Abstract
Rationale
It has been suggested that endocannabinoid mechanisms are involved in the control of ethanol consumption.
Objectives
The aims of the present study were (1) to evaluate the role of the endocannabinoid system in the control of operant ethanol self-administration and in the reinstatement of ethanol seeking, when induced by stress or conditioned stimuli and (2) to offer new insights on the specificity of such a role.
Methods
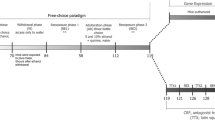
Rats were administered intraperitoneally with the selective cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, SR-141716A, 30 min before operant self-administration or reinstatement sessions. Two schedules of reinforcement, the fixed-ratio 1 (FR1) and the progressive ratio (PR), were used to study 10% (w/v) alcohol and 5.0% sucrose self-administration. NaCl (2% w/v) intake in sodium-depleted rats was studied only under the FR1 program.
Results
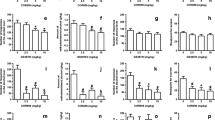
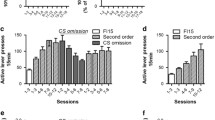
Treatment with SR-141716A (0.3–3.0 mg/kg) significantly attenuated FR1 alcohol self-administration and lowered the break point for ethanol under PR. SR-141716A also markedly inhibited the reinstatement of alcohol seeking elicited by presentation of cues predictive of drug availability. Conversely, the cannabinoid antagonist did not prevent the reinstatement of alcohol seeking induced by foot-shock stress. Lever pressing for sucrose under FR1 and PR schedules was also significantly decreased by SR-141716A treatment, whereas the drug modestly and only at the highest dose decreased 2% NaCl self-administration.
Conclusions
Results emphasize that endocannabinoid mechanisms play a major role in the control of ethanol self-administration and in the reinstatement of conditioned ethanol seeking. However, these effects extend to the control of operant behaviours motivated by natural rewards (i.e. sucrose). On the other hand, SR-141716A only weakly reduces NaCl self-administration in sodium-depleted rats, in which salt intake is largely controlled by homeostatic mechanisms. Overall, these observations demonstrate that the inhibition of operant behaviour following blockade of CB1 receptors by SR-141716A is linked to a reduction of reward-related responding and is not related to drug-induced motor deficits.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinshola BE, Chakrabarti A, Onaivi ES (1999) In-vitro and in-vivo action of cannabinoids. Neurochem Res 24:1233–1240
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Arnone M, Maruani J, Chaperon F, Thiébot M-E, Poncelet M, Soubrié P, Le Fur G (1997) Selective inhibition of sucrose and alcohol intake by SR 141716, an antagonist of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. Psychopharmacology 132:104–106
Basavarajappa BS, Hungund BL (1999) Chronic ethanol increases the cannabinoid receptor agonist anandamide and its precursor N-arachidonoylphosphatidylethanolamine in SK-N-SH cells. J Neurochem 72:522–528
Basavarajappa BS, Cooper TB, Hungund BL (1998) Chronic ethanol administration down-regulates cannabinoid receptors in mouse brain synaptic plasma membrane. Brain Res 793:212–218
Berridge KC, Flynn FW, Schulkin J, Grill HJ (1984) Sodium depletion enhances salt palatability in rats. Behav Neurosci 98:652–660
Caille S, Parsons LH (2003) SR141716A reduces the reinforcing properties of heroin but not heroin-induced increases in nucleus accumbens dopamine in rats. Eur J Neurosci 18:3145–3149
Ciccocioppo R, Sanna PP, Weiss F (2001) Cocaine-predictive stimulus induces drug-seeking behavior and neural activation in limbic brain regions after multiple months of abstinence: reversal by D1 antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:1976–1981
Ciccocioppo R, Martin-Fardon R, Weiss F (2002) Effect of selective blockade of μu(1) or δelta opioid receptors on reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behavior by drug-associated stimuli in rats. Neuropsycopharmacology 27:391–399
Ciccocioppo R, Economidou D, Fedeli A, Angeletti S, Weiss F, Heilig M, Massi M (2004) Attenuation of ethanol self-administration and of conditioned reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behaviour by the antiopioid peptide nociceptin/orphanin FQ in alcohol-preferring rats. Psychopharmacology 172:170–178
Clark JJ, Ilene BL (2004) Reciprocal cross-sensitization between amphetamine and salt appetite. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 78:691–698
Cohen C, Perrault G, Voltz C, Steinberg R, Soubrie P (2002) SR-141716, a central cannabinoid (CB(1)) receptor antagonist, blocks the motivational and dopamine-releasing effects of nicotine in rats. Behav Pharmacol 13:451–463
Colombo G, Agabio R, Fa M, Guano L, Lobina C, Loche A, Reali R, Gessa GL (1998a) Reduction of voluntary ethanol intake in ethanol-preferring (sP) rats by the cannabinoid antagonist SR-141716. Alcohol Alcohol 33:126–130
Colombo G, Agabio R, Diaz G, Lobina C, Reali R, Gessa GL (1998b) Appetite suppression and weight loss after the cannabinoid antagonist SR141716. Life Sci 63:113–117
Corchero J, Fuentes JA, Manzanares J (1999) Chronic treatment with CP-55,940 regulates corticotropin releasing factor and proopiomelanocortin gene expression in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland of the rat. Life Sci 64:905–911
Czachowski CL, Chappell AM, Samson HH (2001) Effects of raclopride in the nucleus accumbens on ethanol seeking and consumption. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:1431–1440
De Vries TJ, Shaham Y, Homberg JR, Crombag H, Schuurman K, Dieben J, Vanderschuren LJ, Schoffelmeer AN (2001) A cannabinoid mechanism in relapse to cocaine seeking. Nat Med 7:1151–1154
De Vries TJ, Homberg JR, Binnekade R, Raaso H, Schoffelmeer AN (2003) Cannabinoid modulation of the reinforcing and motivational properties of heroin and heroin-associated cues in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 168:164–169
De Vry J, Schreiber R, Eckel G, Jentzsch KR (2004) Behavioral mechanisms underlying inhibition of food-maintained responding by the cannabinoid receptor antagonist/inverse agonist SR141716A. Eur J Pharmacol 483:55–63
Diana M, Rossetti ZL, Gessa G (1993) Rewarding and aversive effects of ethanol: interplay of GABA, glutamate and dopamine. Alcohol Alcohol Suppl 2:315–319
Freedland CS, Poston JS, Porrino LJ (2000) Effects of SR141716A, a central cannabinoid receptor antagonist, on food-maintained responding. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:265–270
Freedland CS, Sharpe AL, Samson HH, Porrino LJ (2001) Effects of SR141716A on ethanol and sucrose self-administration. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:277–282
Gallate JE, McGregor IS (1999) The motivation for beer on rats: effects of ritanserin, naloxone and SR141716. Psychopharmacology 142:302–308
Gallate JE, Saharov T, Mallet PE, McGregor IS (1999) Increased motivation for beer in rats following administration of a cannabinoid CB1 receptor agonist. Eur J Pharmacol 370:233–240
Gessa GL, Casu MA, Carta G, Mascia MS (1998) Cannabinoids activate mesolimbic dopamine neurons by an action on cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 341:39–44
Giuliani D, Ferrari F, Ottani A (2000) The cannabinoid agonist HU 210 modifies rat behavioural responses to novelty and stress. Pharmacol Res 41:47–53
Haller J, Varga B, Ledent C, Barna I, Freund TF (2004) Context-dependent effects of CB1 cannabinoid gene disruption anxiety-like and social behaviour in mice. Eur J Neurosci 19:1906–19912
Hungund BL, Basavarajappa BS (2000) Are anandamide and cannabinoid receptors involved in ethanol tolerance? A review of the evidence. Alcohol Alcohol 35:126–133
Hungund BL, Szakall I, Adam A, Basavarajappa BS, Vadasz C (2003) Cannabinoid CB1 receptor knockout mice exhibit markedly reduced voluntary alcohol consumption and lack alcohol-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurochem 84:698–704
Jarbe TU, Andrzejewski ME, DiPatrizio NV (2002) Interactions between the CB1 receptor agonist Delta 9-THC and the CB1 receptor antagonist SR-141716 in rats: open-field revisited. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 73:911–999
Katner SN, Weiss F (1999) Ethanol-associated olfactory stimuli reinstate ethanol-seeking behavior after extinction and modify extracellular dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23:1751–1760
Katner SN, Magalong JG, Weiss F (1999) Reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behavior by drug-associated discriminative stimuli after prolonged extinction in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:471–479
Lallemand F, Soubrie PH, De Witte PH (2001) Effects of CB1 receptor blockade on ethanol preference after chronic ethanol administration. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:1317–1323
Le AD, Quan B, Juzytch W, Fletcher PJ, Joharchi N, Shaham Y (1998) Reinstatement of alcohol-seeking by priming injections of alcohol and exposure to stress in rats. Psychopharmacology 135:169–174
Liu X, Weiss F (2002) Reversal of ethanol-seeking behavior by D1 and D2 antagonists in an animal model of relapse: differences in antagonist potency in previously ethanol-dependent versus nondependent rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 300:882–889
Majchrowicz E (1975) Induction of physical dependence upon ethanol and the associated behavioral changes in rats. Psychopharmacologia 43:245–54
Manzanares J, Corchero J, Fuentes JA (1999) Opioid and cannabinoid receptor-mediated regulation of the increase in adrenocorticotropin hormone and corticosterone plasma concentrations induced by central administration of delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol in rats. Brain Res 839:173–179
Martin-Fardon R, Ciccocioppo R, Massi M, Weiss F (2000) Nociceptin prevents stress-induced ethanol- but not cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Neuroreport 11:1939–1943
Massi M, Polidori C, Perfumi M, Gentili L, de Caro G (1991) Tachykinin receptor subtypes involved in the central effects of tachykinins on water and salt intake. Brain Res Bull 26:155–160
McMillan DE, Snodgrass SH (1991) Effects of acute and chronic administration of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol or cocaine on ethanol intake in a rat model. Drug Alcohol Depend 27:263–274
Melis M, Gessa GL, Diana M (2000) Different mechanisms for dopaminergic excitation induced by opiates and cannabinoids in the rat midbrain. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 24:993–1006
Monti PM, Rohsenow DJ, Hutchison KE, Swift RM, Mueller TI, Colby SM, Brown RA, Gulliver SB, Gordon A, Abrams DB (1999) Naltrexone's effect on cue-elicited craving among alcoholics in treatment. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23:1386–1394
Navarro M, Carrera MR, Fratta W, Valverde O, Cossu G, Fattore L, Chowen JA, Gomez R, del Arco I, Villanua MA, Maldonado R, Koob GF, Rodriguez de Fonseca F (2001) Functional interaction between opioid and cannabinoid receptors in drug self-administration. J Neurosci 21:5344–5350
Newman LM, Lutz MP, Gould MH, Domino EF (1972) 9-Tetrahydrocannabinol and ethyl alcohol: evidence for cross-tolerance in the rat. Science 175:1022–1023
O'Brien CP, McLellan AT (1996) Myths about the treatment of addiction. Lancet 347:237–240
O'Brien C, Childress AR, McLellan AT, Ehrman R (1990) Integrating systematic cue exposure with standard treatment in recovering drug dependent patients. Addict Behav 15:355–365
O'Brien CP, Childress AR, Ehrman R, Robbins SJ (1998) Conditioning factors in drug abuse: can they explain compulsion? J Psychopharmacol 12:15–22
Patel S, Hillard CJ (2003) Cannabinoid-induced Fos expression within A10 dopaminergic neurons. Brain Res 963:15–25
Pistis M, Ferraro L, Pira L, Flore G, Tanganelli S, Gessa GL, Devoto P (2002) Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol decreases extracellular GABA and increases extracellular glutamate and dopamine levels in the rat prefrontal cortex: an in vivo microdialysis study. Brain Res 948:155–158
Poncelet M, Maruani J, Calassi R, Soubrie P (2003) Overeating, alcohol and sucrose consumption decrease in CB1 receptor deleted mice. Neurosci Lett 343:216–218
Rinaldi-Carmona M, Barth F, Heaulme M, Shire D, Calandra B, Congy C, Martinez S, Maruani J, Neliat G, Caput D et al (1994) SR 141716A, a potent and selective antagonist of the brain cannabinoid receptor. FEBS Lett 350:240–244
Rodriguez de Fonseca F, Roberts AJ, Bilbao A, Koob GF, Navarro M (1999) Cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR 141716A decreases operant ethanol self administration in rats exposed to ethanol-vapor chambers. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao 20:1109–1114
Rohsenow DJ, Monti PM, Hutchison KE, Swift RM, Colby SM, Kaplan GB (2000) Naltrexone's effects on reactivity to alcohol cues among alcoholic men. J Abnorm Psychol 109:738–742
Serra S, Carai MA, Brunetti G, Gomez R, Melis S, Vacca G, Colombo G, Gessa GL (2001) The cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR 141716A prevents acquisition of drinking behavior in alcohol-preferring rats. Eur J Pharmacol 430:369–371
Serra S, Brunetti G, Pani M, Vacca G, Carai MA, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2002) Blockade by the cannabinoid CB(1) receptor antagonist, SR 141716, of alcohol deprivation effect in alcohol-preferring rats. Eur J Pharmacol 443:95–97
Shalev U, Grimm JW, Shaham Y (2002) Neurobiology of relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking: a review. Pharmacol Rev 54:1–42
Simiand J, Keane M, Keane PE, Soubrie P (1998) SR141716, a CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonist, selectively reduces sweet food intake in marmoset. Behav Pharmacol 9:179–181
Tanda G, Pontieri FE, Di Chiara G (1997) Cannabinoid and heroin activation of mesolimbic dopamine transmission by a common mu 1 opioid receptor mechanism. Science 276:2048–2050
Vacca G, Serra S, Brunettiu G, Carai MA, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2002) Boosting effect of morphine on alcohol drinking is suppressed not only by naloxone but also by the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, SR 141716A. Eur J Pharmacol 445:55–59
Wang L, Liu J, Harvey-White J, Zimmer A, Kunos G (2003) Endocannabinoid signaling via cannabinoid receptor 1 is involved in ethanol preference and its age-dependent decline in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:1393–1398
Weiss F, Lorang MT, Bloom FE, Koob GF (1993) Oral alcohol self-administration stimulates dopamine release in the rat nucleus accumbens: genetic and motivational determinants. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:250–258
Weiss F, Ciccocioppo R, Parsons LH, Katner S, Liu X, Zorrilla EP, Valdez GR, Ben-Shahar O, Angeletti S, Richter RR (2001) Compulsive drug-seeking behavior and relapse. Neuroadaptation, stress and conditioning factors. Ann N Y Acad Sci 937:1–26
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grant from MIUR, Rome, Italy (COFIN 2002 to MM, FIRB 2002 to VC) and by the EU 5th Framework Program, grant QLRT-2001-01048 (TargAlc Consortium).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Economidou, D., Mattioli, L., Cifani, C. et al. Effect of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist SR-141716A on ethanol self-administration and ethanol-seeking behaviour in rats. Psychopharmacology 183, 394–403 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0199-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0199-9