Abstract
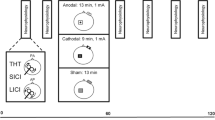
Short interval intracortical inhibition (SICI) is a common paired-pulse TMS technique that is used to measure GABAa-ergic inhibition in the cerebral motor cortex. However, inhibition evaluated with an interstimulus interval (ISI) between the TMS pulses of 2.5 ms has quite different properties from that seen at 1 ms. It is thought that the latter may represent either (or both) a different type of synaptic inhibition or refractoriness of neural membranes. The present experiments provide further evidence about the early and late components of SICI using transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), a technique thought to change neural excitability by polarising the nerve membranes. We assessed SICI using a threshold tracking method at a range of ISIs during concurrent application of tDCS in 11 healthy volunteers (8 males, 27–43 years old). Each subject underwent both anodal and cathodal tDCS with two different intensities of stimulation (1 and 2 mA). Because there was no significant difference between the results at the two intensities, the data were combined. Principal component analysis was used to separate the contributions of early and late SICI to the time course of inhibition from 1 to 5 ms tDCS had opposite effects on early and late SICI. Anodal tDCS reduced late SICI but enhanced early SICI, whereas cathodal tDCS had the opposite effect. This is further evidence that the two phases of SICI are produced by different mechanisms, perhaps involving different sets of neurones or different locations on the same neurone that respond oppositely to tDCS.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bestmann S, Siebner HR, Modugno N, Amassian VE, Rothwell JC (2004) Inhibitory interactions between pairs of subthreshold conditioning stimuli in the human motor cortex. Clin Neurophysiol 115:755–764
Bikson M, Inoue M, Akiyama H, Deans JK, Fox JE, Miyakawa H, Jefferys JG (2004) Effects of uniform extracellular DC electric fields on excitability in rat hippocampal slices in vitro. J Physiol 557:175–190
Boroojerdi B, Kopylev L, Battaglia F, Facchini S, Ziemann U, Muellbacher W, Cohen LG (2000) Reproducibility of intracortical inhibition and facilitation using the paired-pulse paradigm. Muscle Nerve 23:1594–1597
Creutzfeldt OD, Fromm GH, Kapp H (1962) Influence of transcortical d-c currents on cortical neuronal activity. Exp Neurol 5:436–452
Day BL, Dressler D, de Maertens NA, Marsden CD, Nakashima K, Rothwell JC, Thompson PD (1989) Electric and magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex: surface EMG and single motor unit responses [published erratum appears in J Physiol (Lond) 1990 Nov; 430:617]. J Physiol Lond 412:449–473
Di Lazzaro V, Restuccia D, Oliviero A, Profice P, Ferrara L, Insola A, Mazzone P, Tonali P, Rothwell JC (1998) Magnetic transcranial stimulation at intensities below active motor threshold activates intracortical inhibitory circuits. Exp Brain Res 119:265–268
Di Lazzaro V, Ziemann U, Lemon RN (2008) State of the art: physiology of transcranial motor cortex stimulation. Brain Stimul 1:345–362
Fisher RJ, Nakamura Y, Bestmann S, Rothwell JC, Bostock H (2002) Two phases of intracortical inhibition revealed by transcranial magnetic threshold tracking. Exp Brain Res 143:240–248
Hanajima R, Ugawa Y, Terao Y, Ogata K, Kanazawa I (1996) Ipsilateral cortico-cortical inhibition of the motor cortex in various neurological disorders. J Neurol Sci 140:109–116
Hanajima R, Ugawa Y, Terao Y, Sakai K, Furubayashi T, Machii K, Kanazawa I (1998) Paired-pulse magnetic stimulation of the human motor cortex: differences among I waves. J Physiol Lond 509:607–618
Hanajima R, Furubayashi T, Iwata NK, Shiio Y, Okabe S, Kanazawa I, Ugawa Y (2003) Further evidence to support different mechanisms underlying intracortical inhibition of the motor cortex. Exp Brain Res 151:427–434
Ilic TV, Meintzschel F, Cleff U, Ruge D, Kessler KR, Ziemann U (2002) Short-interval paired-pulse inhibition and facilitation of human motor cortex: the dimension of stimulus intensity. J Physiol 545:153–167
Kiernan MC, Burke D, Andersen KV, Bostock H (2000) Multiple measures of axonal excitability: a new approach in clinical testing. Muscle Nerve 23:399–409
Kujirai T, Caramia MD, Rothwell JC, Day BL, Thompson PD, Ferbert A, Wroe S, Asselman P, Marsden CD (1993) Corticocortical inhibition in human motor cortex. J Physiol Lond 471:501–519
Lackmy A, Marchand-Pauvert V (2010) The estimation of short intra-cortical inhibition depends on the proportion of spinal motoneurones activated by corticospinal inputs. Clin Neurophysiol 121:612–621
Lang N, Nitsche MA, Paulus W, Rothwell JC, Lemon RN (2004) Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation over the human motor cortex on corticospinal and transcallosal excitability. Exp Brain Res 156:439–443
Lang N, Nitsche MA, Dileone M, Mazzone P, De Andres-Ares J, Diaz-Jara L, Paulus W, Di Lazzaro V, Oliviero A (2011) Transcranial direct current stimulation effects on I-wave activity in humans. J Neurophysiol 105:2802–2810
Lee H, Gunraj C, Chen R (2007) The effects of inhibitory and facilitatory intracortical circuits on interhemispheric inhibition in the human motor cortex. J Physiol 580:1021–1032
Martin PG, Gandevia SC, Taylor JL (2006) Output of human motoneuron pools to corticospinal inputs during voluntary contractions. J Neurophysiol 95:3512–3518
Nitsche MA, Paulus W (2000) Excitability changes induced in the human motor cortex by weak transcranial direct current stimulation. J Physiol 527:633–639
Nitsche MA, Liebetanz D, Antal A, Lang N, Tergau F, Paulus W (2003) Modulation of cortical excitability by weak direct current stimulation–technical, safety and functional aspects. Suppl Clin Neurophysiol 56:255–276
Nitsche MA, Seeber A, Frommann K, Klein CC, Rochford C, Nitsche MS, Fricke K, Liebetanz D, Lang N, Antal A, Paulus W, Tergau F (2005) Modulating parameters of excitability during and after transcranial direct current stimulation of the human motor cortex. J Physiol 568:291–303
Orth M, Snijders AH, Rothwell JC (2003) The variability of intracortical inhibition and facilitation. Clin Neurophysiol 114:2362–2369
Ortu E, Deriu F, Suppa A, Tolu E, Rothwell JC (2008) Effects of volitional contraction on intracortical inhibition and facilitation in the human motor cortex. J Physiol 586:5147–5159
Peurala SH, Muller-Dahlhaus JF, Arai N, Ziemann U (2008) Interference of short-interval intracortical inhibition (SICI) and short-interval intracortical facilitation (SICF). Clin Neurophysiol 119:2291–2297
Ridding MC, Inzelberg R, Rothwell JC (1995a) Changes in excitability of motor cortical circuitry in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 37:181–188
Ridding MC, Sheean G, Rothwell JC, Inzelberg R, Kujirai T (1995b) Changes in the balance between motor cortical excitation and inhibition in focal, task specific dystonia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 59:493–498
Roshan L, Paradiso GO, Chen R (2003) Two phases of short-interval intracortical inhibition. Exp Brain Res 151:330–337
Sakai K, Ugawa Y, Terao Y, Hanajima R, Furubayashi T, Kanazawa I (1997) Preferential activation of different I waves by transcranial magnetic stimulation with a figure-of-eight-shaped coil. Exp Brain Res 113:24–32
Sanger TD, Garg RR, Chen R (2001) Interactions between two different inhibitory systems in the human motor cortex. J Physiol 530:307–317
Stagg CJ, Bestmann S, Constantinescu AO, Moreno ML, Allman C, Mekle R, Woolrich M, Near J, Johansen-Berg H, Rothwell JC (2011) Relationship between physiological measures of excitability and levels of glutamate and GABA in the human motor cortex. J Physiol 589:5845–5855
Tokimura H, Ridding MC, Tokimura Y, Amassian VE, Rothwell JC (1996) Short latency facilitation between pairs of threshold magnetic stimuli applied to human motor cortex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 101:263–272
Vucic S, Howells J, Trevillion L, Kiernan MC (2006) Assessment of cortical excitability using threshold tracking techniques. Muscle Nerve 33:477–486
Vucic S, Cheah BC, Krishnan AV, Burke D, Kiernan MC (2009) The effects of alterations in conditioning stimulus intensity on short interval intracortical inhibition. Brain Res 1273:39–47
Vucic S, Cheah BC, Kiernan MC (2011) Dissecting the mechanisms underlying short-interval intracortical inhibition using exercise. Cereb Cortex 21:1639–1644
Wassermann EM (2002) Variation in the response to transcranial magnetic brain stimulation in the general population. Clin Neurophysiol 113:1165–1171
Wessel K, Tegenthoff M, Vorgerd M, Otto V, Nitschke MF, Malin JP (1996) Enhancement of inhibitory mechanisms in the motor cortex of patients with cerebellar degeneration: a study with transcranial magnetic brain stimulation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 101:273–280
Ziemann U, Lonnecker S, Steinhoff BJ, Paulus W (1996a) Effects of antiepileptic drugs on motor cortex excitability in humans: a transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Ann Neurol 40:367–378
Ziemann U, Lonnecker S, Steinhoff BJ, Paulus W (1996b) The effect of lorazepam on the motor cortical excitability in man. Exp Brain Res 109:127–135
Ziemann U, Tergau F, Wassermann EM, Wischer S, Hildebrandt J, Paulus W (1998) Demonstration of facilitatory I wave interaction in the human motor cortex by paired transcranial magnetic stimulation. J Physiol Lond 511:181–190
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by REPLACES: Restorative Plasticity at Corticostriatal Excitatory Synapses: an FP7 Collaborative Project (222918). Bülent Cengiz is supported by The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) under the programme 2219.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cengiz, B., Murase, N. & Rothwell, J.C. Opposite effects of weak transcranial direct current stimulation on different phases of short interval intracortical inhibition (SICI). Exp Brain Res 225, 321–331 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-012-3369-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-012-3369-0