Abstract
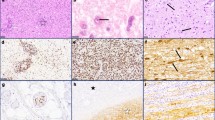
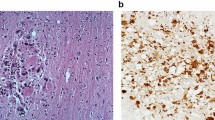
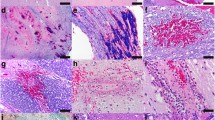
We have examined brain sections from 55 autopsy cases of AIDS for the prevalence and severity of axonal damage, assessed using β-amyloid precursor protein (βAPP) immunoreactivity as a marker of such damage. The cases were subdivided into cases with HIV encephalitis with multinucleated giant cells (MGC), cases with other specific pathology, such as cerebral toxoplasmosis or lymphoma, cases with non-specific pathology and cases with no pathology. Significantly more foci containing βAPP+ axons were found in cases with HIV encephalitis with MGC (80%) and in cases with other specific pathology (58%) than in those with non-specific (30%) or no pathology (30%). The prevalence and abundance of βAPP+ axons generally paralleled the severity of pallor of myelin staining of cerebral white matter in cases without other specific pathology but in 4 cases without any pallor of myelin staining βAPP+ axons were present, suggesting that it may be a more sensitive marker of some forms of white matter damage in HIV infection than myelin pallor. Foci of βAPP+ axons were found in subcortical and deep white matter but did not convincingly co-localise with foci of demonstrable HIV infection as indicated by the presence of MGC and HIV p24 immunoreactivity. In contrast, they showed an approximately perivascular distribution at some sites in all of the disease categories studied. We consider this localisation to be more suggestive of a vascular pathogenetic mechanism of deep white matter damage in HIV infection than a mechanism dependent on diffusion of local myelinotoxic products from foci of cerebral HIV infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 11 March 1996 / Revised: 31 July 1996 / Accepted: 10 September 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raja, F., Sherriff, F., Morris, C. et al. Cerebral white matter damage in HIV infection demonstrated using β-amyloid precursor protein immunoreactivity. Acta Neuropathol 93, 184–189 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010050601
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010050601