Summary
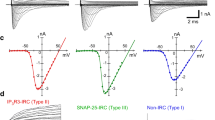
Isolated taste receptor cells from the frog tongue were investigated under whole-cell patch-clamp conditions. With the cytosolic potential head at −80 mV, more than 50% of the cells had a stationary inward Na current of 10 to 700 pA in Ringer's solution. This current was in some cells partially, in others completely, blockable by low concentrations of amiloride. With 110mm Na in the external and 10mm Na in the internal solution, the inhibition constant of amiloride was (at −80 mV) near 0.3 μm. In some cells the amiloride-sensitive conductance was Na specific; in others it passed both Na and K. The Na/K selectivity (estimated from reversal potentials) varied between 1 and 100. The blockability bysmall concentrations of amiloride resembled that of channels found in some Na-absorbing epithelia, but the channels of taste cells showed a surprisingly large range of ionic specificities. Receptor cells, whichin situ express these channels in their apical membrane, may be competent to detect the taste quality “salty.” The same cells also express TTX-blockable voltage-gated Na channels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike, N., Noma, A., Sato, M. 1976. Electrical responses of frog taste cells to chemical stimuli.J. Physiol. (London) 254:87–107
Asher, C., Cragoe, E.J., Jr., Garty, H. 1987. Effects of amiloride on Na+ transport in toad bladder membrane vesicles.J. Biol. Chem. 262:8566–8573
Avenet, P., Hofmann, F., Lindemann, B. 1988. Transduction in taste-receptor cells requires cAMP-dependent protein kinase.Nature (London) 331:351–354
Avenet, P., Lindemann, B. 1987. Action potentials in epithelial taste receptor cells induced by mucosal Calcium.J. Membrane Biol. 95:265–269
Avenet, P., Lindemann, B. 1987. Patch-clamp study of siolated taste receptor cells of the frog.J. Membrane Biol. 97:223–240
Benos, D.J. 1982. Amiloride: A molecular probe of sodium transport in tissues and cells.Am. J. Physiol. 242:C131-C145
Bjorkman, D.J., Allan, C.H., Hagen, S.J., Trier, J.S. 1986. Structural features of absorptive cell and microvillus membrane preparations from rat small intestine.Gastroenterology 91:1401–1414
Brand, J.G., Teeter, J.H., Silver, W.L. 1985. Inhibition by chorda tympani responses evoked by monovalent salts.Brain Res. 334:207–214
DeSimone, J.A., Ferrell, F. 1985. Analysis of amiloride inhibition of chorda tympani taste response of rat to NaCl.Am. J. Physiol. 249:R52-R61
DeSimone, J.A., Heck, G.L., DeSimone, S.K. 1981. Active ion transport in dog tongue: A possible role in taste.Science 214:1039–1041
DeSimone, J.A., Heck, G.L., Mierson, S., DeSimone, S.K. 1984. The active ion transport properties of canine lingual epithelia in vitro. Implications for gustatory transduction.J. Gen. Physiol. 83:633–656
Dragsten, P.R., Blumenthal, R., Handler, J.S. 1981. Membrane asymmetry in epithelia: Is the tight junction a barrier to diffusion in the plasma membrane?Nature (London) 294:718–722
Formaker, B.K., Hill, D.L. 1986. The suppressed response of NaCl following amiloride.IX Int. Symp. Olfact. Taste Abstr. Snowmass Village, Colo. p. 95
Frelin, C., Vigne, P., Barbry, P., Lazdunski, M. 1987. Molecular properties of amiloride action and of its Na transporting targets.Kidney Int. 32:785–793
Frings, S., Lindemann, B. 1988. Odorant response of isolated olfactory receptor cells is blocked by amiloride.J. Membrane Biol. 105:233–243
Fujimoto, T., Ogawa, K. 1983. Cell membrane polarity in dissociated frog urinary bladder epithelial cells.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 31:131–138
Garty, H., Benos, D.J. 1988. Characteristics and regulatory mechanisms of the amiloride-blockable Na+ channel.Physiol. Rev. 68:309–337
Garty, H., Edelman, I.S. 1983. Amiloride-sensitive trypsinization of apical sodium channels: Analysis of hormonal regulation of sodium transport in toad bladder.J. Gen. Physiol. 81:785–803
Goldman, D.E. 1943. Potential, impedance and rectification in membranes.J. Gen. Physiol. 27:37–60
Hamill, O.P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., Sigworth, F. 1981. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches.Pfluegers Arch. Ges. Physiol. 391:85–100
Hamilton, K.L., Eaton, D.C. 1985. Single-channel recordings from amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channel.Am. J. Physiol. 249:C200-C207
Heck, G.L., Mierson, S., DeSimone, J.A. 1984. Salt taste transduction occurs through an amiloride-sensitive sodium transport pathway.Science 223:403–405
Heck, G.L., Welter, M.E., DeSimone, J.A. 1985. Simultaneous recordings of the transepithelial lingual potential and integrated neural response of the rat.Chem. Senses 10:427–428
Herness, S. 1986. Effect of amiloride on iontophoretic and chemical stimulation in hamster and frog.IX Int. Symp. Olfact. Taste Abstr. Snowmass Village, Colo. p. S41
Hettinger, T.P., Frank, M.E. 1986. Amiloride produces acute inhibition and chronic sensitization of neural taste responses to sodium chloride.IX. Int. Symp. Olfact. Taste Abstr. Snowmass Village, Colo. p. S40
Hill, D.L., Bour, T.C. 1985. Addition of functional amiloride-sensitive components to the receptor membrane: A possible mechanism for altered taste responses during development.Dev. Brain Res. 20:310–313
Hodgkin, A.L., Katz, B. 1949. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of the giant axon of the squid.J. Physiol. (London) 108:37–77
Kaczorowski, G.J., Barros, F., Dethmers, J.K., Trumble, M.J., Cragoe, E.J., Jr. 1985. Inhibition of Na/Ca exchange in pituitary plasma membrane vesicles by analogues of amiloride.Biochemistry 24:1394–1403
Kinnamon, S.C., Roper, S.D. 1986. Passive and active membrane properties of mudpuppy taste receptor cells.J. Physiol. (London) 383:601–614
Kinnamon, S.C., Roper, S.D. 1988. Membrane properties of isolated mudpuppy taste cells.J. Gen. Physiol. 91:351–371
Lancet, D., Striem, B.J., Pace, U., Zehavi, U., Naim, M. 1987. Adenylate cyclase and GTP binding protein in rat sweet taste transduction.Neurosci. Soc. Abstr. 13:361
Lewis, S.A., Wills, N.K. 1981. Localisation of the aldosterone response in rabbit urinary bladder by electrophysiological techniques.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 372:56–63
Li, J.H.-Y., Cragoe, E.J., Jr., Lindemann, B. 1987. Structure-activity relationship of amiloride analogs as blockers of epithelial Na channels: II. Side-chain modifications.J. Membrane Biol. 95:171–185
Li, J.H.-Y., Palmer, L.G., Edelman, I.S., Lindemann, B. 1982. The role of sodium-channel density in the natriferic response of the toad urinary bladder to an antidiuretic hormone.J. Membrane Biol. 64:77–89
Lindemann, B. 1984. Fluctuation analysis of sodium channels in epithelia.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 46:497–515
McPheeters, M., Roper, S.D. 1985. Amiloride does not block taste transduction in the mudpuppy,Necturus maculosus.Chem. Senses 10:341–352
Mierson, S., Heck, G.L., DeSimone, S.K., Biber, T.U.L., DeSimone, J.A. 1985. The identity of the current carriers in canine lingual epithelium in vitro.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 816:283–293
Nagahama, S., Kurihara, K. 1985. Norepinephrine as a possible transmitter involved in synaptic transmission in frog taste organs and Ca dependence of its release.J. Gen. Physiol. 85:431–442
Nakamura, T., Gold, G.H. 1987. A cyclic nucleotide-gated conductance in olfactory cilia.Nature (London) 325:442–444
Okada, Y., Miyamoto, T., Sato, T. 1985. Arterial perfusion of frog tongue for intracellular recording of taste cell receptor potential.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 81A:247–250
Okada, Y., Miyamoto, T., Sato, T. 1986. Contribution of the receptor and basolateral membranes to the resting potential of a frog taste cell.Jpn. J. Physiol. 36:139–150
Okada, Y., Miyamoto, T., Sato, T. 1987. Depolarization induced by injection of cyclic nucleotides into frog taste cell.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 904:187–190
Palmer, L.G. 1982. Ion selectivity of the apical membrane Na channel in the toad urinary bladder.J. Membrane Biol. 67:91–98
Palmer, L.G. 1984. Voltage-dependent block by amiloride and other monovalent cations of apical Na channels in the toad urinary bladder.J. Membrane Biol. 80:153–165
Palmer, L.G., Frindt, G. 1988. Amiloride sensitive Na channels from the apical membrane of the rat cortical collecting tubule.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:2767–2770
Parsons, R. 1959. Handbook of Electrochemical Constants. Butterworth Scientific, London
Pisam, M., Ripoche, P. 1976. Redistribution of surface macromolecules in dissociated epithelial cells.J. Cell Biol. 71:907–920
Richter, H.-P., Avenet, P., Mestres, P., Lindemann, B. 1988. Gustatory receptors and neighbouring cells in the surface layer of the frog's taste disc:In situ relationships and response to cell isolation.Cell Tissue Res. 254:83–96
Sariban-Sohraby, S., Benos, D.J. 1986. The amiloride-sensitive sodium channel.Am. J. Physiol. 250:C175-C190
Sato, M. 1980. Recent advances in the physiology of taste cells.Prog. Neurobiol. 14:25–67
Sato, T. 1972. Multiple sensitivity of single taste cells of the frog tongue to four basic taste stimuli.J. Cell. Physiol. 80:207–218
Schiffman, S.S., Lockhead, E., Maes, F.W. 1983. Amiloride reduces the taste intensity of Na and Li salts and sweeteners.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:6136–6140
Schiffman, S.S., Simon, S.A., Gill, J.M., Beeker, T.G. 1986. Bretylium tosylate enhances salt taste.Physiol. Behav. 36:1129–1137
Simon, S.A., Garvin, J.L. 1985. Salt and acid studies on canine lingual epithelium.Am. J. Physiol. 249:C398-C408
Simon, S.A., Robb, R., Garvin, J.L. 1986. Epithelial responses of rabbit tongues and their involvement in taste transduction.Am. J. Physiol. 251:R598-R608
Tang, C.-M., Presser, F., Morad, M. 1988. Amiloride selectively blocks the low threshold (T) calcium channel.Science 240:213–215
Tonosaki, K., Funakoshi, M. 1984. Intracellular taste cell response of mouse.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 78A:651–656
Tonosaki, K., Funakoshi, M. 1988. Cyclic nucleotides may mediate taste transduction.Nature (London) 331:354–356
Tonosaki, K., Funakoshi, M. 1988. Voltage- and currentclamp recordings of the receptor potential in mouse taste cells.Brain Res. 445:363–366
Van Driessche, W., Zeiske, W. 1985. Ionic channels in epithelial cell membranes.Physiol. Rev. 65:833–903
Warncke, J., Lindemann, B., 1987. Voltage dependence of Na channel blockage by amiloride: Relaxation effects in admittance spectra.J. Membrane Biol. 86:255–265
Warncke, J., Lindemann, B. 1987. Voltage dependence of the blocking rate constants of amiloride at apical Na channels.Pfluegers Arch. 405:S89-S94
Wills, N.K., Zweifach, A. 1987. Recent advances in the characterization of epithelial ionic channels.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 906:1–31
Yoshii, K., Kiyomoto, Y., Kurihara, K. 1986. Taste receptor mechanism of salts in frog and rat.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 85:501–507
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avenet, P., Lindemann, B. Amiloride-blockable sodium currents in isolated taste receptor cells. J. Membrain Biol. 105, 245–255 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871001
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871001