Abstract
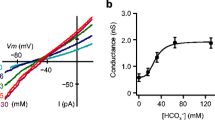
We used the whole-cell patch-clamp technique to identify a hyperpolarization-activated Cl–current (≈50 pA/pF at –60 mV) in acutely isolated, voltage-clamped, single, pig pancreatic acinar cells. This current had characteristic properties of inward rectification, a Cl– = Br–>I–selectivity sequence and activation by extracellular hypotonicity. These properties are similar to those reported for the ClC-2 Cl–channel recently cloned from rat and expressed in oocytes. An antiserum raised against the C-terminus of ClC-2 localized the channel to secretory granules containing amylase that were situated exclusively at the apical pole of the pig pancreatic acinar cells, but the channel was not localized in the basolateral membrane. Our study combines a functional assessment and immunohistochemical localization of ClC-2-like channels in a native mammalian cell. The data suggest that the ClC-2-like Cl–channel may function as a Cl–efflux pathway in pancreatic acinar cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 August 1996 / Received after revision and accepted: 6 August 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carew, M., Thorn, P. Identification of ClC-2-like chloride currents in pig pancreatic acinar cells. Pfluegers Arch 433, 84–90 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050252
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050252