Abstract
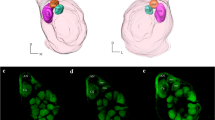
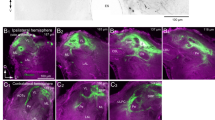
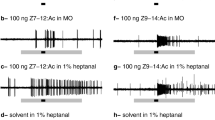
The sphinx moth Manduca sexta is a well-studied insect with regard to central olfactory functions. Until now, the innervation patterns of olfactory receptor neurons into the array of olfactory glomeruli in the antennal lobe have, however, been unclear. Using optical imaging to visualize calcium dynamics within the antennal lobe we demonstrate specific patterns elicited by sex pheromone components and plant-derived odours. These patterns mainly reflect receptor neuron activity. Within the male-specific macroglomerular complex the two major pheromone components evoke stereotyped activity in either of two macroglomerular complex glomeruli. Based on previous knowledge of output neuron specificity, our results suggest a matching of information between input and output in the macroglomerular complex. Plant odours evoked activity in the sexually isomorphic glomeruli. Two major results were obtained: (1) terpenes and aromatic compounds activate different clusters of glomeruli with only minor overlapping, and (2) the position of certain key glomeruli is fixed in both males and females, which suggests that host-plant related odorants are processed in a similar way in both sexes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AL:
-
antennal lobe
- bombykal:
-
E10, Z12-hexadecadienal
- EE bombykal:
-
E10, E12-hexadecadienal
- EEZ:
-
E10, E12, Z12-hexadecatrienal
- LFG:
-
large female glomerulus
- MGC:
-
macroglomerular complex
- Z11–16:Ald:
-
Z11-hexadecenal
References
Anton S, Hansson BS (1995) Sex pheromone and plant-associated odour processing in antennal lobe interneurons of male Spodoptera littoralis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Comp Physiol A 176:773–789
Anton S, Hansson BS (1999) Physiological mismatching between neurons innervating olfactory glomeruli in a moth. Proc R Soc Lond Ser B 266:1813–1820
Bell RA, Joachim FA (1976) Techniques for rearing laboratory colonies of tobacco hornworms and pink bollworms. Ann Entomol Soc Am 69:365–373
Berg BG, Almaas TJ, Bjaalie JG, Mustaparta H (1998) The macroglomerular complex of the antennal lobe in the tobacco budworm moth Heliothis virescens: specified subdivision in four compartments according to information about biologically significant compounds. J Comp Physiol A 183:669–682
Carlsson MA, Galizia CG, Hansson BS (2002) Spatial representation of odours in the antennal lobe of the moth Spodoptera littoralis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Chem Senses 27:231–244
Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1987) Male-specific, sex pheromone-selective projection neurons in the antennal lobes of the moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol 160:553–569
Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG, Tumlinson JH, Doolittle RE (1989a) Sex pheromone blend of Manduca sexta: responses of central olfactory interneurones to antennal stimulation in male moths. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 10:281–291
Christensen TA, Mustaparta H, Hildebrand JG (1989b) Discrimination of sex-pheromone blends in the olfactory system of the moth. Chem Senses 14:463–477
Christensen TA, Mustaparta H, Hildebrand JG (1995a) Chemical communication in heliothine moths. VI. Parallel pathways for information processing in the macroglomerular complex of the male tobacco budworm moth Heliothis virescens. J Comp Physiol A 177:545–557
Christensen TA, Harrow ID, Cuzzocrea CH, Randolph PW, Hildebrand JG (1995b) Distinct projections of two populations of olfactory receptor axons in the antennal lobe of the sphinx moth Manduca sexta. Chem Senses 20:313–323
Galizia CG, Menzel R (2001) The role of glomeruli in the neural representation of odours: results from optical recording studies. J Insect Physiol 47:115–130
Galizia GC, Joerges J, Küttner A, Faber T, Menzel R (1997) A semi-in vivo preparation for optical recording of the insect brain. J Neurosci Methods 76:61–69
Galizia CG, Nägler K, Hölldobler B, Menzel R (1998) Odour coding is bilaterally symmetrical in the antennal lobes of honeybees (Apis mellifera). Eur J Neurosci 10:2964–2974
Galizia GG, Sachse S, Mustaparta H (2000) Calcium responses to pheromones and plant odours in the antennal lobe of the male and female moth Heliothis virescens. J Comp Physiol A 186:1049–1063
Hansson BS, Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1991) Functionally distinct subdivisions of the macroglomerular complex in the antennal lobe of the male sphinx moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Neurol 312:264–278
Hansson BS, Anton S, Christensen TA (1994) Structure and function of antennal lobe interneurons in the male turnip moth, Agrotis segetum (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Comp Physiol A 175:547–562
Heinbockel T, Kloppenburg P, Hildebrand JG (1998) Pheromone-evoked potentials and oscillations in the antennal lobes of the sphinx moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol A 182 6:703–714
Joerges J, Küttner A, Galiza CG, Menzel R (1997) Representations of odours and odour mixtures visualized in the honeybee brain. Nature 387:285–288
Kaissling KE, Hildebrand JG,Tumlinson JH (1989) Pheromone receptor cells in the male moth Manduca sexta. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 10:273–279
Kalinová B, Hoskovec M, Liblikas I, Unelius CR, Hansson BS (2001) Detection of sex pheromone components in Manduca sexta (L.) Chem Senses 26:1175–1186
Kauer JS, White J (2001) Imaging and coding in the olfactory system. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:963–979
King JR, Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (2000) Response characteristics of an identified, sexually dimorphic olfactory glomerulus. J Neurosci 20:2391–2399
Korsching S (2002) Olfactory maps and odor images. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12:387–392
Lei H, Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (2002) Local inhibition modulates odor-evoked synchronization of glomerulus-specific output neurons. Nat Neurosci 5:557–565
Matsumoto SG, Hildebrand JG (1981) Olfactory mechanisms in the moth Manduca sexta: response characteristics and morphology of central neurons in the antennal lobes. Proc R Soc Lond Ser B 213:249–277
Rospars JP, Hildebrand JG (2000) Sexually dimorphic and isomorphic glomeruli in the antennal lobes of the sphinx moth Manduca sexta. Chem Senses 25:119–129
Shields VDC, Hildebrand JG (2001) Responses of a population of antennal olfactory receptor cells in the female moth Manduca sexta to plant-associated volatile organic compounds. J Comp Physiol A 186:1135–1151
Starrat AN, Dahm KH, Allen N, Hildebrand JG, Payne TL, Röller H (1979) Bombykal, a sex pheromone of the sphinx moth Manduca sexta. Z Naturforsch 34C:9–12
Todd JL, Baker TC (1996) Antennal lobe partitioning of behaviorally active odors in female cabbage looper moths. Naturwissenschaften 83:324–326
Tumlinson JH, Brennan MM, Doolittle RE, Mitchell ER, Brabham A, Mazomenos BE, Baumhover AH, Jackson DM (1989) Identification of a pheromone blend attractive to Manduca sexta (L.) males in a wind tunnel. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 10:255−271
Tumlinson JH, Mitchell ER, Doolittle RE, Jackson DM (1994) Field tests of synthetic Manduca sexta sex pheromone. J Chem Ecol 20:579–591
Vickers NJ, Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1998) Combinatorial odor discrimination in the brain: attractive and antagonist odor blends are represented in distinct combinations of uniquely identifiable glomeruli. J Comp Neurol 400:35–56
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hansson, B.S., Carlsson, M.A. & Kalinovà, B. Olfactory activation patterns in the antennal lobe of the sphinx moth, Manduca sexta . J Comp Physiol A 189, 301–308 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-003-0403-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-003-0403-5