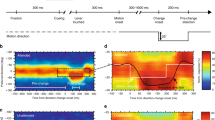
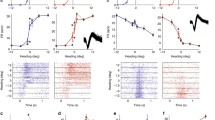
Abstract
Sensation, memories, and predictions contribute to choices in everyday life, and their relative impact should change with task constraints. To investigate how the impact from sensory cortex on decision making varies with task constraints we trained macaque monkeys in a direction discrimination task where they could maximize reward by waiting for sensory visual information early in a trial, while focusing on memory and reward prediction as a trial progressed. The task constraints caused animals to indicate decisions in complete absence of visual motion stimuli (stimulus independent decisions), as 25% of the trials were ‘no stimulus’ trials. On ‘no stimulus’ trials reward delivery depended on the current decision in relation to the decision history. Stimulus independent decisions occurred during an epoch when a stimulus could in principle have been presented, or afterwards when stimuli could not occur anymore. Stimulus independent decisions were significantly different during these two periods. Reward exploitation was more efficient late in the trial, but it was not associated with systematic activity changes in directionally selective neurons in area MT. Conversely, systematic changes of neuronal activity and firing rate correlation in directionally selective middle temporal area (MT) neurons were restricted to a short time period before early decisions. Changing task constraints in the course of a single trial thus determines how neurons in sensory areas contribute to decision making.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aertsen AM, Gerstein GL, Habib MK, Palm G (1989) Dynamics of neuronal firing correlation: modulation of “effective connectivity”. J Neurophysiol 61:900–917
Bair W, Zohary E, Newsome WT (2001) Correlated firing in macaque visual area MT: time scales and relationship to behavior. J Neurosci 21:1676–1697
Barraclough DJ, Conroy ML, Lee D (2004) Prefrontal cortex and decision making in a mixed-strategy game. Nat Neurosci 7:404–410
Bisley JW, Goldberg ME (2003) Neuronal activity in the lateral intraparietal area and spatial attention. Science 299:81–86
Bisley JW, Goldberg ME (2006) Neural correlates of attention and distractibility in the lateral intraparietal area. J Neurophysiol 95:1696–1717
Bradley DC, Chang GC, Andersen RA (1998) Encoding of three-dimensional structure-from-motion by primate area MT neurons. Nature 392:714–717
Britten KH, Shadlen MN, Newsome WT, Movshon JA (1992) The analysis of visual motion: a comparison of neuronal and psychophysical performance. J Neurosci 12:4745–4765
Britten KH, Newsome WT, Shadlen MN, Celebrini S, Movshon JA (1996) A relationship between behavioral choice and the visual responses of neurons in macaque MT. Vis Neurosci 13:87–100
Bruno RM, Sakmann B (2006) Cortex is driven by weak but synchronously active thalamocortical synapses. Science 312:1622–1627
Cook EP, Maunsell JH (2002) Dynamics of neuronal responses in macaque MT and VIP during motion detection. Nat Neurosci 5:985–994
de Oliveira SC, Thiele A, Hoffmann KP (1997) Synchronization of neuronal activity during stimulus expectation in a direction discrimination task. J Neurosci 17:9248–9260
Desimone R (1998) Visual attention mediated by biased competition in extrastriate visual cortex. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 353:1245–1255
Desimone R, Duncan J (1995) Neural mechanisms of selective visual attention. Annu Rev Neursci 18:193–222
Ding L, Hikosaka O (2006) Comparison of reward modulation in the frontal eye field and caudate of the macaque. J Neurosci 26:6695–6703
Dodd JV, Krug K, Cumming BG, Parker AJ (2001) Perceptually bistable three-dimensional figures evoke high choice probabilities in cortical area MT. J Neurosci 21:4809–4821
Dorris MC, Glimcher PW (2004) Activity in posterior parietal cortex is correlated with the relative subjective desirability of action. Neuron 44:365–378
Fries P, Reynolds JH, Rorie AE, Desimone R (2001) Modulation of oscillatory neuronal synchronization by selective visual attention. Science 291:1560–1563
Hoffmann KP, von Seelen W (1980) Performance in the cat’s visual system: a behavioral and neurophysiological analysis. Behav Brain Res 12:101–120
Ichihara-Takeda S, Funahashi S (2006) Reward-period activity in primate dorsolateral prefrontal and orbitofrontal neurons is affected by reward schedules. J Cogn Neurosci 18:212–226
Konishi S, Nakajima K, Uchida I, Kameyama M, Nakahara K, Sekihara K, Miyashita Y (1998) Transient activation of inferior prefrontal cortex during cognitive set shifting. Nat Neurosci 1:80–84
Kreiter AK, Singer W (1996) Stimulus-dependent synchronization of neuronal responses in the visual cortex of the awake macaque monkey. J Neurosci 16:2381–2396
Krug K (2004) A common neuronal code for perceptual processes in visual cortex? Comparing choice and attentional correlates in V5/MT. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 359:929–941
Kusunoki M, Gottlieb J, Goldberg ME (2000) The lateral intraparietal area as a salience map: the representation of abrupt onset, stimulus motion, and task relevance. Vision Res 40:1459–1468
Mansouri FA, Matsumoto K, Tanaka K (2006) Prefrontal cell activities related to monkeys’ success and failure in adapting to rule changes in a Wisconsin Card Sorting Test analog. J Neurosci 26:2745–2756
Miller EK, Li L, Desimone R (1993) Activity of neurons in anterior inferior temporal cortex during a short-term memory task. J Neurosci 13:1460–1478
Miller EK, Erickson CA, Desimone R (1996) Neural mechanisms of visual working memory in prefrontal cortex of the macaque. J Neurosci 16:5154–5167
Morris G, Nevet A, Arkadir D, Vaadia E, Bergman H (2006) Midbrain dopamine neurons encode decisions for future action. Nat Neurosci 9:1057–1063
Nakahara K, Hayashi T, Konishi S, Miyashita Y (2002) Functional MRI of macaque monkeys performing a cognitive set-shifting task. Science 295:1532–1536
Newsome WT, Britten KH, Salzman CD, Movshon JA (1990) Neuronal mechanisms of motion perception. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 55:697–705
Platt ML, Glimcher PW (1999) Neural correlates of decision variables in parietal cortex. Nature 400:233–238
Rainer G, Asaad WF, Miller EK (1998) Memory fields of neurons in the primate prefrontal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15008–15013
Roberts M, Delicato LS, Herrero J, Gieselmann MA, Thiele A (2007) Attention alters spatial integration in macaque V1 in an eccentricity-dependent manner. Nat Neurosci 10:1483–1491
Roelfsema PR, Lamme VA, Spekreijse H (1998) Object-based attention in the primary visual cortex of the macaque monkey. Nature 395:376–381
Roelfsema PR, Lamme VA, Spekreijse H (2004) Synchrony and covariation of firing rates in the primary visual cortex during contour grouping. Nat Neurosci 7:982–991
Roitman JD, Shadlen MN (2002) Response of neurons in the lateral intraparietal area during a combined visual discrimination reaction time task. J Neurosci 22:9475–9489
Saalmann YB, Pigarev IN, Vidyasagar TR (2007) Neural mechanisms of visual attention: how top-down feedback highlights relevant locations. Science 316:1612–1615
Salzman CD, Britten KH, Newsome WT (1990) Cortical microstimulation influences perceptual judgements of motion direction. Nature 346:174–177
Schultz W, Tremblay L, Hollerman JR (2000) Reward processing in primate orbitofrontal cortex and basal ganglia. Cereb Cortex 10:272–284
Seidemann E, Zohary E, Newsome WT (1998) Temporal gating of neural signals during performance of a visual discrimination task. Nature 394:72–75
Shadlen MN, Britten KH, Newsome WT, Movshon JA (1996) A computational analysis of the relationship between neuronal and behavioral responses to visual motion. J Neurosci 16:1486–1510
Singer W (1999) Neuronal synchrony: a versatile code for the definition of relations. Neuron 24:49–65
Smith P (1995) Psychophysically principled models of visual simple reaction time. Psychol Rev 102:567–593
Sugrue LP, Corrado GS, Newsome WT (2004) Matching behavior and the representation of value in the parietal cortex. Science 304:1782–1787
Thiele A, Hoffmann KP (1996) Neuronal activity in MST and STPp, but not MT changes systematically with stimulus-independent decisions. Neuroreport 7:971–976
Thiele A, Distler C, Hoffmann KP (1999) Decision-related activity in the macaque dorsal visual pathway. Eur J Neurosci 11:2044–2058
Thiele A, Dobkins KR, Albright TD (2001) Neural correlates of chromatic motion perception. Neuron 32:351–358
Treue S, Maunsell JHR (1996) Attentional modulation of visual motion processing in cortical areas MT and MST. Nature 382:539–541
Treue S, Trujillo JCM (1999) Feature-based attention influences motion processing gain in macaque visual cortex. Nature 399:575–579
Tsujimoto S, Sawaguchi T (2005) Neuronal activity representing temporal prediction of reward in the primate prefrontal cortex. J Neurophysiol 93:3687–3692
von Seelen W, Hoffmann KP (1976) Analysis of neuronal networks in the visual system of the cat using statistical signals. Part I Biol Cybern 22:7–20
Wallis JD, Miller EK (2003) From rule to response: neuronal processes in the premotor and prefrontal cortex. J Neurophysiol 90:1790–1806
Wallis JD, Anderson KC, Miller EK (2001) Single neurons in prefrontal cortex encode abstract rules. Nature 411:953–956
Womelsdorf T, Fries P, Mitra PP, Desimone R (2006) Gamma-band synchronization in visual cortex predicts speed of change detection. Nature 439:733–736
Yang T, Shadlen MN (2007) Probabilistic reasoning by neurons. Nature 447:1075–1080
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank J. Read, P. Dayan, and N. Daw for valuable help, feedback, and discussions. Supported by Deutsche-Forschungs-Gemeinschaft, Neurovision, SFB 509. AT was supported by the Wellcome Trust.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thiele, A., Hoffmann, KP. Neuronal firing rate, inter-neuron correlation and synchrony in area MT are correlated with directional choices during stimulus and reward expectation. Exp Brain Res 188, 559–577 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1391-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1391-z