Summary.
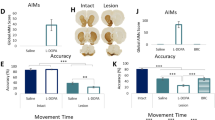
L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia (abnormal involuntary movements) is one of the most debilitating complications of chron-ic L-DOPA pharmacotherapy in Parkinson's disease. It is generally agreed that dyskinesia arises as a consequence of pulsatile dopamine-receptor stimulation in the brain, causing downstream changes in genes and proteins. Advance in our understanding of such changes is critically dependent on the availability of suitable animal models. We have introduced a new method to classify and rate L-DOPA-induced abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs) in 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) lesioned rats. This method allows us to dissect the molecular correlates of a dyskinetic motor response to L-DOPA in this species. One of the most prominent molecular changes underlying the development of dyskinesia in the rat consists in the striatal induction of prodynorphin gene expression by L-DOPA. This effect is mediated by FosB-related transcription factors of 32–37 kDa, which are co-induced with prodynophin in striatal neurons of the “direct pathway”. Both AIM development and the associated upregulation of prodynorphin mRNA by L-DOPA are significantly inhibited by the intrastriatal infusion of fosB antisense. Antisense-mediated knockdown of CREB (cyclic AMP response-element binding proteins) has however no effect. Our results identify fosB as a potential target for adjunctive antiparkinsonian therapies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received July 6, 2001 Accepted August 6, 2001 Published online June 17, 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cenci, M. Transcription factors involved in the pathogenesis of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Amino Acids 23, 105–109 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-001-0116-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-001-0116-4