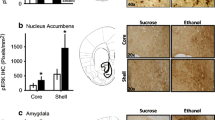
Abstract
Rationale
The type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR5) and the epsilon isoform of protein kinase C (PKCɛ) regulate ethanol intake, and we have previously demonstrated that mGluR5 receptor antagonism reduces ethanol consumption via a PKCɛ-dependent mechanism.
Objectives
We explored the potential neuroanatomical substrates of regulation of ethanol reinforcement by this mGluR5-PKCɛ signaling pathway by infusing selective inhibitors of these proteins into the shell or core region of the nucleus accumbens (NAc).
Methods
Male Wistar rats were trained to self-administer ethanol intravenously and received intra-NAc infusions of vehicle or the selective mGluR5 antagonist 3-((2-methyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)ethynyl)pyridine (MTEP) alone and in combination with a PKCɛ translocation inhibitor (ɛV1–2) or a scrambled control peptide (sɛV1–2). The effects of intra-NAc MTEP on food-reinforced responding and open-field locomotor activity were also determined.
Results
MTEP (1 μg/μl) had no effect on ethanol or food reinforcement or locomotor activity when infused into either region. MTEP (3 μg/μl) reduced ethanol reinforcement when infused into the NAc shell but not the core, and this effect was reversed by ɛV1–2 (1 μg/μl) but not sɛV1–2 (1 μg/μl). In both regions, this concentration of MTEP did not alter food-reinforced responding or locomotor activity, and infusion of ɛV1–2 alone did not alter ethanol reinforcement. MTEP (10 μg/μl) reduced locomotor activity when infused into the shell; therefore, this concentration was not further tested on responding for ethanol or food.
Conclusions
Blockade of mGluR5 receptors in the NAc shell reduces ethanol reinforcement via a PKCɛ-dependent mechanism.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alagarsamy S, Marino MJ, Rouse ST, Gereau RW, Heinemann SF, Conn PJ (1999) Activation of NMDA receptors reverses desensitization of mGluR5 in native and recombinant systems. Nat Neurosci 2:234–240
Alagarsamy S, Rouse ST, Junge C, Hubert GW, Gutman D, Smith Y, Conn PJ (2002) NMDA-induced phosphorylation and regulation of mGluR5. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 73:299–306
Backstrom P, Bachteler D, Koch S, Hyytia P, Spanagel R (2004) mGluR5 antagonist MPEP reduces ethanol-seeking and relapse behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:921–928
Besheer J, Faccidomo S, Grondin JJ, Hodge CW (2008) Regulation of motivation to self-administer ethanol by mGluR5 in alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32:209–221
Bird MK, Kirchhoff J, Djouma E, Lawrence AJ (2008) Metabotropic glutamate 5 receptors regulate sensitivity to ethanol in mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:765–774
Chang HT, Kitai ST (1985) Projection neurons of the nucleus accumbens: an intracellular labelling study. Brain Res 347:112–116
Chiamulera C, Epping-Jordan MP, Zocchi A, Marcon C, Cottiny C, Tacconi S, Corsi M, Orzi F, Conquet F (2001) Reinforcing and locomotor stimulant effects of cocaine are absent in mGluR5 null mutant mice. Nat Neurosci 4:873–874
Choi DS, Wang D, Dadgar J, Chang WS, Messing RO (2002) Conditional rescue of protein kinase C ɛ regulates ethanol preference and hypnotic sensitivity in adult mice. J Neurosci 22:9905–9911
Conn PJ, Pin J-P (1997) Pharmacology and functions of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 37:205–237
Cowen MS, Djouma E, Lawrence AJ (2005) The metabotropic glutamate 5 receptor antagonist 3-[(2-methyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)ethynyl)-pyridine reduces ethanol self-administration in multiple strains of alcohol-preferring rats and regulates olfactory glutamatergic systems. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315:590–600
Cowen MS, Krstew E, Lawrence AJ (2007) Assessing appetitive and consummatory phases of ethanol self-administration in C57BL/6J mice under operant conditions: regulation by mGlu5 receptor antagonism. Psychopharmacology 190:21–29
Cozzoli DK, Goulding SP, Szumlinski KK (2007) Accumbens mGluR5 blockade reduces excessive alcohol consumption in mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31(Suppl 2):17A
Dahchour A, Hoffman A, Deitrich R, De Witte P (2000) Effects of ethanol on extracellular amino acid levels in high- and low-alcohol sensitive rats: a microdialysis study. Alcohol Alcohol 35:548–553
Eichholtz T, de Bont DB, de Widt J, Liskamp RM, Ploegh HL (1993) A myristoylated pseudosubstrate peptide, a novel protein kinase C inhibitor. J Biol Chem 268:1982–1986
Gass JT, Olive MF (2007) Reinstatement of ethanol-seeking behavior following intravenous self-administration in Wistar rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:1441–1445
Gass JT, Olive MF (2008) Glutamatergic substrates of drug addiction and alcoholism. Biochem Pharmacol 75:218–265
Gereau RW, Heinemann SF (1998) Role of protein kinase C phosphorylation in rapid desensitization of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5. Neuron 20:143–151
Gonzales RA, Job MO, Doyon WM (2004) The role of mesolimbic dopamine in the development and maintenance of ethanol reinforcement. Pharmacol Ther 103:121–146
Gray MO, Karliner JS, Mochly-Rosen D (1997) A selective epsilon-protein kinase C antagonist inhibits protection of cardiac myocytes from hypoxia-induced cell death. J Biol Chem 272:30945–30951
Groenewegen HJ, Russchen FT (1984) Organization of the efferent projections of the nucleus accumbens to pallidal, hypothalamic, and mesencephalic structures: a tracing and immunohistochemical study in the cat. J Comp Neurol 223:347–367
Groenewegen HJ, Wright CI, Beijer AV (1996) The nucleus accumbens: gateway for limbic structures to reach the motor system? Prog Brain Res 107:485–511
Grupp LA (1981) An investigation of intravenous ethanol self-administration in rats using a fixed ratio schedule of reinforcement. Physiol Psychol 9:359–363
Heimer L, Alheid GF, de Olmos JS, Groenewegen HJ, Haber SN, Harlan RE, Zahm DS (1997) The accumbens: beyond the core-shell dichotomy. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 9:354–381
Hermans E, Challiss RA (2001) Structural, signalling and regulatory properties of the group I metabotropic glutamate receptors: prototypic family C G-protein-coupled receptors. Biochem J 359:465–484
Hodge CW, Mehmert KK, Kelley SP, McMahon T, Haywood A, Olive MF, Wang D, Sanchez-Perez AM, Messing RO (1999) Supersensitivity to allosteric GABAA receptor modulators and alcohol in mice lacking PKCɛ. Nat Neurosci 2:997–1002
Hodge CW, Miles MF, Sharko AC, Stevenson RA, Hillmann JR, Lepoutre V, Besheer J, Schroeder JP (2006) The mGluR5 antagonist MPEP selectively inhibits the onset and maintenance of ethanol self-administration in C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacology 183:429–438
Homayoun H, Stefani MR, Adams BW, Tamagan GD, Moghaddam B (2004) Functional interaction between NMDA and mGlu5 receptors: effects on working memory, instrumental learning, motor behaviors, and dopamine release. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1259–1269
Howard EC, Schier CJ, Wetzel JS, Duvauchelle CL, Gonzales RA (2008) The shell of the nucleus accumbens has a higher dopamine response compared with the core after non-contingent intravenous ethanol administration. Neuroscience 154:1042–1053
Hyytia P, Schulteis G, Koob GF (1996) Intravenous heroin and ethanol self-administration by alcohol-preferring AA and alcohol-avoiding ANA rats. Psychopharmacology 125:248–254
Imperato A, Honore T, Jensen LH (1990) Dopamine release in the nucleus caudatus and in the nucleus accumbens is under glutamatergic control through non-NMDA receptors: a study in freely-moving rats. Brain Res 530:223–228
Johnson JA, Gray MO, Chen C-H, Mochly-Rosen D (1996) A protein kinase C translocation inhibitor as an isozyme-selective antagonist of cardiac function. J Biol Chem 271:24962–24966
Kalivas PW, Nakamura M (1999) Neural systems for behavioral activation and reward. Curr Opin Neurobiol 9:223–227
Kapasova Z, Szumlinski KK (2008) Strain differences in alcohol-induced neurochemical plasticity: a role for accumbens glutamate in alcohol intake. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32:617–631
Koob GF (1999) The role of the striatopallidal and extended amygdala systems in drug addiction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 877:445–460
Kuzmin A, Semenova S, Zvartau E, De Vry J (1999) Effects of calcium channel blockade on intravenous self-administration of ethanol in rats. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 9:197–203
Lawrence AJ (2007) Therapeutics for alcoholism: what’s the future? Drug Alcohol Rev 26:3–8
Lee JH, Lee J, Choi KY, Hepp R, Lee JY, Lim MK, Chatani-Hinze M, Roche PA, Kim DG, Ahn YS, Kim CH, Roche KW (2008) Calmodulin dynamically regulates the trafficking of the metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:12575–12580
Lesscher HMB, Wallace M, Zeng L, Wang V, Deitchman K, McMahon T, Messing RO, Newton PM (2009) Amygdala protein kinase C epsilon controls alcohol consumption. Genes Brain Behav, in press
Lominac KD, Kapasova Z, Hannun RA, Patterson C, Middaugh LD, Szumlinski KK (2006) Behavioral and neurochemical interactions between group I mGluR antagonists and ethanol: potential insight into their anti-addictive properties. Drug Alcohol Depend 85:142–156
Lu XY, Ghasemzadeh MB, Kalivas PW (1999) Expression of glutamate receptor subunit/subtype messenger RNAS for NMDAR1, GLuR1, GLuR2 and mGLuR5 by accumbal projection neurons. Mol Brain Res 63:287–296
Lyness WH, Smith FL (1992) Influence of dopaminergic and serotonergic neurons on intravenous ethanol self-administration in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 42:187–192
Mao LM, Liu XY, Zhang GC, Chu XP, Fibuch EE, Wang LS, Liu Z, Wang JQ (2008) Phosphorylation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR1/5) in vitro and in vivo. Neuropharmacology 55:403–408
McMillen BA, Crawford MS, Kulers CM, Williams HL (2005) Effects of a metabotropic, mglu5, glutamate receptor antagonist on ethanol consumption by genetic drinking rats. Alcohol Alcohol 40:494–497
Melendez RI, Hicks MP, Cagle SS, Kalivas PW (2005) Ethanol exposure decreases glutamate uptake in the nucleus accumbens. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:326–333
Mitrano DA, Smith Y (2007) Comparative analysis of the subcellular and subsynaptic localization of mGluR1a and mGluR5 metabotropic glutamate receptors in the shell and core of the nucleus accumbens in rat and monkey. J Comp Neurol 500:788–806
Mochly-Rosen D, Gordon AS (1998) Anchoring proteins for protein kinase C: a means for isozyme selectivity. FASEB J 12:35–42
Mogenson GJ, Swanson LW, Wu M (1983) Neural projections from nucleus accumbens to globus pallidus, substantia innominata, and lateral preoptic-lateral hypothalamic area: an anatomical and electrophysiological investigation in the rat. J Neurosci 3:189–202
Moghaddam B, Bolinao ML (1994) Biphasic effect of ethanol on extracellular accumulation of glutamate in the hippocampus and nucleus accumbens. Neurosci Lett 178:99–102
National Research Council (2003) Guidelines for the care and use of mammals in neuroscience and behavioral research. National Academic Press, Washington, DC
O’Brian CA, Ward NE, Liskamp RM, de Bont DB, Earnest LE, van Boom JH, Fan D (1991) A novel N-myristylated synthetic octapeptide inhibits protein kinase C activity and partially reverses murine fibrosarcoma cell resistance to adriamycin. Invest New Drugs 9:169–179
Oei TP, Singer G (1979) Effects of a fixed time schedule and body weight on ethanol self-administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 10:767–770
Olive MF, Messing RO (2004) Protein kinase C isozymes and addiction. Mol Neurobiol 29:139–153
Olive MF, Mehmert KK, Messing RO, Hodge CW (2000) Reduced operant ethanol self-administration and in vivo mesolimbic dopamine responses to ethanol in PKCɛ deficient mice. Eur J Neurosci 12:4131–4140
Olive MF, McGeehan AJ, Kinder JR, McMahon T, Hodge CW, Janak PH, Messing RO (2005) The mGluR5 antagonist 6-methyl-2-(phenylethynyl)pyridine decreases ethanol consumption via a protein kinase Cɛ-dependent mechanism. Mol Pharmacol 67:349–355
Paxinos G, Watson C (2005) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 5th edn. Academic, San Diego
Pierce RC, Kumaresan V (2006) The mesolimbic dopamine system: the final common pathway for the reinforcing effect of drugs of abuse? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 30:215–238
Quertemont E, de Neuville J, De Witte P (1998) Changes in the amygdala amino acid microdialysate after conditioning with a cue associated with ethanol. Psychopharmacology 139:71–78
Roberto M, Schweitzer P, Madamba SG, Stouffer DG, Parsons LH, Siggins GR (2004) Acute and chronic ethanol alter glutamatergic transmission in rat central amygdala: an in vitro and in vivo analysis. J Neurosci 24:1594–1603
Romano C, Sesma MA, McDonald CT, O’Malley K, Van den Pol AN, Olney JW (1995) Distribution of metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 immunoreactivity in rat brain. J Comp Neurol 355:455–469
Saito N, Itouji A, Totani Y, Osawa I, Koide H, Fujisawa N, Ogita K, Tanaka C (1993) Cellular and intracellular localization of epsilon-subspecies of protein kinase C in the rat brain; presynaptic localization of the epsilon-subspecies. Brain Res 607:241–248
Schotanus SM, Chergui K (2008) Dopamine D1 receptors and group I metabotropic glutamate receptors contribute to the induction of long-term potentiation in the nucleus accumbens. Neuropharmacology 54:837–844
Schroeder JP, Overstreet DH, Hodge CW (2005) The mGluR5 antagonist MPEP decreases operant ethanol self-administration during maintenance and after repeated alcohol deprivations in alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Psychopharmacology 179:262–270
Schumann G, Johann M, Frank J, Preuss U, Dahmen N, Laucht M, Rietschel M, Rujescu D, Lourdusamy A, Clarke T-K, Krause K, Dyer A, Depner M, Wellek S, Treutlein J, Szegedi A, Giegling I, Cichon S, Blomeyer D, Heinz A, Heath S, Lathrop M, Wodarz N, Soyka M, Spanagel R, Mann K (2008) Systematic analysis of glutamatergic neurotransmission genes and alcohol dependence in adolescent risky drinking behavior. Arch Gen Psychiatry 65:826–838
Selim M, Bradberry CW (1996) Effect of ethanol on extracellular 5-HT and glutamate in the nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex: comparison between the Lewis and Fischer 344 rat strains. Brain Res 716:157–164
Shigemoto R, Nomura S, Ohishi H, Sugihara H, Nakanishi S, Mizuno N (1993) Immunohistochemical localization of a metabotropic glutamate receptor, mGluR5, in the rat brain. Neurosci Lett 163:53–57
Sinden JD, Le Magnen J (1982) Parameters of low-dose ethanol intravenous self-administration in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 16:181–183
Steffensen SC, Walton CH, Hansen DM, Yorgason JT, Gallegos RA, Criado JR (2009) Contingent and non-contingent effects of low-dose ethanol on GABA neuron activity in the ventral tegmental area. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 92:68–75
Szumlinski KK, Diab ME, Friedman R, Henze LM, Lominac KD, Bowers MS (2007) Accumbens neurochemical adaptations produced by binge-like alcohol consumption. Psychopharmacology 190:415–431
Takayama S, Uyeno ET (1985) Intravenous self-administration of ethanol and acetaldehyde by rats. Yakubutsu Seishin Kodo 5:329–334
Testa CM, Standaert DG, Young AB, Penney JB Jr. (1994) Metabotropic glutamate receptor mRNA expression in the basal ganglia of the rat. J Neurosci 14:3005–18
Vengeliene V, Bilbao A, Molander A, Spanagel R (2008) Neuropharmacology of alcohol addiction. Br J Pharmacol 154:299–315
Ward NE, O’Brian CA (1993) Inhibition of protein kinase C by N-myristoylated peptide substrate analogs. Biochemistry 32:11903–11909
Young WS (1988) Expression of three (and a putative four) protein kinase C genes in brains of rat and rabbit. J Chem Neuroanat 1:177–194
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant AA013852 (MFO) and an Institutional Training Grant AA007474 (JTG). The authors wish to thank Ms. Noreen Watson for technical assistance in conducting these studies. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gass, J.T., Olive, M.F. Role of protein kinase C epsilon (PKCɛ) in the reduction of ethanol reinforcement due to mGluR5 antagonism in the nucleus accumbens shell. Psychopharmacology 204, 587–597 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1490-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1490-y