoreceptor function. J Neurochem 43: 83–90
Pineyro G, Blier P (1996) Regulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine release from rat midbrain raphe nuclei by 5-hydroxytryptamine1d receptors: effect of tetrodotoxin, G protein inactivation and long-term antidepressant administration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 276: 697–707
Pineyro G, de Montigny C, Blier P (1995) 5-HT1d Receptors regulate 5-HT release in the rat raphe nuclei. In vivo voltammetry and in vitro superfusion studies. Neuropsychopharmacology 13: 249–260
Rigdon GC, Wang CM (1991) Serotonin uptake blockers inhibit the firing of presumed serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons in vitro. Drug Dev Res 22: 135–140
Roberts C, Thorn L, Price GW, Middlemiss DN, Jones BJ (1994) Effect of the selective 5-HT1d receptor antagonist, GR 127935, on in vivo 5-HT release, synthesis and turnover in the guinea-pig frontal cortex. Br J Pharmacol 112: 489P
Schechter LE, Bolanos FJ, Gozlan H, Lanfumey L, Haj-Dahmane S, Laporte A-M, Fattaccini C-M, Hamon M (1990) Alterations of central serotoninergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission in rats chronically treated with ipsapirone: biochemical and electrophysiological studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 255: 1335–1347
Schubert J, Nybäck H, Sedvall G (1970) Effect of antidepressant drugs on accumulation and disappearance of monoamines formed in vivo from labelled precursors in mouse brain. J Pharm Pharmacol 22: 136–139
Sharp T, Bramwell SR, Clark D, Grahame-Smith DG (1989) In vivo measurement of brain extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine using microdialysis; changes in relation to 5-hydroxytryptaminergic neuronal activity. J Neurochem 53: 234–240
Sharp T, McQuade R, Bramwell S, Hjorth S (1993) Effect of acute and repeated administration of 5-HT1a receptor agonists on 5-HT release in rat brain in vivo. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 348: 339–346
Sheard MH, Zolovick A, Aghajanian GK (1972) Raphe neurons: effect of tricyclic antidepressant drugs. Brain Res 43: 690–694
Sprouse JS, Aghajanian GK (1987) Electrophysiological responses of serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons to 5-HT1a and 5-HT1b agonists. Synapse 1: 3–9
Sprouse JS, Aghajanian GK (1988) Responses of hippocampal pyramidal cells to putative serotonin 5-HT1a and 5-HT1b agonists: a comparative study with dorsal raphe neurons. Neuropharmacology 27: 707–715
Starkey SJ, Skingle M (1994) 5-HT1d as well as 5-HT1a autoreceptors modulate 5-HT release in the guinea-pig dorsal raphe nucleus. Neuropharmacology 33: 393–402
Svensson TH (1978) Attenuated feed-back inhibition of brain serotonin synthesis following chronic administration of imipramine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 302: 115–118
Zgombick JM, Schechter LE, Adham N, Kucharewicz SA, Weinshank RL, Branchek TA (1996) Pharmacological characterizations of recombinant human 5-HT1dα and 5-HT1dβ receptor subtypes coupled to adenylate cyclase inhibition in clonal cell lines: apparent differences in drug intrinsic efficacies between human 5-HT1d subtypes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 354: 226–236
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moret, C., Briley, M. Ex vivo inhibitory effect of the 5-HT uptake blocker citalopram on 5-HT synthesis. J. Neural Transmission 104, 147–160 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01273177
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01273177