Abstract
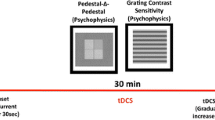
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) at low intensity induces changes in cortical excitability that persist after polarization ends. The effects of anodal and cathodal polarization remain controversial. We studied changes in visual evoked potentials (VEPs) during and after anodal and cathodal tDCS by applying, in healthy volunteers, 1 mA polarization through surface electrodes placed over the occipital scalp (polarizing) and over the anterior or posterior neck-base (reference). We compared tDCS applied at two durations, 3 and 10 min and both polarities. We assessed VEP-P100 latencies and amplitudes in response to pattern-reversal checkerboard stimuli before, during, and after polarization. Anodal polarization reduced VEP-P100 amplitude whereas cathodal polarization significantly increased amplitude but both polarities left latency statistically unchanged. These changes persisted for some minutes after polarization ended depending on the duration of tDCS and on the contrast level of visual stimuli. tDCS-induced changes in VEPs seem to depend on the duration of polarization and type of visual stimuli used. The effects induced on visual cortical neurones during polarization are more consistent than the aftereffects. Studying these changes during polarization may therefore improve our understanding of these phenomena.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accornero N, Bini G, Lenzi GL, Manfredi M (1977) Selective Activation of peripheral nerve fibre groups of different diameter by triangular shaped stimulus pulses. J Physiol 273(3):539–60
Antal A, Tamas Z. Kincses, Michael A. Nitsche, Orsolya Bartfai, Walter Paulus. (2004a) Excitability changes induced in the human primary visual cortex by transcranial direct current stimulation: direct electrophysiological evidence. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:702–707
Antal A, Varga ET, Kincses TZ, Nitsche MA, Paulus W (2004b) Oscillatory brain activity and transcranial direct current stimulation in humans. Neuroreport 7, 15(8):1307–1310
Antal A, Varga ET, Nitsche MA, Chadaide Z, Paulus W, Kovacs G, Vidnyanszky Z (2004c) Direct current stimulation over MT + /V5 modulates motion aftereffect in humans. Neuroreport 15, 15(16):2491–2494
Antal A, Nitsche Ma,Paulus V (2006) Transcranial direct current stimulation and the visual cortex. Brain Res Bull 15, 68(6):459–463
Ardolino G, Bossi B, Barbieri S, Priori A (2005) Non-synaptic mechanisms underlie the after-effects of cathodal transcutaneous direct current stimulation of the human brain. J Physiol 15, 568(Pt2):653–663
Bodis-wollner I (1992) Sensory evoked potentials: PERG, VEP, and SEP. Curr Opin Neurol Neurosurg 5(5):716–726
Fregni F, Boggio PS, Nitsche M, Bermpohl F, Antal A, Feredoes E, Marcolin MA, Rigonatti SP, Silva MT, Paulus W, Pascual-Leone A (2005) Anodal transcranial direct current stimulation of prefrontal cortex enhances working memory. Exp Brain Res 166(1):23–30
Iyer MB, Mattu U, Grafman J, Lomarev M, Sato S, Wassermann EM (2005) Safety and cognitive effect of frontal DC brain polarization in healthy individuals. Neurology 8 64(5):872–875
Lang N, Nitsche MA, Paulus W, Rothwell JC, Lemon RN (2004a) Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation over the human motor cortex on corticospinal and transcallosal excitability. Exp Brain Res 156(4):439–443
Lang N, Siebner HR, Ernst D, Nitsche MA, Paulus W, Lemon RN, Rothwell JC (2004b) Preconditioning with transcranial direct current stimulation sensitizes the motor cortex to rapid-rate transcranial magnetic stimulation and controls the direction of after-effects. Biol Psychiatry 1, 56(9):634–639
Marshall L, Molle M, Siebner HR, Born J (2005) Bifrontal transcranial direct current stimulation slows reaction time in a working memory task. BMC Neurosci 8, 6(1):23
Matsunaga K, Nitsche MA, Tsuji S, Rothwell JC (2004) Effect of transcranial DC sensorimotor cortex stimulation on somatosensory evoked potentials in humans. Clin Neurophysiol 115(2):456–460
Nitsche MA, Paulus W (2000) Excitability changes induced in the human motor cortex by weak transcranial direct current stimulation. J Physiol 527(Pt3):633–639
Nitsche MA, Seeber A, Frommann K, Klein CC, Rochford C, Nitsche MS, Fricke K, Liebetanz D, Lang N, Antal A, Paulus W, Tergau F (2005) Modulating parameters of excitability during and after transcranial direct current stimulation of the human motor cortex. J Physiol 1, 568(Pt1):291–303
Odom JV, Bach M, Barber C, Brigell M, Michael Marmor MF, Tormene AP, Holder GE, Vaegan (2004) Visual evoked potentials standard. Doc Ophthalmol 108:115–123
Priori A, Berardelli A, Rona S, Accornero N, Manfredi M (1998) Polarization of the human motor cortex through the scalp. Neuroreport 13, 9(10):2257–2260
Priori A, Brain (2003) Polarization in humans: a reappraisal of an old tool for prolonged non-invasive modulation of brain excitability. Clin Neurophysiol 114(4):589–595
Quartarone A, Morgante F, Bagnato S, Rizzo V, Sant’Angelo A, Aiello E, Reggio E, Battaglia F, Messina C, Girlanda P (2004) Long lasting effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on motor imagery. Neuroreport 7 15(8):1287–1291
Rogalewski A, Breitenstein C, Nitsche MA, Paulus W, Knecht S (2004) Transcranial direct current stimulation disrupts tactile perception. Eur J Neurosci 20(1):313–316
Stratton J (1941) Electromagnetic theory, McGraw-Hill Book Company NY, 205–212
Uy J, Ridding MC (2003) Increased cortical excitability induced by transcranial DC and peripheral nerve stimulation. J Neurosci Methods 15, 127(2):193–197
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Accornero, N., Li Voti, P., La Riccia, M. et al. Visual evoked potentials modulation during direct current cortical polarization. Exp Brain Res 178, 261–266 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0733-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0733-y