Abstract
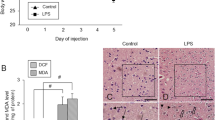
Neuroinflammation facilitates seizure acquisition and epileptogenesis in developing brain. Yet, the studies on impact of neuroinflammation on mature brain epileptogenesis have led to inconsistent results. Hippocampus is particularly vulnerable to damage caused by ischemia, hypoxia and trauma, and the consequent neuroinflammation, which can lead in turn to epilepsy. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is extensively used in experimental studies to induce neuroinflammation. In this study, effect of acute and chronic intra-CA1 infusion of LPS on amygdala-kindled seizures and epileptogenesis was examined in mature rats. LPS (5 μg/rat) inhibited evoked amygdala afterdischarges and behavioral seizures. Anticonvulsant effect of LPS was observed 0.5 h after administration and continued up to 24 h. This effect was accompanied by intra-hippocampal elevation of nitric oxide (NO), interleukin1-β, and tumor necrosis factor-α and was prevented by microglia inhibitor, naloxone, NO synthase inhibitor, Nω-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester, cyclooxygenase inhibitor, piroxicam, and interleukin1-β receptor antagonist, interleukin1-ra. Moreover, daily intra-hippocampal injection of LPS significantly retarded kindling rate. In order to further elucidate the effect of LPS on synaptic transmission and short-term plasticity, changes in field excitatory postsynaptic potentials and population spikes were measured in stratum radiatum and stratum pyramidale of LPS-treated kindled rats. LPS impaired baseline synaptic transmission in hippocampal Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapse and reduced the magnitude of paired-pulse facilitation. Our results suggest that direct suppression of presynaptic mechanisms in Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses, as well as the inflammatory mediators released by LPS in the hippocampus, is involved in antiepileptic effect of LPS.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin1-β
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- IL-1ra:
-
Interleukin1ra
- l-NAME:
-
N ω-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester
- i.h:
-
Intra-hippocampal
- i.p:
-
Intra-peritoneally
- AD:
-
Afterdischarge
- ADD:
-
AD duration
- SS:
-
Behavioral seizure severity
- S5D:
-
Duration of stage 5 seizure behavior
- SD:
-
Duration of seizure behavior
- fEPSP:
-
Field excitatory postsynaptic potential
- PS:
-
Population spike
- PPI:
-
Paired-pulse index
- PPF:
-
Paired-pulse facilitation
- TGF-β1:
-
Transforming growth factor-β1
- PTZ:
-
Pentylenetetrazole
References
Akarsu ES, Mamuk S, Comert A (1998) Inhibition of pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures in rats by prostaglandin D2. Epilepsy Res 30:63–68
Akarsu ES, Ozdayi S, Algan E, Ulupinar F (2006) The neuronal excitability time-dependently changes after lipopolysaccharide administration in mice: possible role of cyclooxygenase-2 induction. Epilepsy Res 71:181–187
Ambrosini A, Louin G, Croci N, Plotkine M, Jafarian-Tehrani M (2005) Characterization of a rat model to study acute neuroinflammation on histopathological, biochemical and functional outcomes. J Neurosci Methods 144:183–191
Arican N, Kaya M, Kalayci R, Uzun H, Ahishali B, Bilgic B, Elmas I, Kucuk M, Gurses C, Uzun M (2006) Effects of lipopolysaccharide on blood-brain barrier permeability during pentylenetetrazole-induced epileptic seizures in rats. Life Sci 79:1–7
Auvin S, Mazarati A, Shin D, Sankar R (2010a) Inflammation enhances epileptogenesis in the developing rat brain. Neurobiol Dis 40:303–310
Auvin S, Shin D, Mazarati A, Sankar R (2010b) Inflammation induced by LPS enhances epileptogenesis in immature rat and may be partially reversed by IL1RA. Epilepsia 51:34–38
Baik EJ, Kim EJ, Lee SH, Moon CH (1999) Cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors aggravate kainic acid induced seizure and neuronal cell death in the hippocampus. Brain Res 843:118–129
Balosso S, Ravizza T, Perego C, Peschon J, Campbell IL, De Simoni MG, Vezzani A (2005) Tumor necrosis factor inhibits seizures in mice via p75 receptors. Ann Neurol 57:804–812
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bruce AJ, Boling W, Kindy MS, Peschon J, Kraemer PJ, Carpenter MK, Holtsberg FW, Mattson MP (1996) Altered neuronal and microglial responses to excitotoxic and ischemic brain injury in mice lacking TNF receptors. Nat Med 2:788–794
Carson FL, Hladik C (1990) Histotechnology: a self-instructional text. American Society of Clinical Pathology Press, Chicago, pp 170–171
Chen R, Zhou H, Beltran J, Malellari L, Chang SL (2005) Differential expression of cytokines in the brain and serum during endotoxin tolerance. J Neuroimmunol 163:53–72
Clark KA, Randall AD, Collingridge GL (1994) A comparison of paired-pulse facilitation of AMPA and NMDA-receptor mediatedexcitatory postsynaptic currents in the hippocampus. Exp Brain Res 101:272–278
Commins S, O’Neill L, O’Mara S (2001) The effects of the bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide on synaptic transmission and plasticity in the CA1-subiculum pathway in vivo. Neuroscience 102:273–280
Cunningham A, Murray C, O’Neill L, Lynch M, O’Connor J (1996) Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibit long-term potentiation in the rat dentate gyrus in vitro. Neurosci Lett 203:17–20
Czapski GA, Cakala M, Chalimoniuk M, Gajkowska B, Strosznajder JB (2007) Role of nitric oxide in the brain during lipopolysaccharide evoked systemic inflammation. J Neurosci Res 85:1694–1703
de Vasconcelos APGF, Marescaux C, Nehlig A (2000) Role of nitric oxide in pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures: age dependent effects in the immature rat. Epilepsia 41:363–371
Dmowska M, Cybulska R, Schoenborn R, Piersiak T, Jaworska-Adamu J, Gawron A (2010) Behavioural and histological effects of preconditioning with lipopolysaccharide in epileptic rats. Neurochem Res 35:262–272
Elkabes S, Peng L, Black IB (1998) Lipopolysaccharide differentially regulates microglial trk receptor and neurotrophin expression. J Neurosci Res 54:117–122
Gavilán MP, Revilla E, Pintado C, Castaño A, Vizuete ML, Moreno-González I, Baglietto-Vargas D, Sánchez-Varo R, Vitorica J, Gutiérrez A, Ruano D (2007) Molecular and cellular characterization of the age-related neuroinflammatory processes occurring in normal rat hippocampus: potential relation with the loss of somatostatin GABAergic neurons. J Neurochem 103:984–996
Godlevsky LS, Shandra AA, Oleinik AA, Vastyanov RS, Kostyushov VV, Timchishin OL (2002) TNF-alpha in cerebral cortex and cerebellum is affected by amygdalar kindling but not by stimulation of cerebellum. Pol J Pharmacol 54:655–660
Heese K, Fiebich BL, Bauer J, Otten U (1998) NF-kappa B modulates lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial nerve growth factor expression. Glia 22:401–407
Hellstrom JC, Danik M, Luheshi GN, Williams S (2005) Chronic LPS exposure produces changes in intrinsic membrane properties and a sustained IL-1β-dependent increase in GABAergic inhibition in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Hippocampus 15:656–664
Hughes PE, Alexi T, Waltson M, Williams CE, Dragunow M, Clark RG, Gluckman PD (1999) Activity and injury-dependent depression of inducible transcription factors, growth factors and apoptosis-related genes within the central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 57:421–450
Jacobsson J, Persson M, Hansson E, Rönnbäck L (2006) Corticosterone inhibits expression of the microglial glutamate transporter GLT-1 in vitro. Neuroscience 139:475–483
Jakubs K, Bonde S, Iosif RE, Ekdahl CT, Kokaia Z, Kokaia M, Lindvall O (2008) Inflammation regulates functional integration of neurons born in adult brain. J Neurosci 28:12477–12488
Jan W, Chen C, Hsu K, Tsai P, Huang C (2010) L-type calcium channels and μ-opioid receptors are involved in mediating the anti-inflammatory effects of naloxone. J Surg Res 167:263–272
Jayakumar A, Sujatha R, Paul V, Puviarasan K, Jayakumar R (1999) Involvement of nitric oxide and nitric oxide synthase activity in anticonvulsive action. Brain Res Bull 48:387–394
Jo JH, Park EJ, Lee JK, Jung MW, Lee CJ (2001) Lipopolysaccharide inhibits induction of long-term potentiation and depression in the rat hippocampal CA1 area. Eur J Pharmacol 422:69–76
Kelly ME, McIntyre DC (1994) Hippocampal kindling protects several structures from the neuronal damage resulting from kainic acid-induced status epilepticus. Brain Res 634:245–256
Khurgel M, Ivy GO (1996) Astrocytes in kindling: relevance to epileptogenesis. Epilepsy Res 26:63–75
Kim WG, Mohney RP, Wilson B, Jeohn GH, Liu B, Hong JS (2000) Regional difference in susceptibility to lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity in the rat brain: role of microglia. J Neurosci 20:6309–6316
Klein SL, Nelson RJ (1999) Activation of the immune–endocrine system with lipopolysaccharide reduces affiliative behaviors in voles. Behav Neurosci 113:1042–1048
Kovacs Z, Kekesi KA, Szilagyl N, Abraham I, Szekacs D, Kiraly N, Papp E, Csaszar I, Szego E, Barabas K, Heterfy H, Erdei A, Bartfai T, Juhasz G (2006) Facilitation of spike-wave discharge activity by lipopolysaccharides in Wistar Albino Glaxo/Rigswijk rats. Neuroscience 140:731–742
Kovács Z, Czurkó A, Kékesi K, Juhász G (2011) Intracerebroventricularly administered lipopolysaccharide enhances spike-wave discharges in freely moving WAG/Rij rats. Brain Res Bull 85:410–416
Liu J, Marino MW, Wong G, Grail D, Dunn A, Bettadapura J, Slavin AJ, Old L, Bernard CC (1998) TNF is a potent anti-inflammatory cytokine autoimmune-mediated demyelination. Nat Med 4:78–83
Liu B, Du L, Hong JS (2000a) Naloxone protects rat dopaminergic neurons against inflammatory damage through inhibition of microglia activation and superoxide generation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293:607–617
Liu B, Jiang JW, Wilson BC, Du L, Yang SN, Wang JY, Wu GC, Cao XD, Hong JS (2000b) Systemic infusion of naloxone reduces degeneration of rat substantia nigral dopaminergic neurons induced by intranigral injection of lipopolysaccharide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:125–132
Magni DV, Souza MA, Oliveira APF, Furian AF, Oliveira MS, Ferreira J, Santos ARS, Mello CF, Royes LFF, Fighera MR (2011) Lipopolysaccharide enhances glutaric acid-induced seizure susceptibility in rat pups: behavioral and electroencephalographic approach. Epilepsy Res 93:138–148
Markram H, Toledo-Rodriguez M, Wang Y, Gupta A, Silberberg G, Wu C (2004) Interneurons of the neocortical inhibitory system. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:793–807
McNamara JO, Byrne MC, Dasheiff RM, Fitz JG (1980) The kindling model of epilepsy: a review. Prog Neurobiol 15:139–159
Mirrione MM, Konomos DK, Gravanis I, Dewey SL, Aguzzi A, Heppner FL, Tsirka SE (2010) Microglial ablation and lipopolysaccharide preconditioning affects pilocarpine-induced seizures in mice. Neurobiol Dis 39:85–97
Miwa T, Furukawa S, Nakajima K, Furukawa Y, Kohsaka S (1997) Lipopolysaccharide enhances synthesis of brain derived neurotrophic factor in cultured rat microglia. J Neurosci Res 50:1023–1029
Nakajima K, Honda S, Tohyama Y, Imai Y, Kohsaka S, Kurihara T (2001) Neurotrophin secretion from cultured microglia. J Neurosci Res 65:322–331
Nathan T, Lambert JDC (1991) Depression of the fast IPSP underlies paired-pulse facilitation in area CA1 of the rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 66:1704–1715
Ni YQ, Xu GZ, Hu WZ, Shi L, Qin Y, Da C (2008) Neuroprotective effects of naloxone against light-induced photoreceptor degeneration through inhibiting retinal microglial activation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49:2589–2598
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, NewYork
Persson M, Brantefjord M, Hansson E, Ronnback L (2005) Lipopolysaccharide increases microglial GLT-1 expression and glutamate uptake capacity in vitro by a mechanism dependent on TNF-alpha. Glia 51:111–120
Plata-Salaman CR, Ilyin SE, Turin NP, Gayle D, Flynn MC, Romanovitch AE, Kelly ME, Bureau Y, Anisman H, McIntyre D (2000) Kindling modulates the IL-1β system, TNF-α, TGF-β1, and neuropeptide mRNAs in specific brain regions. Mol Brain Res 75:248–258
Prow NA, Irani DN (2007) The opioid receptor antagonist, naloxone, protects spinal motor neurons in a murine model of alphavirus encephalomyelitis. Exp Neurol 205:461–470
Ravizza T, Noe F, Zardoni D, Vaghi V, Sifringer M, Vezzani A (2008) Interleukin converting enzyme inhibition impairs kindling epileptogenesis in rats by blocking astrocytic IL-1 [beta] production. Neurobiol Dis 31:327–333
Rodgers KM, Hutchinson MR, Northcutt A, Maier SF, Watkins LR, Barth DS (2009) The cortical innate immune response increases local neuronal excitability leading to seizures. Brain 132:2478–2486
Rosi S, Vazdarjanova A, Ramirez-Amaya V, Worley PF, Barnes CA, Wenk GL (2006) Memantine protects against LPS-induced neuroinflammation, restores behaviorally-induced gene expression and spatial learning in the rat. Neuroscience 142:1303–1315
Sayyah M, Javad-Pour M, Ghazi-Khansari M (2003a) The bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide enhances seizure susceptibility in mice: involvement of proinflammatory factors: nitric oxide and prostaglandins. Neuroscience 122:1073–1080
Sayyah M, Najafabadi IT, Beheshti S, Majzoob S (2003b) Lipopolysaccharide retards development of amygdala kindling but does not affect fully-kindled seizures in rats. Epilepsy Res 57:175–180
Sayyah M, Beheshti S, Shokrgozar MA, Eslami-far A, Deljoo Z, Khabiri AR, Haeri Rohani A (2005) Antiepileptogenic and anticonvulsant activity of interleulin-1 β in amygdala-kindled rats. Exp Neurol 191:145–153
Schuligoi R, Ulcar R, Peskar BA, Amann R (2003) Effect of endotoxin treatment on the expression on cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin synthases in spinal cord, dorsal root ganglia, and skin of rats. Neuroscience 116:1043–1052
Shandra AA, Godlevsky LS, Vastyanov RS, Oleinik AA, Konovalenko VL, Rapoport EN, Korobka NN (2002) The role of TNF-α in amygdala kindled rats. Neurosci Res 42:147–153
Shimizu H, Miyoshi M, Matsumoto K, Goto O, Imoto T, Watanabe T (2004) The effect of central injection of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and the angiotensin type 1 receptor antagonist on the induction by lipopolysaccharide of fever and brain interleukin-1β response in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 308:865–873
Varona P, Ibarz J, López-Aguado L, Herreras O (2000) Macroscopic and subcellular factors shaping population spikes. J Neurophysiol 83:2192–2208
Vezzani A, French J, Bartfai T, Baram TZ (2010) The role of inflammation in epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol 7:31–40
Voss LJ, Jacobson G, Sleigh JW, Steyn Ross A, Steyn Ross M (2009) Excitatory effects of gap junction blockers on cerebral cortex seizure like activity in rats and mice. Epilepsia 50:1971–1978
Wiebe S (2000) Epidemiology of temporal lobe epilepsy. Can J Neurol Sci 27:S6–S21
Wu LG, Saggau P (1993) Presynaptic calcium is increased during normal synaptic transmission and paired pulse facilitation, but not in long term potentiation in area CA1 of hippocampus. J Neurosci 14:645–654
Yang L, Ling DSF (2007) Carbenoxolone modifies spontaneous inhibitory and excitatory synaptic transmission in rat somatosensory cortex. Neurosci Lett 416:221–226
Yang L, Li F, Ge W, Mi C, Wang R, Sun R (2010) Protective effects of naloxone in two hit seizure model. Epilepsia 51:344–353
Conflict of interest
None of authors has any conflict of interest to disclose. We confirm that we have read Journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadi, A., Sayyah, M., Khoshkholgh-Sima, B. et al. Intra-hippocampal injection of lipopolysaccharide inhibits kindled seizures and retards kindling rate in adult rats. Exp Brain Res 226, 107–120 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-013-3415-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-013-3415-6