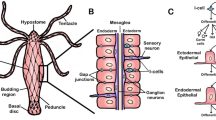
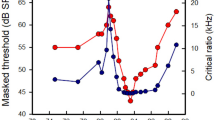
Abstract
The lateral line is a hydrodynamic sensory system that allows fishes and aquatic amphibians to detect the water motions caused, for instance, by conspecifics, predators or prey. Typically the peripheral lateral line of fishes consists of several hundred neuromasts spread over the head, trunk, and tail fin. Lateral line neuromasts are mechanical low-pass filters that have an operating range from <1 Hz up to about 150 Hz. Within this frequency range, neuromasts encode the duration, local direction, amplitude, frequency, and phase of a hydrodynamic stimulus. This paper reviews the peripheral and central processing of lateral line information in fishes. Special attention is given to the coding of simple and complex hydrodynamic stimuli, to parallel processing, the roles of the various brain areas that process hydrodynamic information and the centrifugal (efferent) control of lateral line information. The review argues that in order to fully comprehend peripheral and central lateral line information processing, it is imperative to do comparative studies that take into account the ecology of fishes, meaning that natural stimulus and noise conditions have to be considered.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALLN:
-
Anterior lateral line nerve
- CN:
-
Canal neuromast
- MON :
-
Medial octavolateralis nucleus
- PLLN :
-
Posterior lateral line nerve
- SN:
-
Superficial neuromast
- RF:
-
Receptive field
References
Alexandre D, Ghysen A (1999) Somatotopy of the lateral line projection in larval zebrafish. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7558–7562
Alnaes E (1973) Unit activity of ganglionic and medullary second order neurones in the eel lateral line system. Acta Physiol Scand 88:160–174
Altman JS, Dawes EA (1981) Mapping of lateral line and auditory input to the brain of Xenopus laevis. J Physiol 317:78–79
Baker CF, Montgomery JC (1999a) Lateral line mediated rheotaxis in the Antarctic fish Pagnothenia borchgrevinki. Polar Biol 21:305–309
Baker CF, Montgomery JC (1999b) The sensory basis of rheotaxis in the blind Mexican cave fish, Astyanax fasciatus. J Comp Physiol A 184:519–527
Bartels M, Münz H, Claas B (1990) Representation of lateral line and electrosensory systems in the midbrain of the axolotl, Ambystoma mexicanum. J Comp Physiol A 167:347–356
Behrend O, Branoner F, Zhivko Z, Ziehm U (2006) Neural responses to water surface waves in the midbrain of the aquatic predator Xenopus laevis. Eur J Neurosc 23:729–744
Bell C, Bodznick D, Montgomery J, Bastian J (1997) The generation and subtraction of sensory expectations within cerebellum-like structures. Brain Behav Evol 50(Suppl. 1):17–31
Bleckmann H (1985) Discrimination between prey and non-prey wave signals in the fishing spider Dolomedes triton (Pisauridae). In: Kalmring K, Elsner N (eds) Acoustic and vibrational communication in insects. Paul Parey, Berlin, pp 215–222
Bleckmann H (1988a) Prey identification and prey localization in surface-feeding fish and fishing spiders. In: Atema J, Fay RR, Popper AN, Tavolga WN (eds) Sensory biology of aquatic animals. Springer, New York, pp 619–641
Bleckmann H (1988b) The water surface as trophic niche: prey identification and prey localization with aid of capillary surface waves. In: Elsner N, Barth FG (eds) Sense organs. Interfaces between environment and behavior. Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 89–96
Bleckmann H (1994) Reception of hydrodynamic stimuli in aquatic and semiaquatic animals. In: Rathmayer W (ed) Progress in zoology, vol 41. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart, pp 1–115
Bleckmann H (2004) 3-D-orientation with the octavolateralis system. J Physiol Paris 98:53–63
Bleckmann H (2006) The lateral line system of fish. In: Hara T, Zielinski B (eds) Fish physiology. Sensory systems neuroscience. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 411–453
Bleckmann H, Bullock TH (1989) Central nervous physiology of the lateral line system, with special reference to cartilaginous fishes. In: Coombs S, Görner P, Münz H (eds) The mechanosensory lateral line. Neurobiology and evolution. Springer, New York, pp 387–408
Bleckmann H, Münz H (1990) Physiology of lateral-line mechanoreceptors in a teleost with highly branched, multiple lateral lines. Brain Behav Evol 35:240–250
Bleckmann H, Topp G (1981) Surface wave sensitivity of the lateral line organs of the topminnow Aplocheilus lineatus. Naturwissenschaften 68:624–625
Bleckmann H, Zelick R (1993) The responses of peripheral and central mechanosensory lateral line units of weakly electric fish to moving objects. J Comp Physiol A 172:115–128
Bleckmann H, Waldner I, Schwartz E (1981) Frequency discrimination of the surface-feeding fish Aplocheilus lineatus—a prerequisite for prey localization? J Comp Physiol A 143:485–490
Bleckmann H, Bullock TH, Jorgensen JM (1987) The lateral line mechanoreceptive mesencephalic, diencephalic, and telencephalic regions in the thornback ray, Platyrhinoidis triseriata (Elasmobranchii). J Comp Physiol A 161:67–84
Bleckmann H, Tittel G, Blübaum-Gronau E (1989a) The lateral line system of surface-feeding fish: Anatomy, physiology, and Behavior. In: Coombs S, Görner P, Münz H (eds) The mechanosensory lateral line. Neurobiology and evolution. Springer, New York, pp 501–526
Bleckmann H, Weiss O, Bullock TH (1989b) Physiology of lateral line mechanoreceptive regions in the elasmobranch brain. J Comp Physiol A 164:459–474
Bleckmann H, Niemann U, Fritzsch B (1991a) Peripheral and central aspects of the acoustic and lateral line system of a bottom dwelling catfish, Ancistrus spec. J Comp Neurol 314:452–466
Blickhan R, Krick C, Breithaupt T, Zehren D, Nachtigall W (1992) Generation of a vortex-chain in the wake of a subundulatory swimmer. Naturwissenschaften 79:220–221
Boord RL, Montgomery JC (1989) Central mechanosensory lateral line centers and pathways among the elasmobranchs. In: Coombs S, Görner P, Münz H (eds) The mechanosensory lateral line. Neurobiology and evolution. Springer, New York, pp 323–340
Bullock TH (1989) Lateral line research: prospects and opportunities. In: Coombs S, Görner P, Münz H (eds) The mechanosensory lateral line. Neurobiology and evolution. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 681–685
Bullock TH, Horridge GA (1965) Structure and function in the nervous system of invertebrates. Vol. I and II. Freeman and Company
Burt de Perera T (2004) Spatial parameters encoded in the spatial map of the blind Mexican cave fish, Astyanax fasciatus. Anim Behav 68:291–295
Caird DM (1978) A simple cerebellar system: the lateral line lobe of the goldfish. J Comp Physiol A 127:61–74
Callens M, Vandenbussche E, Greenway PH (1967) Convergence of retinal and lateral line stimulation on tectum opticum and cerebellar neurons. Arch Int Physiol Biochem 75:148–150
Chagnaud B, Bleckmann H, Hofmann M (2007a) Kármán vortex street detection by the lateral line. J Comp Physiol A 193: 753–763
Chagnaud B, Bleckmann H, Hofmann MH (2007b) Lateral line nerve fibers do not respond to bulk water flow direction. Zoology (in press)
Chagnaud B, Hofmann MH, Mogdans J (2007c) Responses to dipole stimuli of anterior lateral line nerve fibres in goldfish, Carassius auratus, under still and running water conditions. J Comp Physiol A 193:249–263
Claas B (1980) Die Projektionsgebiete des Rumpfseitenliniensystems von Sarotherodon niloticus L. (Cichlidae, Teleostei): Neuroanatomische und neurophysiologische Untersuchungen. Dissertation, Universität Bielefeld, pp 1–136
Claas B, Münz H (1981) Projection of lateral line afferents in a teleost brain. Neurosc Letters 23:287–290
Claas B, Fritzsch B, Münz H (1981) Common efferents to lateral line and labyrinthine hair cells in aquatic vertebrates. Neurosci Lett 27:231–235
Claas B, Münz H, Zittlau KE (1989) Direction coding in central parts of the lateral line system. In: Coombs S, Görner P, Münz H (eds) The mechanosensory lateral line. Neurobiology and evolution. Springer, New York, pp 409–419
Coombs S, Conley RA (1997a) Dipole source localization by mottled sculpin II. The role of lateral line excitation patterns. J Comp Physiol A 180:401–416
Coombs S, Conley RA (1997b) Dipole source localization by mottled sculpin. I. Approach strategies. J Comp Physiol A 180:387–400
Coombs S, Montgomery J (1992) Fibers innervating different parts of the lateral line system of an Antarctic Notothenioid, Trematomus bernachii, have similar frequency responses despite large variation in the peripheral morphology. Brain Behav Evol 40:217–233
Coombs S, Janssen J, Webb JF (1988) Diversity of lateral line systems: evolutionary and functional considerations. In: Atema J, Fay RR, Popper AN, Tavolga WN (eds) Sensory biology of aquatic animals, Springer, New York, pp 553–593
Coombs S, Hastings M, Finneran J (1996) Modeling and measuring lateral line excitation patterns to changing dipole source locations. J Comp Physiol A 178:359–371
Coombs S, Mogdans J, Halstead M, Montgomery J (1998) Transformation of peripheral inputs by the first-order lateral line brainstem nucleus. J Comp Physiol A 182:609–626
Coombs S, Braun CB, Donovan B (2001) The orienting response of Lake Michigan mottled sculpin is mediated by canal neuromasts. J Exp Biol 204:337–348
Curcic-Blake B, van Netten SM (2006) Source localization encoding in the fish lateral line. J Exp Biol 209:1548–1559
Dehnhardt G, Mauck B, Hanke W, Bleckmann H (2001) Hydrodynamic trail-following in Harbor Seals (Phoca vitulina). Science 293:102–104
DeRosa F, Fine ML (1988) Primary connections of the anterior and posterior lateral line nerves in the oyster toadfish. Brain Behav Evol 31:312–317
Drucker EG, Lauder GV (1999) Locomotor forces on a swimming fish: Three-dimensional vortex wake dynamics quantified using digital particle image velocimetry. J Exp Biol 202:2393–2412
Echteler SM (1985) Organization of central auditory pathways in a teleost fish, Cyprinus carpio. J Comp Physiol A 156:267–280
Engelmann J, Bleckmann H (2004) Coding of lateral line stimuli in the goldfish midbrain in still- and running water. Zoology 107:135–151
Engelmann J, Hanke W, Mogdans J, Bleckmann H (2000) Hydrodynamic stimuli and the fish lateral line. Nature 408:51–52
Engelmann J, Hanke W, Bleckmann H (2002a) Lateral line reception in still- and running water. J Comp Physiol A 188:513–526
Engelmann J, Kröther S, Mogdans J, Bleckmann H (2002b) Responses of primary and secondary lateral line units to dipole stimuli applied under still and running water conditions. Bioacoustics 12:158–160
Fiebig E (1988) Connections of the corpus cerebelli in the thornback guitarfish, Platyrhinoidis triseriata (Elasmobranchii): a study with WGA-HRP and extracellular granule cell recording. J Comp Neurol 268:567–583
Finger TE, Bullock TH (1982) Thalamic center for the lateral line system in the catfish Ictalurus nebulosus: evoked potential evidence. J Neurobiol 13:39–47
Finger TE, Tong S-L (1984) Central organization of eighth nerve and mechanosensory lateral line systems in the brainstem of Ictalurid catfish. J Comp Neurol 229:129–151
Flock A, Wersäll J (1962) A study of the orientation of sensory hairs of the receptor cells in the lateral line organ of a fish with special reference to the function of the receptors. J Cell Biol 15:19–27
Franosch J-MP, Sichert A, Suttner M, van Hemmen JL (2005) Estimating position and velocity of a submerged moving object by the clawed frog Xenopus and by fish—a cybernetic approach. Biol Cybern 93:231–238
Fritzsch B (1989) Diversity and regression in the amphibian lateral line and electrosensory system. In: Coombs S, Görner P, Münz H (eds) The mechanosensory lateral line. Neurobiology and evolution. Springer, New York, pp 99–114
Frühbeis B (1984) Verhaltensphysiologische Untersuchungen zur Frequenzunterscheidung und Empfindlichkeit durch das Seitenlinienorgan des blinden Höhlenfisches Anoptichthys jordani. Dissertation, University of Mainz, pp 1–73
Görner P, Kalmijn AJ (1989) Frequency response of lateral line neuromasts in the thornback ray (Platyrhinoidis triseriata). In: Erber J, Menzel R, Pflüger H-J, Todt D (eds) Proceedings of the 2nd international congress of neuroetholgy, 1st edn. Thieme, Stuttgart
Hanke W (2001) Hydrodynamische Spuren schwimmender Fische und ihre mögliche Bedeutung für das Jagdverhalten fischfressender Tiere. PhD thesis, University of Bonn, Bonn, pp 1–72
Hanke W, Bleckmann H (2004) The hydrodynamic trails of Lepomis gibbosus (Centrarchidae), Colomesus psittacus (Tetraodontidae) and Thysochromis ansorgii (Cichlidae) investigated with scanning particle image velocimetry. J Exp Biol 207:1585–1596
Hanke W, Brücker C, Bleckmann H (2000) The ageing of the low frequency water disturbances caused by swimming goldfish and its possible relevance to prey detection. J Exp Biol 203:1193–1200
Heiligenberg W, Bastian J (1984) The electric sense of weakly electric fish. Annu Rev Psychol 46:561–583
Hubel DH, Wiesel TN (1962) Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture of the cat’s visual cortex. J Physiol 160:106–154
Ivry RB, Baldo JV (1992) Is the cerebellum involved in learning and cognition? Curr Opin Neurobiol 2:212–216
Janssen J (2004) Lateral line sensory ecology. In: von der Emde G, Mogdans J, Kapoor BG (eds) The senses of fish. Adaptations for the reception of natural stimuli. Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi, pp 231–264
Jayne MG, Atema J (2007) Sharks need the lateral line to locate odor sources: rheotaxis and eddy chemotaxis. J Exp Biol 210:1925–1934
Kalmijn AJ (1988) Hydrodynamic and acoustic field detection. In: Atema J, Fay RR, Popper AN, Tavolga WN (eds) Sensory biology of aquatic animals, Springer, New York, pp 83–130
Kalmijn AJ (1989) Functional evolution of lateral line and inner ear sensory systems. In: Coombs S, Görner P, Münz H (eds) The mechanosensory lateral line. Neurobiology and evolution. Springer, New York, pp 187–216
Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM (2000) Principles of neural science, 3 edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Kanter MJ, Coombs S (2003) Rheotaxis and prey detection in uniform currents by Lake Michigan mottled sculpin (Cottus bairdii). J Exp Biol 206:59–70
Kirsch JA, Hofmann MH, Mogdans J, Bleckmann H (2002) Response properties of diencephalic neurons to visual, acoustic and hydrodynamic stimulation in the goldfish, Carassius auratus. Zoology 105: 61–70
Knudsen EI (1977) Distinct auditory and lateral line nuclei in the midbrain of catfishes. J Comp Neurol 173:417–432
Konishi M (1983) Neuroethology of acoustic prey localization in the barn owl. In: Huber F, Markl H (eds) Neuroethology and behavioral physiology. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 304–317
Kotchabhakdi N (1976) Functional organization of the goldfish cerebellum. Information processing of input from peripheral sense organs. J Comp Physiol A 112:75–93
Kröther S, Mogdans J, Bleckmann H (2002) Brainstem lateral line responses to sinusoidal wave stimuli in still- and running water. J Exp Biol 205:1471–1484
Kröther S, Bleckmann H, Mogdans J (2004) Effects of running water on brainstem lateral line responses in trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, to sinusoidal wave stimuli. J Comp Physiol A 190:437–448
Lee LT, Bullock TH (1984) Sensory representation in the cerebellum of the catfish. J Comp Physiol A 13:157–169
Liao JC (2006) The role of the lateral line and vision on body kinematics and hydrodynamic preference of rainbow trout in turbulent flow. J Exp Biol 209:4077–4090
Lowe DA (1986) Organisation of lateral line and auditory areas in the midbrain of Xenopus laevis. J Comp Neurol 245:498–513
Maturana HR, Lettvin JY, McCulloch WS, Pitts WH (1960) Anatomy and physiology of vision in the frog (Rana pipiens). J Gen Physiol 43:129–175
McCormick CA (1989) Central lateral line mechanosensory pathways in bony fish. In: Coombs S, Görner P, Münz H (eds) The mechanosensory lateral line. Neurobiology and Evolution. Springer, New York, pp 341–364
McCormick CA, Hernandez DV (1996) Connections of the octaval and lateral line nuclei of the medulla in the goldfish, including the cytoarchitecture of the secondary octaval population in goldfish and catfish. Brain Behav Evol 47:113–138
Mogdans J, Bleckmann H (1998) Responses of the goldfish trunk lateral line to moving objects. J Comp Physiol A 182:659–676
Mogdans J, Goenechea L (1999) Responses of medullary lateral line units in the goldfish, Carassius auratus, to sinusoidal and complex wave stimuli. Zoology 102:227–237
Mogdans J, Kröther S (2001) Brainstem lateral line responses to sinusoidal wave stimuli in the goldfish, Carassius auratus. Zoology 104:153–166
Mogdans J, Bleckmann H, Menger N (1997) Sensitivity of central units in the goldfish, Carassius auratus, to transient hydrodynamic stimuli. Brain Behav Evol 50:261–283
Montgomery JC, Bodznick D (1994) An adaptive filter that cancels self-induced noise in the electrosensory and lateral line mechanosensory systems of fish. Neurosci Lett 174:145–148
Montgomery JC, Macdonald JA, Housley GD (1988) Lateral line function in an antarctic fish related to the signals produced by planktonic prey. J Comp Physiol A 163:827–833
Montgomery JC, Coombs S, Janssen J (1994) Form and function relationships in the lateral line systems: comparative data from six species of antarctic notothenioid fish. Brain Behav Evol 44:299–306
Montgomery JC, Coombs S, Conley RA, Bodznick D (1995) Hindbrain sensory processing in lateral line, electrosensory, and auditory systems: a comparative overview of anatomical and functional similarities. Aud Neurosci 1:207–231
Montgomery JC, Baker CF, Carton AG (1997) The lateral line can mediate rheotaxis in fish. Nature 389:960–963
Montgomery JC, Coombs S (1998) Peripheral encoding of moving sources by the lateral line system of a sit-and-wait predator. J Exp Biol 201:91–102
Montgomery J, Garton G, Voigt R, Baker C, Diebel C (2000) Sensory processing of water currents by fishes. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 355:1325–1327
Montgomery JC, Macdonald F, Baker CF, Carton AG (2002) Hydrodynamic contributions to multimodal guidance of prey capture behavior in fish. Brain Behav Evol 59:190–198
Müller HM (1993) Neuronale Verarbeitung von Seitenlinieninformationen im Mittelhirn eines Welses. Dissertation, University of Bielefeld, pp 1–100
Müller HM, Bleckmann H (1993) The responses of central octavolateralis cells to moving sources. J Comp Physiol A 179:455–471
Münz H (1985) Single unit activity in the peripheral lateral line system of the cichlid fish Sarotherodon niloticus L. J Comp Physiol A 157:555–568
Münz H (1989) Functional organization of the lateral line periphery. In: Coombs S, Görner P, Münz H (eds) The mechanosensory lateral line. Neurobiology and evolution. Springer, New York, pp 285–298
New JG (2002) Multimodal integration in the feeding behaviors of predatory teleost fishes. Brain Behav Evol 59:177–189
New JG, Bodznick D (1985) Segregation of electroreceptive and mechanoreceptive lateral line afferents in the hindbrain of chondrostean fishes. Brain Res 336:89–98
New JG, Coombs S, McCormick CA, Oshel PE (1996) Cytoarchitecture of the medial octavolateralis nucleus in the goldfish, Carassius auratus. J Comp Neurol 366:534–546
New J, Braun CB, Walter K (2000) Central projections of nerve fibers innervating individual canal neuromast organs in the muskellunge, Esox masquinongy. Soc Neurosci 26:146
Northcutt GR (1988) Sensory and other neural traits and the adaptationist program: Mackarels of San Marco? In: Atema J, Fay RR, Popper AN, Tavolga WN (eds) Sensory biology of aquatic animals. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 869–879
O’Bennar JD (1976) Electrophysiology of neural units in the goldfish optic tectum. Brain Res Bull 1:529–541
Palmer LM, Giuffrida BA, Mensinger AF (2003) Neural recordings from the lateral line in free-swimming toadfish, Opsanus tau. Biol Bull 205:216–218
Plachta D, Mogdans J, Bleckmann H (1999) Responses of midbrain lateral line units of the goldfish, Carassius auratus, to constant-amplitude and amplitude modulated water wave stimuli. J Comp Physiol A 185:405–417
Plachta D, Hanke W, Bleckmann H (2003) A hydrodynamic topographic map and two hydrodynamic subsystems in a vertebrate brain. J Exp Biol 206:3479–3486
Pohlmann K, Atema J, Breithaupt T (2004) The importance of the lateral line in nocturnal predation of piscivorous catfish. J Exp Biol 207:2971–2978
Portavella M, Torres B, Salas C (2004) Avoidance response in goldfish: emotional and temporal involvement of medial and lateral telencephalic pallium. J Neurosci 24:2335–2342
Prechtl JC, von der Emde G, Wolfart J, Karamürsel S, Akoev GN, Andrianov YN, Bullock TH (1998) Sensory processing in the pallium of a mormyrid fish. J Neurosci 18:7381–7393
Puzdrowski RL (1989) Peripheral distribution and central projections of the lateral-line nerves in goldfish, Carassius auratus. Brain Behav Evol 34:110–131
Puzdrowski RL, Leonard RB (1993) The octavolateral systems in the stingray, Dasyatis sabina. I. Primary projections of the octaval and lateral line nerves. J Comp Neurol 332:21–37
Roberts BL, Meredith GE (1989) The efferent system. In: Coombs S, Görner P, Münz H (eds) The mechanosensory lateral line. Neurobiology and evolution. Springer, New York, pp 445–459
Roberts BL, Russell IJ (1972) The activity of lateral-line efferent neurones in stationary and swimming dogfish. J Exp Biol 57:435–448
Rosen MW (1959) Waterflow about a swimming fish. Tech Publ U.S. Naval Test Station, China Lake, Calif.; NOTS TP 2298, pp 1–94
Salas C, Rodríguez F, Vargas JP, Durán E, Torres B (1996) Spatial learning and memory deficits after telencephalic ablation in goldfish trained in place and turn maze procedures. Behav Neurosci 110:965–980
Sand O (1981) The lateral line and sound perception. In: Tavolga WN, Popper AN, Fay RR (eds) Hearing and sound communication in fishes. Springer, New York, pp 459–446
Schellart NAM, Kroese ABA (1989) Interrelationship of acousticolateral and visual systems in the teleost midbrain. In: Coombs S, Görner P, Münz H (eds) The mechanosensory lateral line. Neurobiology and evolution. Springer, New York, pp 421–443
Schellart NAM, Prins M, Kroese ABA (1992) The pattern of trunk lateral line afferents and efferents in the rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Brain Behav Evol 39:371–380
Song J, Northcutt RG (1991) The primary projections of the lateral-line nerves of the Florida gar, Lepisosteus platyrhincus. Brain Behav Evol 37:38–63
Striedter GF (1991) Auditory, electrosensory, and mechanosensory lateral line pathways through the diencephalon and telencephalon of channel catfish. J Comp Neurol 312:311–331
Tomchik SM, Lu Z (2005) Octavolateral projections and organization in the medulla of a teleost fish, the sleeper goby (Dormitator latifrons). J Comp Neurol 481:96–117
Tomchik SM, Lu Z (2006) Auditory physiology and anatomy of octavolateral efferent neurons in a teleost fish. J Comp Physiol A 192:51–68
Tricas TC, Highstein SM (1990) Visually mediated inhibition of lateral line primary afferent activity by the octavolateralis efferent system during predation in the free-swimming toadfish, Opsanus tau. Exp Brain Res 83:233–236
Tricas TC, Highstein SM (1991) Action of the octavolateralis efferent system upon the lateral line of free-swimming toadfish, Opsanus tau. J Comp Physiol A 169:25–37
Vogel D, Bleckmann H (1997) Surface wave discrimination in the topminnow Aplocheilus lineatus. J Comp Physiol A 180:671–681
Vogel D, Bleckmann H (2000) Behavioral discrimination of water motions caused by moving objects. J Comp Physiol A 186:1107–1117
Voigt R, Carton AG, Montgomery JC (2000) Responses of anterior lateral line afferent neurones to water flow. J Exp Biol 203:2495–2502
von der Emde G, Bleckmann H (1998) Finding food: Senses involved in foraging for insect larvae in the electric fish Gnathonemus petersii. J Exp Biol 201:969–980
von der Emde G, Schwarz S, Gomez L, Budelli R, Grant K (1998) Electric fish measure distance in the dark. Nature 395:890–894
Wagner T, Schwartz E (1992) Efferent lateral-line neurons of teleosts and their projection to lateral-line segments. In: Elsner N, Richter WD (eds) Rhythmogenesis in neurons and networks. Proceedings of the 20th Göttingen neurobiology conference. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, pp 251
Waterman TH, Wiersma CAG (1963) Electrical responses in decapod crustaceans visual systems. J Cell Comp Physiol 61:1–16
Webb JF (1989) Developmental constraints and evolution of the lateral line system in teleost fishes. In: Coombs S, Görner P, Münz H (eds) The mechanosensory lateral line. Neurobiology and evolution. Springer, New York, pp 79–98
Weeg MS, Bass A (2002) Frequency response properties of lateral line superficial neuromasts in a vocal fish, with evidence for acoustic sensitivity. J Neurophysiol 88:1252–1262
Weeg MS, Bass AH (2000) Central lateral line pathways in a vocalizing fish. J Comp Neurol 418:41–64
Wehner R (1987) Matched filters—neural models of the external world. J Comp Physiol A 161:511–531
Weissert R, von Campenhausen C (1981) Discrimination between stationary objects by the blind cave fish Anoptichthys jordani. J Comp Physiol A 143:375–382
Wojtenek W, Mogdans J, Bleckmann H (1998) The responses of midbrain lateral line units of the goldfish Carassius auratus to moving objects. Zoology 101:69–82
Wubbels RJ, Kroese ABA, Schellart NAM (1993) Response properties of lateral line and auditory units in the medulla oblongata of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Exp Biol 179:77–92
Wullimann MF (1998) The central nervous system. In: Evans DH (eds) The physiology of fishes, 2nd edn. CRC, New York, pp 245–282
Wullimann MF, Hofmann MH, Meyer DL (1991) The valvula cerebelli of the spiny eel, Macrognathus aculeatus, receives primary lateral-line afferents from the rostrum of the upper jaw. Cell Tissue Res 266:285–293
Zittlau KE, Claas B, Münz H (1986) Directional sensitivity of lateral line units in the clawed toad Xenopus laevis Daudin. J Comp Physiol A 158:469–477
Acknowledgments
The author is grateful for the wonderful time he was allowed to spend in the laboratory of Ted Bullock. I thank J. Mogdans and R. Zelick for their helpful comments on an earlier draft of this chapter. The original research of the author was generously supported by the DFG, the BMBF, DARPA, the BfG, DAAD, and the EU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bleckmann, H. Peripheral and central processing of lateral line information. J Comp Physiol A 194, 145–158 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-007-0282-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-007-0282-2