Abstract
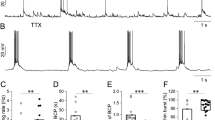
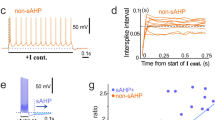
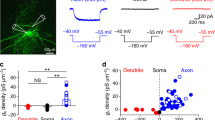
In several neuronal preparations, the ryanodine-sensitive calcium store was reported to participate in the generation of slow afterhyperpolarization currents (IsAHP) involved in spike frequency adaptation. We show that calcium release from the ryanodine-sensitive calcium store is a major determinant of the triggering of IsAHP in mouse CA1 pyramidal neurons. Whole-cell patch clamp recordings in hippocampus slices show that the intracellular calcium stores depletion using an inhibitor of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (5 μM cyclopiazonic acid), as well as the specific blockade of ryanodine receptors (100 μM ryanodine) both reduced the IsAHP by about 70%. Immunohistology, using an anti-RyR3 specific antibody, indicates that RyR3 expression is particularly enriched in the CA1 apical dendrites (considered as the most important site for sAHP generation). We show that our anti-RyR3 antibody acts as a functional RyR3 antagonist and induced a reduction in IsAHP by about 70%. The additional ryanodine application (100 μ M) did not further affect IsAHP, thus excluding RyR2 in IsAHP activation. Our results argue in favor of a specialized function of RyR3 in CA1 pyramidal cells in triggering IsAHP due to their localization in the apical dendrite.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekkers JM (2000) Distribution of slow AHP channels on hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 83:1756–1759
Berridge MJ (1998) Neuronal calcium signaling. Neuron 21(1):13–26
Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL (2003) Calcium signaling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodeling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4(7):517–529
Bouchard R, Pattarini R, Geiger JD (2003) Presence and functional significance of presynaptic ryanodine receptors. Prog Neurobiol 69:391–418
Bootman MD, Lipp P, Berridge MJ (2001) The organisation and functions of local Ca(2+) signals. J Cell Sci 114(12):2213–2222
Borde M, Bonansco C, de Sevilla F, Le Ray D, Buno W (2000) Voltage-clamp analysis of the potentiation of the slow Ca2+-activated K+ current in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Hippocampus 10(2):198–206
Bowden SE, Fletcher S, Loane DJ, Marrion NV (2001) Somatic colocalization of rat SK1 and D class (Ca(v)1.2) L-type calcium channels in rat CA1 hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 21(20):RC175
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chen SR, Zhang L, MacLennan DH (1993) Antibodies as probes for Ca2+ activation sites in the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 268(18):13414–13421
Chen SR, Ebisawa K, Li X, Zhang L (1998) Molecular identification of the ryanodine receptor Ca2+ sensor. J Biol Chem 273(24):14675–14678
Cohen AS, Coussens CM, Raymond CR, Abraham WC (1999) Long-lasting increase in cellular excitability associated with the priming of LTP induction in hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 82(6):3139–3148
Demaurex N, Lew DP, Krause KH (1992) Cyclopiazonic acid depletes intracellular Ca2+stores and activates an influx pathway for divalent cations in HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem 267:2318–2324
Fill M, Copello JA (2002) Ryanodine receptor calcium release channels. Physiol Rev 82(4):893–922
Furuichi T, Furutama D, Hakamata Y, Nakai J, Takeshima H, Mikoshiba K (1994) Multiple types of ryanodine receptor/Ca2+ release channels are differentially expressed in rabbit brain. J Neurosci 14(8):4794–4805
Futatsugi A, Kato K, Ogura H, Li ST, Nagata E, Kuwajima G, Tanaka K, Itohara S, Mikoshiba K (1999) Facilitation of NMDAR-independent LTP and spatial learning in mutant mice lacking ryanodine receptor type 3. Neuron 24(3):701–713
Gerlach AC, Maylie J, Adelman JP (2004) Activation kinetics of the slow afterhyperpolarization in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Pflugers Arch 448(2):187–196
Giannini G, Conti A, Mammarella S, Scrobogna M, Sorrentino V (1995) The ryanodine receptor/calcium channel genes are widely and differentially expressed in murine brain and peripheral tissues. J Cell Biol 128(5):893–904
Harlow E, Lane D (1988). Antibodies: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA
Hell JW, Westenbroek RE, Warner C, Ahlijanian MK, Prystay W, Gilbert MM, Snutch TP, Catterall WA (1993) Identification and differential subcellular localization of the neuronal class C and class D L-type calcium channel alpha 1 subunits. J Cell Biol 123(4):949–962
Hillsley K, Kenyon JL, Smith TK (2000) Ryanodine-sensitive stores regulate the excitability of AH neurons in the myenteric plexus of guinea-pig ileum. J Neurophysiol 84(6):2777–2785
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227(5259):680–685
Lancaster B, Adams PR (1986) Calcium-dependent current generating the afterhyperpolarization of hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol 55(6):1268–1282
Lancaster B, Nicoll RA (1987) Properties of two calcium-activated hyperpolarizations in rat hippocampal neurons. J Physiol 389:187–203
Lancaster B, Zucker RS (1994) Photolytic manipulation of Ca2+ and the time course of slow, Ca2+-activated K+ current in rat hippocampal neurons. J Physiol 475(2):229–239
Lancaster B, Hu H, Ramakers GMJ, Storm JF (2001) Interaction between synaptic excitation and slow afterhyperpolarization current in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol 536(3):809–823
Madison DV, Nicoll RA (1984) Control of the repetitive discharge of rat CA 1 pyramidal neurones in vitro. J Physiol 354:319–331
Marrion NV, Tavalin SJ (1998) Selective activation of Ca2+-activated K+ channels by co-localized Ca2+ channels in hippocampal neurons. Nature 395(6705):900–905
Mironneau J, Macrez N, Morel JL, Sorrentino V, Mironneau C (2002) Identification and function of ryanodine receptor subtype 3 in non-pregnant mouse myometrial cells. J Physiol 538:707–716
Moore KA, Cohen AS, Kao JPY, Weinreich D (1998) Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release mediates a slow post-spike hyperpolarization in rabbit vagal afferent neurons. J Neurophysiol 79:688–694
Mori F, Fukaya M, Abe H, Wakabayashi K, Watanabe M (2000) Developmental changes in expression of the three ryanodine receptor mRNAs in the mouse brain. Neurosci Lett 285(1):57–60
Moyer JR Jr, Thompson LT, Black JP, Disterhoft JF (1992) Nimodipine increases excitability of rabbit CA1 pyramidal neurons in an age- and concentration-dependent manner. J Neurophysiol 68(6):2100–2109
Murayama T, Ogawa Y (1996) Properties of Ryr3 ryanodine receptor isoform in mammalian brain. J Biol Chem 271(9):5079–5084
Nakanishi S, Kuwajima G, Mikoshiba K (1992) Immunohistochemical localization of ryanodine receptors in mouse central nervous system. Neurosci Res 15(1-2):130–142
Power JM, Wu WW, Sametsky E, Oh MM, Disterhoft JF (2002) Age-related enhancement of the slow outward calcium-activated potassium current in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons in vitro. J Neurosci 22(16):7234–7243
Rascol O, Potier B, Lamour Y, Dutar P (1991) Effects of calcium channel agonist and antagonists on calcium-dependent events in CA1 hippocampal neurons. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 5(4):299–317
Rizzuto R (2001) Intracellular Ca(2+) pools in neuronal signalling. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11(3):306–311
Rossi D, Sorrentino V (2002) Molecular genetics of ryanodine receptors Ca2+-release channels. Cell Calcium 32(5–6):307–319
Sah P, Faber ES (2002) Channels underlying neuronal calcium-activated potassium currents. Prog Neurobiol 66(5):345–353
Sah P, Bekkers JM (1996) Apical dendritic location of slow afterhyperpolarization current in hippocampal pyramidal neurons: implications for the integration of long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 16(15):4537–4542
Sah P, McLachlan EM (1991) Ca(2+)-activated K+ currents underlying the afterhyperpolarization in guinea pig vagal neurons: a role for Ca(2+)-activated Ca2+ release. Neuron 7(2):257–264
Sah P (1996) Ca(2+)-activated K+ currents in neurones: types, physiological roles and modulation. Trends Neurosci 19(4):150–154
Serysheva II, Orlova EV, Chiu W, Sherman MB, Hamilton SL, van Heel M (1995) Electron cryomicroscopy and angular reconstitution used to visualize the skeletal muscle calcium release channel. Nat Struct Biol 2(1):18–24
Seymour-Laurent KJ, Barish ME (1995) Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and ryanodine receptor distributions and patterns of acetylcholine- and caffeine-induced calcium release in cultured mouse hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 15(4):2592–2608
Shah M, Haylett DG (2000) Ca(2+) channels involved in the generation of the slow afterhyperpolarization in cultured rat hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 83(5):2554–2561
Shoshan-Barmatz V, Ashley RH (1998) The structure, function, and cellular regulation of ryanodine-sensitive Ca2+ release channels. Int Rev Cytol 183:185–270
Sitsapesan R, Williams AJ (1997) Regulation of current flow through ryanodine receptors by luminal Ca2+. J Membr Biol 159:179–185
Sutko JL, Airey JA, Welch W, Ruest L (1997) The pharmacology of ryanodine and related compounds. Pharmacol Rev 49(1):53–98
Tanabe M, Gahwiler BH, Gerber U (1998) L-Type Ca2+ channels mediate the slow Ca2+-dependent afterhyperpolarization current in rat CA3 pyramidal cells in vitro. J Neurophysiol 80(5):2268–2273
Torres GE, Arfken CL, Andrade R (1996) 5-Hydroxytryptamine4 receptors reduce afterhyperpolarization in hippocampus by inhibiting calcium-induced calcium release. Mol Pharmacol 50(5):1316–1322
Uyama Y, Imaizumi Y, Watanabe M (1992) Effects of cyclopiazonic acid, a novel Ca2+-ATPase inhibitor, on contractile responses in skinned ileal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol 106:208–214
Velumian AA, Zhang L, Pennefather P, Carlen PL (1997) Reversible inhibition of IK, IAHP, Ih and ICa currents by internally applied gluconate in rat hippocampal pyramidal neurones. Pflugers Arch 433(3):343–350
Vergara C, Latorre R, Marrion NV, Adelman JP (1998) Calcium-activated potassium channels. Curr Opin Neurobiol 8(3):321–329
Verkhratsky A (2002) The endoplasmic reticulum and neuronal calcium signaling. Cell Calcium 32(5-6):393–404
Vogalis F, Storm JF, Lancaster B (2003) SK channels and the varieties of slow after-hyperpolarizations in neurons. Eur J Neurosci 18(12):3155–3166
Wagenknecht T, Radermacher M (1995) Three-dimensional architecture of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. FEBS Lett 369(1):43–46
Yoshizaki K, Hoshino T, Sato M, Koyano H, Nohmi M, Hua SY, Kuba K (1995) Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release and its activation in response to a single action potential in rabbit otic ganglion cells. J Physiol (Lond) 486:177–187
Zhang L, Weiner JL, Valiante TA, Velumian AA, Watson PL, Jahromi SS, Schertzer S, Pennefather P, Carlen PL (1994) Whole-cell recording of the Ca(2+)-dependent slow afterhyperpolarization in hippocampal neurones: effects of internally applied anions. Pflugers Arch 426(3-4):247–253
Zhang L, Pennefather P, Velumian A, Tymianski M, Charlton M, Carlen PL (1995) Potentiation of a slow Ca(2+)-dependent K+ current by intracellular Ca2+ chelators in hippocampal CA1 neurons of rat brain slices. J Neurophysiol 74(6):2225–2241
Zorzato F, Fujii J, Otsu K, Phillips M, Green NM, Lai FA, Meissner G, MacLennan DH (1990) Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding human and rabbit forms of the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 265:2244–2256
Davies PJ, Ireland DR, McLachlan EM (1996) Sources of Ca2+ for different Ca(2+)-activated K+ conductances in neurones of the rat superior cervical ganglion. J Physiol 495(Pt 2):353–366
Acknowledgment
P.C. was supported by fellowships from the Ministère de l’Education Nationale, de la Recherche Scientifique et de la Technologie and from the Association Française contre les Myopathies. This work was supported by a grant from the Association Française contre les Myopathies. We gratefully acknowledge Dr. Nicolas Morel and Dr. Jean Pierre Denizot (CNRS, Gif/Yvette, France) for their precious expertise in biochemistry and immunohistology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van de Vrede, Y., Fossier, P., Baux, G. et al. Control of IsAHP in mouse hippocampus CA1 pyramidal neurons by RyR3-mediated calcium-induced calcium release. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 455, 297–308 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-007-0277-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-007-0277-4