Abstract
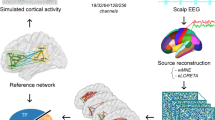
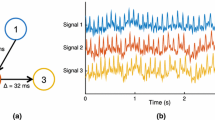
Epilepsy is a network disease. The epileptic network usually involves spatially distributed brain regions. In this context, noninvasive M/EEG source connectivity is an emerging technique to identify functional brain networks at cortical level from noninvasive recordings. In this paper, we analyze the effect of the two key factors involved in EEG source connectivity processing: (i) the algorithm used in the solution of the EEG inverse problem and (ii) the method used in the estimation of the functional connectivity. We evaluate four inverse solutions algorithms (dSPM, wMNE, sLORETA and cMEM) and four connectivity measures (r 2, h 2, PLV, and MI) on data simulated from a combined biophysical/physiological model to generate realistic interictal epileptic spikes reflected in scalp EEG. We use a new network-based similarity index to compare between the network identified by each of the inverse/connectivity combination and the original network generated in the model. The method will be also applied on real data recorded from one epileptic patient who underwent a full presurgical evaluation for drug-resistant focal epilepsy. In simulated data, results revealed that the selection of the inverse/connectivity combination has a significant impact on the identified networks. Results suggested that nonlinear methods (nonlinear correlation coefficient, phase synchronization and mutual information) for measuring the connectivity are more efficient than the linear one (the cross correlation coefficient). The wMNE inverse solution showed higher performance than dSPM, cMEM and sLORETA. In real data, the combination (wMNE/PLV) led to a very good matching between the interictal epileptic network identified from noninvasive EEG recordings and the network obtained from connectivity analysis of intracerebral EEG recordings. These results suggest that source connectivity method, when appropriately configured, is able to extract highly relevant diagnostic information about networks involved in interictal epileptic spikes from non-invasive dense-EEG data.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebimpe A, Aarabi A, Bourel-Ponchel E, Mahmoudzadeh M, Wallois F (2016) EEG resting state functional connectivity analysis in children with benign epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes. Front Neurosci 10:143
Alarcon G, Guy C, Binnie C, Walker S, Elwes R, Polkey C (1994) Intracerebral propagation of interictal activity in partial epilepsy: implications for source localisation Journal of Neurology. Neurosurg Psychiatry 57:435–449
Alarcon G et al (1997) Origin and propagation of interictal discharges in the acute electrocorticogram. Implications for pathophysiology and surgical treatment of temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 120:2259–2282
Astolfi L et al (2007) Comparison of different cortical connectivity estimators for high-resolution EEG recordings. Hum Brain Mapp 28:143–157
Babiloni F et al (2005) Estimation of the cortical functional connectivity with the multimodal integration of high-resolution EEG and fMRI data by directed transfer function. Neuroimage 24:118–131
Barth DS, Sutherling W, Engle J, Beatty J (1984) Neuromagnetic evidence of spatially distributed sources underlying epileptiform spikes in the human brain. Science 223:293–296
Bartolomei F, Wendling F, Bellanger J-J, Régis J, Chauvel P (2001) Neural networks involving the medial temporal structures in temporal lobe epilepsy. Clin Neurophysiol 112:1746–1760
Baumgartner C et al (1995) Propagation of interictal epileptic activity in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology 45:118–122
Becker H et al (2014) EEG extended source localization: tensor-based vs. conventional methods. NeuroImage 96:143–157
Betti V, Della Penna S, de Pasquale F, Mantini D, Marzetti L, Romani GL, Corbetta M (2013) Natural scenes viewing alters the dynamics of functional connectivity in the human brain. Neuron 79:782–797
Bettus G, Wendling F, Guye M, Valton L, Regis J, Chauvel P, Bartolomei F (2008) Enhanced EEG functional connectivity in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 81:58–68. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2008.04.020
Bola M, Sabel BA (2015) Dynamic reorganization of brain functional networks during cognition. NeuroImage 114:398–413
Bourien J, Bellanger JJ, Bartolomei F, Chauvel P, Wendling F (2004) Mining reproducible activation patterns in epileptic intracerebral EEG signals: application to interictal activity. IEEE Trans Bio-Med Eng 51:304–315. doi:10.1109/TBME.2003.820397
Bourien J, Bartolomei F, Bellanger JJ, Gavaret M, Chauvel P, Wendling F (2005) A method to identify reproducible subsets of co-activated structures during interictal spikes. Application to intracerebral EEG in temporal lobe epilepsy. Clin Neurophysiol 116:443–455. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2004.08.010
Brookes MJ et al (2014) Measuring temporal, spectral and spatial changes in electrophysiological brain network connectivity. Neuroimage 91:282–299
Caparos M, Louis-Dorr V, Wendling F, Maillard L, Wolf D (2006) Automatic lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy based on scalp EEG. Clin Neurophysiol 117:2414–2423
Cho J-H, Vorwerk J, Wolters CH, Knösche TR (2015) Influence of the head model on EEG and MEG source connectivity analysis. Neuroimage 110:60–77
Chowdhury RA, Lina JM, Kobayashi E, Grova C (2013) MEG source localization of spatially extended generators of epileptic activity: comparing entropic and hierarchical Bayesian approaches. PLoS One 8:e55969
Clarke C, Janday B (1989) The solution of the biomagnetic inverse problem by maximum statistical entropy. Inverse Prob 5:483
Coito A et al (2015) Dynamic directed interictal connectivity in left and right temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 56:207–217
Coito A et al (2016) Altered directed functional connectivity in temporal lobe epilepsy in the absence of interictal spikes: A high density EEG study. Epilepsia 57(3):402–411
Cosandier-Rimélé D, Merlet I, Badier J-M, Chauvel P, Wendling F (2008) The neuronal sources of EEG: modeling of simultaneous scalp and intracerebral recordings in epilepsy. NeuroImage 42:135–146
Dai Y, Zhang W, Dickens DL, He B (2012) Source connectivity analysis from MEG and its application to epilepsy source localization. Brain Topogr 25:157–166
Dale AM, Liu AK, Fischl BR, Buckner RL, Belliveau JW, Lewine JD, Halgren E (2000) Dynamic statistical parametric mapping: combining fMRI and MEG for high-resolution imaging of cortical activity. Neuron 26:55–67
David O, Garnero L, Cosmelli D, Varela FJ (2002) Estimation of neural dynamics from MEG/EEG cortical current density maps: application to the reconstruction of large-scale cortical synchrony. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 49:975–987
David O, Cosmelli D, Hasboun D, Garnero L (2003) A multitrial analysis for revealing significant corticocortical networks in magnetoencephalography and electroencephalography. Neuroimage 20:186–201
de Pasquale F et al (2010) Temporal dynamics of spontaneous MEG activity in brain networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:6040–6045
Destrieux C, Fischl B, Dale A, Halgren E (2010) Automatic parcellation of human cortical gyri and sulci using standard anatomical nomenclature. Neuroimage 53:1–15
Diessen E, Diederen SJ, Braun KP, Jansen FE, Stam CJ (2013) Functional and structural brain networks in epilepsy: what have we learned? Epilepsia 54:1855–1865
Ding L, Worrell GA, Lagerlund TD, He B (2007) Ictal source analysis: localization and imaging of causal interactions in humans. Neuroimage 34:575–586
Ebersole J (1994) Non-invasive localization of the epileptogenic focus by EEG dipole modeling. Acta Neurol Scand 89:20–28
Emerson RG, Turner CA, Pedley TA, Walczak TS, Forgione M (1995) Propagation patterns of temporal spikes. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 94:338–348
Engel J Jr, Thompson PM, Stern JM, Staba RJ, Bragin A, Mody I (2013) Connectomics and epilepsy. Curr Opin Neurol 26:186
Fischl B (2012) FreeSurfer. Neuroimage 62:774–781
Fornito A, Zalesky A, Breakspear M (2015) The connectomics of brain disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 16:159–172
Fraschini M, Demuru M, Crobe A, Marrosu F, Stam CJ, Hillebrand A (2016) The effect of epoch length on estimated EEG functional connectivity and brain network organisation. J Neural Eng 13:036015
Fuchs M, Wagner M, Kastner J (2007) Development of volume conductor and source models to localize epileptic foci. J Clin Neurophysiol 24:101–119
Gotman J (1983) Measurement of small time differences between EEG channels: method and application to epileptic seizure propagation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 56:501–514
Gotman J (1987) Interhemispheric interactions in seizures of focal onset: data from human intracranial recordings. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 67:120–133
Gramfort A, Papadopoulo T, Olivi E, Clerc M (2010) OpenMEEG: opensource software for quasistatic bioelectromagnetics. Biomed Eng Online 9:45
Hämäläinen M (2005) MNE software user’s guide NMR Center. Mass Gen Hosp Harvard Univ 58:59–75
Hämäläinen MS, Ilmoniemi R (1994) Interpreting magnetic fields of the brain: minimum norm estimates. Med Biol Eng Comput 32:35–42
Hassan M, Wendling F (2015) Tracking dynamics of functional brain networks using dense EEG. IRBM 36:324–328
Hassan M, Dufor O, Merlet I, Berrou C, Wendling F (2014) EEG source connectivity analysis: from dense array recordings to brain networks. PLoS One 9:e105041
Hassan M, Benquet P, Biraben A, Berrou C, Dufor O, Wendling F (2015a) Dynamic reorganization of functional brain networks during picture naming. Cortex 73:276–288
Hassan M, Shamas M, Khalil M, El Falou W, Wendling F (2015b) EEGNET: an open source tool for analyzing and visualizing M/EEG connectome. PLoS One 10:e0138297
Hipp JF, Engel AK, Siegel M (2011) Oscillatory synchronization in large-scale cortical networks predicts perception. Neuron 69:387–396
Hoechstetter K, Bornfleth H, Weckesser D, Ille N, Berg P, Scherg M (2004) BESA source coherence: a new method to study cortical oscillatory coupling. Brain Topogr 16:233–238
Jiruska P, de Curtis M, Jefferys JG, Schevon CA, Schiff SJ, Schindler K (2013) Synchronization and desynchronization in epilepsy: controversies and hypotheses. J Physiol 591:787–797. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2012.239590
Kramer MA, Cash SS (2012) Epilepsy as a disorder of cortical network organization. Neuroscientist 18:360–372
Kuś R, Kamiński M, Blinowska KJ (2004) Determination of EEG activity propagation: pair-wise versus multichannel estimate. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 51:1501–1510
Laufs H (2012) Functional imaging of seizures and epilepsy: evolution from zones to networks. Curr Opin Neurol 25:194–200
Le Van Quyen M, Soss J, Navarro V, Robertson R, Chavez M, Baulac M, Martinerie J (2005) Preictal state identification by synchronization changes in long-term intracranial EEG recordings. Clin Neurophysiol 116:559–568
Liljeström M, Kujala J, Stevenson C, Salmelin R (2015) Dynamic reconfiguration of the language network preceding onset of speech in picture naming. Hum Brain Mapp 36:1202–1216
Lu Y, Yang L, Worrell GA, He B (2012) Seizure source imaging by means of FINE spatio-temporal dipole localization and directed transfer function in partial epilepsy patients. Clin Neurophysiol 123:1275–1283
Malinowska U, Badier JM, Gavaret M, Bartolomei F, Chauvel P, Bénar CG (2014) Interictal networks in magnetoencephalography Human brain mapping 35:2789–2805
Merlet I, Gotman J (1999) Reliability of dipole models of epileptic spikes. Clin Neurophysiol 110:1013–1028
Mheich A, Hassan M, Gripon V, Dufor O, Khalil M, Berrou C, Wendling F (2015a) A novel algorithm for measuring graph similarity: application to brain networks. In: 7th international IEEE EMBS neural engineering conference, Montpellier, France
Mheich A, Hassan M, Khalil M, Berrou C, Wendling F (2015b) A new algorithm for spatiotemporal analysis of brain functional connectivity. J Neurosci Methods 242:77–81
Michel CM, Murray MM (2012) Towards the utilization of EEG as a brain imaging tool. Neuroimage 61:371–385
Mormann F, Lehnertz K, David P, Elger CE (2000) Mean phase coherence as a measure for phase synchronization and its application to the EEG of epilepsy patients. Physica D 144:358–369
O’Neill GC, Barratt EL, Hunt BA, Tewarie PK, Brookes MJ (2015) Measuring electrophysiological connectivity by power envelope correlation: a technical review on MEG methods. Phys Med Biol 60:R271
Pascual-Marqui RD (2002) Standardized low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (sLORETA): technical details. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 24:5–12
Pereda E, Quiroga RQ, Bhattacharya J (2005) Nonlinear multivariate analysis of neurophysiological signals. Prog Neurobiol 77:1–37
Ramon C, Holmes MD (2013) Noninvasive localization of epileptic sites from stable phase synchronization patterns on different days derived from short duration interictal scalp dEEG. Brain Topogr 26:1–8
Schindler KA, Bialonski S, Horstmann MT, Elger CE, Lehnertz K (2008) Evolving functional network properties and synchronizability during human epileptic seizures. Chaos 18:033119. doi:10.1063/1.2966112
Schoffelen JM, Gross J (2009) Source connectivity analysis with MEG and EEG. Hum Brain Mapp 30:1857–1865
Song J, Tucker DM, Gilbert T, Hou J, Mattson C, Luu P, Holmes MD (2013) Methods for examining electrophysiological coherence in epileptic networks. Front Neurol 4:55
Song J et al (2015) EEG source localization: Sensor density and head surface coverage. J Neurosci Methods 256:9–21
Tadel F, Baillet S, Mosher JC, Pantazis D, Leahy RM (2011) Brainstorm: a user-friendly application for MEG/EEG analysis. Comput Intell Neurosci 2011:8
van Mierlo P, Papadopoulou M, Carrette E, Boon P, Vandenberghe S, Vonck K, Marinazzo D (2014) Functional brain connectivity from EEG in epilepsy: seizure prediction and epileptogenic focus localization. Prog Neurobiol 121:19–35
Vecchio F et al (2014) Cortical connectivity in fronto-temporal focal epilepsy from EEG analysis: a study via graph theory. Clin Neurophysiol 126(6):1108–1116
Wendling F, Bellanger J-J, Bartolomei F, Chauvel P (2000) Relevance of nonlinear lumped-parameter models in the analysis of depth-EEG epileptic signals. Biol Cybern 83:367–378
Wendling F, Bartolomei F, Bellanger JJ, Chauvel P (2002) Epileptic fast activity can be explained by a model of impaired GABAergic dendritic inhibition. Eur J Neurosci 15:1499–1508
Wendling F, Bartolomei F, Bellanger J-J, Bourien J, Chauvel P (2003) Epileptic fast intracerebral EEG activity: evidence for spatial decorrelation at seizure onset. Brain 126:1449–1459
Wendling F, Ansari-Asl K, Bartolomei F, Senhadji L (2009) From EEG signals to brain connectivity: a model-based evaluation of interdependence measures. J Neurosci Methods 183:9–18
Wendling F, Chauvel P, Biraben A, Bartolomei F (2010) From intracerebral EEG signals to brain connectivity: identification of epileptogenic networks in partial epilepsy. Front Syst Neurosci 4:154
Acknowledgments
This work has received a French government support granted to the CominLabs excellence laboratory and managed by the National Research Agency in the “Investing for the Future” program under reference ANR-10-LABX-07-01. It was also financed by the Rennes University Hospital (COREC Project named conneXion, 2012-14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, M., Merlet, I., Mheich, A. et al. Identification of Interictal Epileptic Networks from Dense-EEG. Brain Topogr 30, 60–76 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-016-0517-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-016-0517-z