Abstract
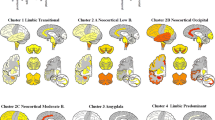
The two current major staging systems in use for Lewy body disorders fail to classify up to 50% of subjects. Both systems do not allow for large numbers of subjects who have Lewy-type α-synucleinopathy (LTS) confined to the olfactory bulb or who pass through a limbic-predominant pathway that at least initially bypasses the brainstem. The results of the current study, based on examination of a standard set of ten brain regions from 417 subjects stained immunohistochemically for α-synuclein, suggest a new staging system that, in this study, allows for the classification of all subjects with Lewy body disorders. The autopsied subjects included elderly subjects with Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, incidental Lewy body disease and Alzheimer’s disease with Lewy bodies, as well as comparison groups without Lewy bodies. All subjects were classifiable into one of the following stages: I. Olfactory Bulb Only; IIa Brainstem Predominant; IIb Limbic Predominant; III Brainstem and Limbic; IV Neocortical. Progression of subjects through these stages was accompanied by a generally stepwise worsening in terms of striatal tyrosine hydroxylase concentration, substantia nigra pigmented neuron loss score, Mini Mental State Examination score and score on the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale Part 3. Additionally, there were significant correlations between these measures and LTS density scores. It is suggested that the proposed staging system would improve on its predecessors by allowing classification of a much greater proportion of cases.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler CH (2005) Nonmotor complications in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 20(Suppl 11):S23–S29. doi:10.1002/mds.20460
Alafuzoff I, Parkkinen L, Al-Sarraj S, Arzberger T, Bell J, Bodi I, Bogdanovic N, Budka H, Ferrer I, Gelpi E, Gentleman S, Giaccone G, Kamphorst W, King A, Korkolopoulou P, Kovacs GG, Larionov S, Meyronet D, Monoranu C, Morris J, Parchi P, Patsouris E, Roggendorf W, Seilhean D, Streichenberger N, Thal DR, Kretzschmar H (2008) Assessment of alpha-synuclein pathology: a study of the BrainNet Europe Consortium. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67:125–143. doi:10.1097/nen.0b013e3181633526
Baba M, Nakajo S, Tu PH, Tomita T, Nakaya K, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Iwatsubo T (1998) Aggregation of alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies of sporadic Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Am J Pathol 152:879–884
Beach TG, Adler CH, Sue LI, Peirce JB, Bachalakuri J, Dalsing-Hernandez JE, Lue LF, Caviness JN, Connor DJ, Sabbagh MN, Walker DG (2008) Reduced striatal tyrosine hydroxylase in incidental Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol 115:445–451. doi:10.1007/s00401-007-0313-7
Beach TG, Sue LI, Walker DG, Roher AE, Lue L, Vedders L, Connor DJ, Sabbagh MN, Rogers J (2008) The Sun Health Research Institute Brain Donation Program: description and experience, 1987–2007. Cell Tissue Bank 9:229–245. doi:10.1007/s10561-008-9067-2
Beach TG, White CL, Hamilton RL, Duda JE, Iwatsubo T, Dickson DW, Roncaroli F, Buttini M, Hladik CL, Sue LI, Noorigian JV, Adler CH (2008) Evaluation of alpha-synuclein immunohistochemical methods used by invited experts. Acta Neuropathol 116:277–288. doi:10.1007/s00401-008-0409-8
Beach TG, White CLIII, Hladik CL, Sabbagh MN, Connor DJ, Shill HA, Sue LI, Sasse J, Bachalakuri J, Henry-Watson J, Akiyama H, Adler CH (2009) Olfactory bulb alpha-LTS has high specificity and sensitivity for Lewy body disorders. Acta Neuropathol 117:169–174. doi:10.1007/s00401-008-0450-7
Bernheimer H, Birkmayer W, Hornykiewicz O, Jellinger K, Seitelberger F (1973) Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington: clinical, morphological and neurochemical correlations. J Neurol Sci 20:415–455. doi:10.1016/0022-510X(73)90175-5
Bloch A, Probst A, Bissig H, Adams H, Tolnay M (2006) Alpha-synuclein pathology of the spinal and peripheral autonomic nervous system in neurologically unimpaired elderly subjects. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 32:284–295. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2006.00727.x
Braak H, Del Tredici K (2008) Invited article: nervous system pathology in sporadic Parkinson disease. Neurology 70:1916–1925. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000312279.49272.9f
Braak H, Braak E, Yilmazer D, de Vos RA, Jansen EN, Bohl J, Jellinger K (1994) Amygdala pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 88:493–500. doi:10.1007/BF00296485
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Bratzke H, Hamm-Clement J, Sandmann-Keil D, Rub U (2002) Staging of the intracerebral inclusion body pathology associated with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease (preclinical and clinical stages). J Neurol 249(Suppl 3):III/1–III/5
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:197–211. doi:10.1016/S0197-4580(02)00065-9
Braak H, Rub U, Gai WP, Del TK (2003) Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: possible routes by which vulnerable neuronal types may be subject to neuroinvasion by an unknown pathogen. J Neural Transm 110:517–536. doi:10.1007/s00702-002-0808-2
Braak H, Ghebremedhin E, Rub U, Bratzke H, Del Tredici K (2004) Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res 318:121–134. doi:10.1007/s00441-004-0956-9
Braak H, Bohl JR, Muller CM, Rub U, de Vos RA, Del Tredici K (2006) Stanley Fahn Lecture 2005: the staging procedure for the inclusion body pathology associated with sporadic Parkinson’s disease reconsidered. Mov Disord 21:2042–2051. doi:10.1002/mds.21065
Braak H, de Vos RA, Bohl J, Del Tredici K (2006) Gastric alpha-synuclein immunoreactive inclusions in Meissner’s and Auerbach’s plexuses in cases staged for Parkinson’s disease-related brain pathology. Neurosci Lett 396:67–72. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2005.11.012
Burke RE, Dauer WT, Vonsattel JP (2008) A critical evaluation of the Braak staging scheme for Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 64:485–491. doi:10.1002/ana.21541
Consensus recommendations for the postmortem diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (1997) The National Institute on Aging, and Reagan Institute Working Group on diagnostic criteria for the neuropathological assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 18:S1–S2
Croisier E, Mres DE, Deprez M, Goldring K, Dexter DT, Pearce RK, Graeber MB, Roncaroli F (2006) Comparative study of commercially available anti-alpha-synuclein antibodies. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 32:351–356. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2006.00722.x
Daniel SE, Hawkes CH (1992) Preliminary diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease by olfactory bulb pathology. Lancet 340:186. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(92)93275-R
Del Tredici K, Rub U, de Vos RA, Bohl JR, Braak H (2002) Where does Parkinson disease pathology begin in the brain? J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:413–426
Delledonne A, Klos KJ, Fujishiro H, Ahmed Z, Parisi JE, Josephs KA, Frigerio R, Burnett M, Wszolek ZK, Uitti RJ, Ahlskog JE, Dickson DW (2008) Incidental Lewy body disease and preclinical Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 65:1074–1080. doi:10.1001/archneur.65.8.1074
den Hartog Jager WA, Bethlem J (1960) The distribution of Lewy bodies in the central and autonomic nervous systems in idiopathic paralysis agitans. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 23:283–290. doi:10.1136/jnnp.23.4.283
Dickson DW, Fujishiro H, DelleDonne A, Menke J, Ahmed Z, Klos KJ, Josephs KA, Frigerio R, Burnett M, Parisi JE, Ahlskog JE (2008) Evidence that incidental Lewy body disease is pre-symptomatic Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 115:437–444. doi:10.1007/s00401-008-0345-7
Doty RL, Deems DA, Stellar S (1988) Olfactory dysfunction in Parkinsonism: a general deficit unrelated to neurologic signs, disease stage, or disease duration. Neurology 38:1237–1244
Duda JE (2004) Pathology and neurotransmitter abnormalities of dementia with Lewy bodies. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 17(Suppl 1):3–14. doi:10.1159/000074677
Duda JE, Shah U, Arnold SE, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (1999) The expression of alpha-, beta-, and gamma-synucleins in olfactory mucosa from patients with and without neurodegenerative diseases. Exp Neurol 160:515–522. doi:10.1006/exnr.1999.7228
Duda JE, Giasson BI, Chen Q, Gur TL, Hurtig HI, Stern MB, Gollomp SM, Ischiropoulos H, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2000) Widespread nitration of pathological inclusions in neurodegenerative synucleinopathies. Am J Pathol 157:1439–1445
Duda JE, Giasson BI, Mabon ME, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2002) Novel antibodies to synuclein show abundant striatal pathology in Lewy body diseases. Ann Neurol 52:205–210. doi:10.1002/ana.10279
Duda JE, Giasson BI, Mabon ME, Miller DC, Golbe LI, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2002) Concurrence of alpha-synuclein and tau brain pathology in the Contursi kindred. Acta Neuropathol 104:7–11. doi:10.1007/s00401-002-0563-3
Ellis RJ, Jan K, Kawas C, Koller WC, Lyons KE, Jeste DV, Hansen LA, Thal LJ (1998) Diagnostic validity of the dementia questionnaire for Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 55:360–365. doi:10.1001/archneur.55.3.360
Fearnley JM, Lees AJ (1991) Ageing and Parkinson’s disease: SN regional selectivity. Brain 114(Pt 5):2283–2301. doi:10.1093/brain/114.5.2283
Fujimi K, Sasaki K, Noda K, Wakisaka Y, Tanizaki Y, Matsui Y, Sekita A, Iida M, Kiyohara Y, Kanba S, Iwaki T (2008) Clinicopathological outline of dementia with Lewy bodies applying the revised criteria: the Hisayama study. Brain Pathol 18:317–325. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2008.00169.x
Fujishiro H, Tsuboi Y, Lin WL, Uchikado H, Dickson DW (2008) Co-localization of tau and alpha-synuclein in the olfactory bulb in Alzheimer’s disease with amygdala Lewy bodies. Acta Neuropathol 116:17–24. doi:10.1007/s00401-008-0383-1
Fujiwara H, Hasegawa M, Dohmae N, Kawashima A, Masliah E, Goldberg MS, Shen J, Takio K, Iwatsubo T (2002) Alpha-Synuclein is phosphorylated in LTS lesions. Nat Cell Biol 4:160–164. doi:10.1038/ncb841
Gelb DJ, Oliver E, Gilman S (1999) Diagnostic criteria for Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 56:33–39. doi:10.1001/archneur.56.1.33
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Murray IV, Chen Q, Souza JM, Hurtig HI, Ischiropoulos H, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2000) Oxidative damage linked to neurodegeneration by selective alpha-synuclein nitration in LTS lesions. Science 290:985–989. doi:10.1126/science.290.5493.985
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Forman MS, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2001) Prominent perikaryal expression of alpha- and beta-synuclein in neurons of dorsal root ganglion and in medullary neurons. Exp Neurol 172:354–362. doi:10.1006/exnr.2001.7805
Hamilton RL (2000) Lewy bodies in Alzheimer’s disease: a neuropathological review of 145 cases using alpha-synuclein immunohistochemistry. Brain Pathol 10:378–384
Hansen L, Salmon D, Galasko D, Masliah E, Katzman R, DeTeresa R, Thal L, Pay MM, Hofstetter R, Klauber M (1990) The Lewy body variant of Alzheimer’s disease: a clinical and pathologic entity. Neurology 40:1–8
Hawkes C (2006) Olfaction in neurodegenerative disorder. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 63:133–151
Hawkes CH, Del Tredici K, Braak H (2007) Parkinson’s disease: a dual-hit hypothesis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 33:599–614. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2007.00874.x
Hishikawa N, Hashizume Y, Yoshida M, Sobue G (2003) Clinical and neuropathological correlates of Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol 105:341–350
Hixson JE, Vernier DT (1990) Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. J Lipid Res 31:545–548
Hladik CL, White CL (2003) Comparison of digestive enzyme and formic acid pretreatment for optimal immunohistochemical demonstration of alpha-synuclein-immunoreactive cerebral cortical Lewy neurites. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:554
Holdorff B (2002) Friedrich Heinrich Lewy (1885–1950) and his work. J Hist Neurosci 11:19–28. doi:10.1076/jhin.11.1.19.9106
Hubbard PS, Esiri MM, Reading M, McShane R, Nagy Z (2007) Alpha-synuclein pathology in the olfactory pathways of dementia patients. J Anat 211:117–124. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2007.00748.x
Iseki E, Marui W, Kosaka K, Akiyama H, Ueda K, Iwatsubo T (1998) Degenerative terminals of the perforant pathway are human alpha-synuclein-immunoreactive in the hippocampus of patients with diffuse Lewy body disease. Neurosci Lett 258:81–84. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(98)00856-8
Jellinger KA (2004) Lewy body-related alpha-LTS in the aged human brain. J Neural Transm 111:1219–1235. doi:10.1007/s00702-004-0138-7
Jellinger KA (2008) A critical reappraisal of current staging of Lewy-related pathology in human brain. Acta Neuropathol 116:1–16. doi:10.1007/s00401-008-0406-y
Kalaitzakis ME, Graeber MB, Gentleman SM, Pearce RK (2008) The dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus is not an obligatory trigger site of Parkinson’s disease: a critical analysis of alpha-synuclein staging. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 34:284–295. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2007.00923.x
Katzenschlager R, Lees AJ (2004) Olfaction and Parkinson’s syndromes: its role in differential diagnosis. Curr Opin Neurol 17:417–423. doi:10.1097/01.wco.0000137531.76491.c2
Klos KJ, Ahlskog JE, Josephs KA, Apaydin H, Parisi JE, Boeve BF, DeLucia MW, Dickson DW (2006) Alpha-synuclein pathology in the spinal cords of neurologically asymptomatic aged individuals. Neurology 66:1100–1102. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000204179.88955.fa
Kosaka K (2007) Dementia with Lewy bodies–from its finding to the present, including the CDLB guideline-revised. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 47:703–707
Kranick SM, Duda JE (2008) Olfactory dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosignals 16:35–40. doi:10.1159/000109757
Kuusisto E, Parkkinen L, Alafuzoff I (2003) Morphogenesis of Lewy bodies: dissimilar incorporation of alpha-synuclein, ubiquitin, and p62. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:1241–1253
Lerner A, Bagic A (2008) Olfactory pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson disease revisited. Mov Disord 23:1076–1084. doi:10.1002/mds.22066
Leverenz J, Hamilton R, Tsuang DW, Schantz A, Vavrek D, Kukull W, Lopez O, Galasko D, Masliah E, Kaye J, Nixon R, Clark C, Trojanowsk JQ, Montine TJ (2008) Empiric refinement of the pathologic assessment of Lewy-related pathology in the dementia patient. Brain Pathol 1:1–2
Leverenz JB, Hamilton R, Tsuang DW, Schantz A, Vavrek D, Larson EB, Kukull WA, Lopez O, Galasko D, Masliah E, Kaye J, Woltjer R, Clark C, Trojanowski JQ, Montine TJ (2008) Empiric refinement of the pathologic assessment of Lewy-related pathology in the dementia patient. Brain Pathol 18:220–224. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00117.x
Lewy FH (1912) Paralysis agitans 1. Pathologisch Anatomie. In: Handbuch der Neurologie III. Springer, Berlin, pp 920–933
Linazasoro G (2007) Classical Parkinson disease versus Parkinson complex–reflections against staging and in favour of heterogeneity. Eur J Neurol 14:721–728. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2007.01853.x
Lippa CF, Smith TW, Swearer JM (1994) Alzheimer’s disease and Lewy body disease: a comparative clinicopathological study. Ann Neurol 35:81–88. doi:10.1002/ana.410350113
Lippa CF, Duda JE, Grossman M, Hurtig HI, Aarsland D, Boeve BF, Brooks DJ, Dickson DW, Dubois B, Emre M, Fahn S, Farmer JM, Galasko D, Galvin JE, Goetz CG, Growdon JH, Gwinn-Hardy KA, Hardy J, Heutink P, Iwatsubo T, Kosaka K, Lee VM, Masliah E, McKeith IG, Nussbaum RL, Olanow CW, Ravina BM, Singleton AB, Tanner CM, Trojanowski JQ, Wszolek ZK (2007) DLB and PDD boundary issues: diagnosis, treatment, molecular pathology, and biomarkers. Neurology 68:812–819. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000256715.13907.d3
Marui W, Iseki E, Nakai T, Miura S, Kato M, Ueda K, Kosaka K (2002) Progression and staging of Lewy pathology in brains from patients with dementia with Lewy bodies. J Neurol Sci 195:153–159. doi:10.1016/S0022-510X(02)00006-0
McKeith IG, Galasko D, Kosaka K, Perry EK, Dickson DW, Hansen LA, Salmon DP, Lowe J, Mirra SS, Byrne EJ, Lennox G, Quinn NP, Edwardson JA, Ince PG, Bergeron C, Burns A, Miller BL, Lovestone S, Collerton D, Jansen EN, Ballard C, de Vos RA, Wilcock GK, Jellinger KA, Perry RH (1996) Consensus guidelines for the clinical and pathologic diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB): report of the consortium on DLB international workshop. Neurology 47:1113–1124
McKeith IG, Dickson DW, Lowe J, Emre M, O’Brien JT, Feldman H, Cummings J, Duda JE, Lippa C, Perry EK, Aarsland D, Arai H, Ballard CG, Boeve B, Burn DJ, Costa D, Del ST, Dubois B, Galasko D, Gauthier S, Goetz CG, Gomez-Tortosa E, Halliday G, Hansen LA, Hardy J, Iwatsubo T, Kalaria RN, Kaufer D, Kenny RA, Korczyn A, Kosaka K, Lee VM, Lees A, Litvan I, Londos E, Lopez OL, Minoshima S, Mizuno Y, Molina JA, Mukaetova-Ladinska EB, Pasquier F, Perry RH, Schulz JB, Trojanowski JQ, Yamada M (2005) Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: third report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 65:1863–1872. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000187889.17253.b1
McKinnon JH, Demaerschalk BM, Caviness JN, Wellik KE, Adler CH, Wingerchuk DM (2007) Sniffing out Parkinson disease: can olfactory testing differentiate Parkinsonian disorders? Neurologist 13:382–385. doi:10.1097/NRL.0b013e31815a351a
Minguez-Castellanos A, Chamorro CE, Escamilla-Sevilla F, Ortega-Moreno A, Rebollo AC, Gomez-Rio M, Concha A, Munoz DG (2007) Do alpha-synuclein aggregates in autonomic plexuses predate Lewy body disorders? A cohort study. Neurology 68:2012–2018. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000264429.59379.d9
Müller CM, de Vos RA, Maurage CA, Thal DR, Tolnay M, Braak H (2005) Staging of sporadic Parkinson disease-related alpha-synuclein pathology: inter- and intra-rater reliability. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:623–628
Obi K, Akiyama H, Kondo H, Shimomura Y, Hasegawa M, Iwatsubo T, Mizuno Y, Mochizuki H (2008) Relationship of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein and tau accumulation to Abeta deposition in the cerebral cortex of dementia with Lewy bodies. Exp Neurol 210:409–420. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.11.019
Orimo S, Oka T, Miura H, Tsuchiya K, Mori F, Wakabayashi K, Nagao T, Yokochi M (2002) Sympathetic cardiac denervation in Parkinson’s disease and pure autonomic failure but not in multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 73:776–777. doi:10.1136/jnnp.73.6.776
Parkinson JD (1817) The shaking palsy. Sherwood, Neely and Jones, London
Parkinson JD (1955) An essay on the shaking palsy. In: Critchley M, Parkinson J (eds) Mcmillan, London
Parkkinen L, Soininen H, Alafuzoff I (2003) Regional distribution of alpha-synuclein pathology in unimpaired aging and Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:363–367
Parkkinen L, Pirttila T, Alafuzoff I (2008) Applicability of current staging/categorization of alpha-synuclein pathology and their clinical relevance. Acta Neuropathol 115:399–407. doi:10.1007/s00401-008-0346-6
Pearce RK, Hawkes CH, Daniel SE (1995) The anterior olfactory nucleus in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 10:283–287. doi:10.1002/mds.870100309
Perry RH, Irving D, Blessed G, Fairbairn A, Perry EK (1990) Senile dementia of Lewy body type: a clinically and neuropathologically distinct form of Lewy body dementia in the elderly. J Neurol Sci 95:119–139. doi:10.1016/0022-510X(90)90236-G
Ross GW, Petrovitch H, Abbott RD, Nelson J, Markesbery W, Davis D, Hardman J, Launer L, Masaki K, Tanner CM, White LR (2004) Parkinsonian signs and SN neuron density in descendents elders without PD. Ann Neurol 56:532–539. doi:10.1002/ana.20226
Saito Y, Kawashima A, Ruberu NN, Fujiwara H, Koyama S, Sawabe M, Arai T, Nagura H, Yamanouchi H, Hasegawa M, Iwatsubo T, Murayama S (2003) Accumulation of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein in aging human brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:644–654
Saito Y, Ruberu NN, Sawabe M, Arai T, Kazama H, Hosoi T, Yamanouchi H, Murayama S (2004) Lewy body-related alpha-LTS in aging. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:742–749
Schiller F (2000) Fritz Lewy and his bodies. J Hist Neurosci 9:148–151. doi:10.1076/0964-704X(200008)9:2;1-Y;FT148
Sengoku R, Saito Y, Ikemura M, Hatsuta H, Sakiyama Y, Kanemaru K, Arai T, Sawabe M, Tanaka N, Mochizuki H, Inoue K, Murayama S (2008) Incidence and extent of Lewy body-related alpha-LTS in aging human olfactory bulb. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67:1072–1083. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e31818b4126
Tsuang DW, Riekse RG, Purganan KM, David AC, Montine TJ, Schellenberg GD, Steinbart EJ, Petrie EC, Bird TD (2006) Lewy body pathology in late-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease: a clinicopathological case series. J Alzheimers Dis 9:235–242
Uchikado H, Lin WL, DeLucia MW, Dickson DW (2006) Alzheimer disease with amygdala Lewy bodies: a distinct form of alpha-LTS. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:685–697. doi:10.1097/01.jnen.0000225908.90052.07
Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H, Takeda S, Ohama E, Ikuta F (1988) Parkinson’s disease: the presence of Lewy bodies in Auerbach’s and Meissner’s plexuses. Acta Neuropathol 76:217–221. doi:10.1007/BF00687767
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by grants to the Sun Health Research Institute Brain Donation Program and the Arizona Parkinson’s Disease Consortium by the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research (The Prescott Family Initiative), the Arizona Biomedical Research Commission (contracts 4001, 0011 and 05-901) and the National Institute on Aging (P30 AG19610).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beach, T.G., Adler, C.H., Lue, L. et al. Unified staging system for Lewy body disorders: correlation with nigrostriatal degeneration, cognitive impairment and motor dysfunction. Acta Neuropathol 117, 613–634 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0538-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0538-8