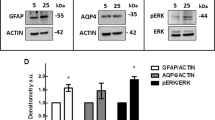
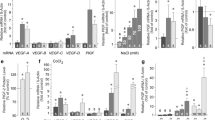
Abstract
Background
Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) has been suggested to mediate activation of Müller glial cells in the ischemic–hypoxic retina. However, the intracellular pathways activated by bFGF in human Müller cells have been little explored. We characterized the signaling transduction pathways which are involved in the control and growth factor-evoked proliferation of a recently described human Müller cell line, MIO-M1. In addition, we investigated whether bFGF evoked the release of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) from the cells.
Methods
The growth factor-evoked proliferation of cultured MIO-M1 cells was estimated by means of a bromodeoxyuridine immunoassay, in the absence and presence of blockers of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and of the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K). The activation state of the p44/p42 MAPK was determined by Western blotting, and the bFGF-evoked release of VEGF and HGF was evaluated by ELISA.
Results
bFGF evoked a concentration-dependent increase of the cell proliferation, with an EC50 of ~1 ng/ml, via activation of both the p44/p42 MAPK and the p38 MAPK. In contrast, the mitogenic effects of the platelet-derived and the heparin-binding epidermal growth factors were dependent on p44/p42 MAPK activation and independent of activation of p38 MAPK. The transforming growth factors β1 and β2 also evoked cell proliferation which was independent of activation of the MAPKs investigated. bFGF evoked a release of VEGF and of HGF by the cells; these effects were independent of MAPK activation and were possibly mediated by activation of the PI3K signaling pathway.
Conclusion
bFGF evokes multiple intracellular signaling pathways in human Müller cells which underlie the gliotic cell responses upon ischemic–hypoxic insults in the retina. Beside the stimulation of cell proliferation, which is dependent on activation of p44/p42 and p38 MAPKs, bFGF induces the secretion of VEGF and HGF by Müller cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiello LP, Northrup JM, Keyt BA, Takagi H, Iwamoto MA (1995) Hypoxic regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in retinal cells. Arch Ophthalmol 113:1538–1544
Akiyama H, Nakazawa T, Shimura M, Tomita H, Tamai M (2002) Presence of mitogen-activated protein kinase in retinal Muller cells and its neuroprotective effect ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neuroreport 13:2103–2107
Briggs MC, Grierson I, Hiscott P, Hunt JA (2000) Active scatter factor (HGF/SF) in proliferative vitreoretinal disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:3085–3094
Bringmann A, Reichenbach A (2001) Role of Müller cells in retinal degenerations. Front Biosci 6: E72-E92
Cassidy L, Barry P, Shaw C, Duffy J, Kennedy S (1998) Platelet derived growth factor and fibroblast growth factor basic levels in the vitreous of patients with vitreoretinal disorders. Br J Ophthalmol 82:181–185
D’Amore PA (1994) Mechanisms of retinal and choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 35:3974–3979
Faktorovich EG, Steinberg RH, Yasumura D, Matthes MT, LaVail MM (1990) Photoreceptor degeneration in inherited retinal dystrophy delayed by basic fibroblast growth factor. Nature 347:83–86
Fischer AJ, McGuire C, Dierks BD, Reh TA (2002) Insulin and FGF2 activate a neurogenic program in Müller glia. J Neurosci 22:9387–9398
Fisher SK, Erickson PA, Lewis GP, Anderson DH (1991) Intraretinal proliferation induced by retinal detachment. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 32:1739–1748
Geller SF, Lewis GP, Fisher SK (2001) FGFR1, signaling, and AP-1 expression after retinal detachment: reactive Müller and RPE cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 42:1363–1369
Guillonneau X, Regnier-Ricard F, Laplace O, Jonet L, Bryckaert M, Courtois Y, Mascarelli F (1998) Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) soluble receptor 1 acts as a natural inhibitor of FGF2 neurotrophic activity during retinal degeneration. Mol Biol Cell 9:2785–2802
He PM, He S, Garner JA, Ryan SJ, Hinton DR (1998) Retinal pigment epithelial cells secrete and respond to hepatocyte growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 249:253–257
Hueber A, Wiedemann P, Esser P, Heimann K (1996) Basic fibroblast growth factor mRNA, bFGF peptide and FGF receptor in epiretinal membranes of intraocular proliferative disorders (PVR and PDR). Int Ophthalmol 20:345–350
Kinkl N, Sahel J, Hicks D (2001) Alternate FGF2-ERK1/2 signaling pathways in retinal photoreceptor and glial cells in vitro. J Biol Chem 276:43871–43878
Kon CH, Occleston NL, Aylward GW, Khaw PT (1999) Expression of vitreous cytokines in proliferative vitreoretinopathy: a prospective study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 40:705–712
Kruchkova Y, Ben-Dror I, Herschkovitz A, David M, Yayon A, Vardimon L (2001) Basic fibroblast growth factor: a potential inhibitor of glutamine synthetase expression in injured neural tissue. J Neurochem 77:1641–1649
Lane HA, Fernandez A, Lamb NJ, Thomas G (1993) p70s6 k function is essential for G1 progression. Nature 363:170–172
Lashkari K, Rahimi N, Kazlauskas A (1999) Hepatocyte growth factor receptor in human RPE cells: implications in proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 40:149–156
Leschey KH, Hackett SF, Singer JH, Campochiaro PA (1990) Growth factor responsiveness of human retinal pigmented epithelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 31:839–846
Lewis GP, Mervin K, Valter K, Maslim J, Kappel PJ, Stone J, Fisher S (1999) Limiting the proliferation and reactivity of retinal Müller cells during experimental retinal detachment: the value of oxygen supplementation. Am J Ophthalmol 128:165–172
Limb GA, Salt TE, Munro PM, Moss SE, Khaw PT (2002) In vitro characterization of a spontaneously immortalized human Muller cell line (MIO-M1). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:864–869
Maher P (1999) p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation is required for fibroblast growth factor-2-stimulated cell proliferation but not differentiation. J Biol Chem 274:17491–17498
Mervin K, Valter K, Maslim J, Lewis G, Fisher S, Stone J (1999) Limiting photoreceptor death and deconstruction during experimental retinal detachment: the value of oxygen supplementation. Am J Ophthalmol 128:155–164
Milenkovic I, Weick M, Wiedemann P, Reichenbach A, Bringmann A (2003) P2Y receptor-mediated stimulation of Müller glial cell DNA synthesis: dependence on EGF and PDGF receptor transactivation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:1211–1220
Moustakas A, Souchelnytskyi S, Heldin CH (2001) Smad regulation in TGF-β signal transduction. J Cell Sci 114:4359–4369
Puro DG (1995) Growth factors and Müller cells. Prog Retin Eye Res 15:89–101
Schiemann WP, Blobe GC, Kalume DE, Pandey A, Lodish HF (2002) Context-specific effects of fibulin-5 (DANCE/EVEC) on cell proliferation, motility, and invasion. Fibulin-5 is induced by transforming growth factor-β and affects protein kinase cascades. J Biol Chem 277:27367–27377
Shibuki H, Katai N, Kuroiwa S, Kurokawa T, Arai J, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, Yoshimura N (2002) Expression and neuroprotective effect of hepatocyte growth factor in retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:528–536
Stone J, Maslim J, Valter-Kocsi K, Mervin K, Bowers F, Chu Y, Barnett N, Provis J, Lewis G, Fisher SK, Bisti S, Gargini C, Cervetto L, Merin S, Peer J (1999) Mechanisms of photoreceptor death and survival in mammalian retina. Prog Retin Eye Res 18:689–735
Wahlin KJ, Campochiaro PA, Zack DJ, Adler R (2000) Neurotrophic factors cause activation of intracellular signaling pathways in Müller cells and other cells of the inner retina, but not photoreceptors. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:927–936
Walsh N, Valter K, Stone J (2001) Cellular and subcellular patterns of expression of bFGF and CNTF in the normal and light stressed adult rat retina. Exp Eye Res 72:495–501
Wen R, Song Y, Cheng T, Matthes MT, Yasumura D, LaVail MM, Steinberg RH (1995) Injury-induced upregulation of bFGF and CNTF mRNAs in the rat retina. J Neurosci 15:7377–7385
Yonekura A, Osaki M, Hirota Y, Tsukazaki T, Miyazaki Y, Matsumoto T, Ohtsuru A, Namba H, Shindo H, Yamashita S (1999) Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates articular chondrocyte cell growth through p44/42 MAP kinase (ERK) activation. Endocr J 46:545–553
Yu L, Hebert MC, Zhang YE (2002) TGF-beta receptor-activated p38 MAP kinase mediates Smad-independent TGF-β responses. EMBO J 21:3749–3759
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mrs. U. Weinbrecht and F. Kutzera for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Ko1547/4-1; Br 1249/2-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hollborn, M., Jahn, K., Limb, G.A. et al. Characterization of the basic fibroblast growth factor-evoked proliferation of the human Müller cell line, MIO-M1. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 242, 414–422 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-004-0879-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-004-0879-x