Abstract
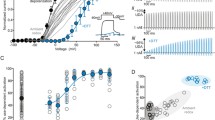
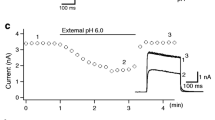
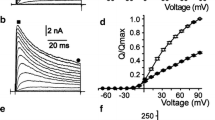
The effects of cysteine-modifying reagents on the gating of rat cloned Kv1.4 channels expressed in HEK-293 cells were examined using the whole-cell patch-clamp technique. Cells transfected with Kv1.4 expressed a rapidly inactivating K+ current with a midpoint of activation of −31 mV and a slope factor of 5 mV measured with tail current protocols in 35 mM Rb+ external solutions. The cysteine-specific oxidizing agents 2,2′-dithiobis-5-nitropyridine (DTBNP, 50 μM) and chloramine-T (CL-T, 500 μM) removed inactivation of Kv1.4. These effects were reversed by the reducing agent dithiothreitol (DTT, 10 mM). In addition, DTBNP and CL-T also slowed Kv1.4 deactivation and increased the voltage sensitivity of deactivation. The action of cysteine-modifying reagents on Kv1.4 suggests that redox state affects channel gating, with oxidation tending to stabilize the open state of the channel, both by removing inactivation and slowing deactivation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiyar J, Nguyen AN, Chandy KG, Grissmer S (1994) The P-region and S6 of Kv3.1 contribute to the formation of the ion conduction pathway. Biophys J 67:2261–2264
Bertoli A, Moran O, Conti F (1994) Activation and deactivation properties of rat brain K+ channels of the Shaker-related subfamily. Eur Biophys J 23:379–384
Blair TA, Roberds SL, Tamkun MM, Hartshorne RP (1991) Functional characterization of RK5, a voltage-gated K+ channel cloned from the rat cardiovasculature system. FEBS Lett 295:211–213
Chandy KG (1991) Simplified gene nomenclature. Nature 352:26
Comer MB, Campbell DL, Rasmusson RL, Lamson DR, Morales MJ, Zhang Y, Strauss HC (1994) Cloning and characterization of an I10-like potassium channel from ferret ventricle. Am J Physiol 267:111383–111395
Conner JA, Stevens CF (1971) Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol (Lond) 213:21–30
Durrell SR, Guy HR (1992) Atomic scale structure and functional models of voltage-gated potassium channels. Biophys J 62:238–247
Ficker E, Heinemann U (1992) Slow and fast transient potassium currents in cultured rat hippocampal cells. J Physiol (Lond) 445:431–455
Hagiwara S, Kusano K, Saito N (1961) Membrane changes in Onchidium nerve cell in potassium-rich media. J Physiol (Lond) 155:470–489
Hille B (1992) Ionic channels of excitable membranes. Sinaeur, Sunderland, Mass.
Krippeit-Drews P, Britsch S, Lang F, Drews G (1994) Effects of SH-group reagents on Ca2+ and K+ channel currents of pancreatic B-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 200:860–866
Ludewig U, Lorra C, Pongs O, Heinemann SH (1993) A site accessible to extracellular TEA+ and K+ influences intracellular Mg2+ block of cloned potassium channels. Eur Biophys 122:237–247
Neher E (1971) Two fast transient current components during voltage clamp on snail neurons. J Gen Physiol 58:36–53
Rudy B, Sen K, Vega-Saenz De Miera E, Lau D, Ried T, Ward DC (1991) Cloning of a human cDNA expressing a high voltage-activating, TEA-sensitive, type-A K+ channel which maps to chromosome 1 band p21. J Neurosci Res 29:401–412
Ruppersberg JP, Stocker M, Pongs O, Heinemann SH, Frank R, Koenen M (1991) Regulation of fast inactivation of cloned mammalian IK(A) channels by cysteine oxidation. Nature 352:711–714
Sheng M, Liao YJ, Jan YH, Jan LY (1992) Presynaptic A-current based on heteromultimeric K+ channels detected in vivo. Nature 365:72–75
Sheng M, Tsaur M-L, Jan YH, Jan LY (1993) Subcellular segregation of two A-type K+ channel proteins in rat central neurons. Neuron 9:271–284
Stephens GJ, Robertson B (1994) Modification of the inactivation induced by synthetic peptides in mouse brain Kv1.1 cloned potassium channels. J Physiol (Lond) 479:116P
Stephens GJ, Robertson B (1995) Inactivation of the cloned potassium channel mKv1.1 by the hKv3.4 ‘ball’ peptide and its chemical modification. J Physiol (Lond) 484:1–13
Stephens GJ, Owen DG, Robertson B (1995) Modulation of the rat cloned potassium channel Kv1.4 by sulfhydryl reagents J Physiol 487:200P
Stühmer W, Ruppersberg JP, Schröter KH, Sakmann B, Stocker M, Giese KP, Perschke A, Baumann A, Pongs O (1989) Molecular basis of functional diversity of voltage-gated potassium channels in mammalian brain. EMBO J 8:3235–3244
Swenson RP, Armstrong CM (1981) K+ channels close more slowly in the presence of external K+ and Rb+. Nature 291:427–429
Vega-Saenz De Miera E, Moreno H, Fruhling D, Kentros C, Rudy B (1991) Cloning of ShIII (Shaw-like) cDNA encoding a novel high voltage-activating, TEA-sensitive, type-A K+ channel. Proc R Soc Lond Biol 248:9–18
Weik R, Neumcke B (1989) ATP-sensitive potassium channels in adult mouse skeletal muscle: characterization of the ATP-binding site. J Membr Biol 110:217–226
Zühlke RD, Zhang H-J, Joho RH (1994) The role of an invariant cysteine in gating and ion permeation of the voltage-sensitive K+ channel Kv2.1. Recept Chan 2:237–248
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stephens, G.J., Owen, D.G. & Robertson, B. Cysteine-modifying reagents alter the gating of the rat cloned potassium channel Kv1.4. Pflugers Arch. 431, 435–442 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02207283
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02207283