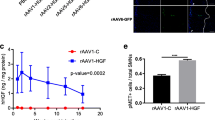
Abstract
Aim Nogo extracellular peptide 1-40 (NEP1-40), a Nogo-66 antagonistic peptide, is one of the potential candidates for therapeutic intervention after central nervous system injury. This study is focused on the generation of TAT-NEP1-40 fusion protein and its transducible effects and biological activity. Methods TAT-NEP1-40 fusion protein was expressed in vitro. Transducible effects of TAT-NEP1-40 were analyzed by using immunofluorescence staining or Western blot in vitro and in vivo. The biological activity of TAT-NEP1-40 was assessed by its effects against oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced PC12 cell damages. Results Our results showed that the TAT-NEP1-40 fusion protein was successfully expressed, purified, and refolded. Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence staining confirmed the delivery of TAT-NEP1-40 protein into PC12 cells and rat brains. OGD caused cell apoptosis or death, decreased cell viability, increased lactate dehydrogenase release in medium and the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, all of which were prevented by the TAT-NEP1-40 fusion proteins when added exogenously to culture medium. In addition, TAT-NEP1-40 promoted neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells exposed to OGD. Conclusion These results demonstrate that the TAT-NEP1-40 can be successfully generated and efficiently transduced into PC12 cells and rat brains. The TAT-NEP1-40 can protect PC12 cells against OGD and promote neurite outgrowth. This finding suggests that the transducible TAT-NEP1-40 fusion protein offers a possibility of the development of novel therapy for cerebral injuries via delivery of the biologically active TAT-NEP1-40 fusion protein into injured sites.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartsch U, Bandtlow CE, Schnell L, Bartsch S, Spillmann AA, Rubin BP et al (1995) Lack of evidence that myelin-associated glycoprotein is a major inhibitor of axonal regeneration in the CNS. Neuron 15:1375–1381. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(95)90015-2
Becker-Hapak M, McAiliste SS, Dowdy SF (2001) TAT-mediated protein transduction into mammalian cells. Methods 24:247–256. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1186
Chou CM, Huang CJ, Shih CM, Chen YP, Liu TP, Chen CT (2005) Identification of three mutations in the Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase (Cu, Zn-SOD) gene with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: transduction of human Cu, Zn-SOD into PC12 cells by HIV-1 TAT protein basic domain. Ann NY Acad Sci 1041:303–313. doi:10.1196/annals.1338.053
Cory S, Adams JM (2002) The Bcl-2 family: regulators of cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2:647–656 . doi:10.1038/nrc883
Denicourt C, Dowdy SF (2003) Protein transduction technology offers novel therapeutic approach for brain ischemia. Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:216–218
Domeniconi M, Cao Z, Spencer T, Sivasankaran R, Wang K, Nikulina E et al (2002) Myelin-associated glycoprotein interacts with the Nogo-66 receptor to inhibit neurite outgrowth. Neuron 35:283–290. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00770-5
Fittipaldi A, Giacca M (2005) Transcellular protein transduction using the TAT protein of HIV-1. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57:597–608. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2004.10.011
Fournier AE, GrandPre T, Strittmatter SM (2001) Identification of a receptor mediating Nogo-66 inhibition of axonal regeneration. Nature 409:341–346. doi:10.1038/35053072
GrandPre T, Nakamura F, Vartanian T, Strittmatter SM (2000) Identification of the Nogo inhibitor of axon regeneration as a Reticulon protein. Nature 403:439–444. doi:10.1038/35000226
GrandPre T, Li S, Strittmatter SM (2002) Nogo-66 receptor antagonist peptide promotes axonal regeneration. Nature 417:547–551. doi:10.1038/417547a
Green JB (2003) Brain reorganization after stroke. Top Stroke Rehabil 10:1–20
Guegan C, Braudeau J, Couriaud C, Dietz GP, Lacombe P, Bahr M et al (2006) PTD-XIAP protects against cerebral ischemia by anti-apoptotic and transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. Neurobiol Dis 22:177–186. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2005.10.014
Guo F, Li SQ, Chu YH, Huang XF, Sun LM, Li HJ et al (2007) High-level expression, polyclonal antibody preparation and sub-cellular localization analysis of mouse Rhox5 protein. Protein Expr Purif 54:247–252. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2007.03.021
He Z, Koprivica V (2004) The Nogo signaling pathway for regeneration block. Annu Rev Neurosci 27:341–368. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.27.070203.144340
Kilic U, Kilic E, Dietz GP, Bahr M (2003) Intravenous TAT-GDNF is protective after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Stroke 34:1304–1310. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000066869.45310.50
Kilic E, Kilic U, Hermann DM (2006) TAT fusion proteins against ischemic stroke: current status and future perspectives. Front Biosci 11:1716–1721. doi:10.2741/1917
Kim DW, Eum WS, Jang SH, Kim SY, Choi HS, Choi SH et al (2005) Transduced TAT-SOD fusion protein protects against ischemic brain injury. Mol Cells 19:88–96
Kim SY, An JJ, Kim DW, Choi SH, Lee SH, Hwang SI et al (2006) TAT-mediated protein transduction of human brain pyridoxine-5-P oxidase into PC12 cells. J Biochem Mol Biol 39:76–83
Koubi D, Jiang H, Zhang L, Tang W, Kuo J, Rodriguez AI et al (2005) Role of Bcl-2 family of proteins in mediating apoptotic death of PC12 cells exposed to oxygen and glucose deprivation. Neurochem Int 46:73–81. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2004.06.006
Lee DH, Strittmatter SM, Sah DW (2003) Targeting the Nogo receptor to treat central nervous system injuries. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2:872–878. doi:10.1038/nrd1228
Lee JK, Kim JE, Sivula M, Strittmatter SM (2004) Nogo receptor antagonism promotes stroke recovery by enhancing axonal plasticity. J Neurosci 24:6209–6217. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1643-04.2004
Li S, Strittmatter SM (2003) Delayed systemic Nogo-66 receptor antagonist promotes recovery from spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 23:4219–4227
Lipton P (1999) Ischemic cell death in brain neurons. Physiol Rev 79:1431–1568
Mi S, Miller RH, Lee X, Scott ML, Shulag-Morskaya S, Shao Z et al (2004) LINGO-1 is a component of the Nogo-66 receptor/p75 signaling complex. Nat Neurosci 7:221–228. doi:10.1038/nn1188
Misra A, Ganesh S, Shahiwala A, Shah SP (2003) Drug delivery to the central nervous system: a review. J Pharm Pharm Sci 6:252–273
Prinsloo E, Oosthuizen V, Muramoto K, Naude RJ (2006) In vitro refolding of recombinant human free secretory component using equilibrium gradient dialysis. Protein Expr Purif 47:179–185. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2005.09.017
Richardson RT, Thompsonc B, Moulton S, Newbold C, Lum MG, Cameron A et al (2007) The effect of polypyrrole with incorporated neurotrophin-3 on the promotion of neurite outgrowth from auditory neurons. Biomaterials 28:513–523. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.09.008
Seymour AB, Andrews EM, Tsai SY, Markus TM, Bollnow MR, Brenneman MM et al (2005) Delayed treatment with monoclonal antibody IN-1 1 week after stroke results in recovery of function and corticorubral plasticity in adult rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:1366–1375. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600134
Tabakman R, Jiang H, Shahar I, Arien-Zakay H, Levine RA, Lazarovici P (2005) Neuroprotection by NGF in the PC12 in vitro OGD model: involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinases and gene expression. Ann NY Acad Sci 1053:84–96. doi:10.1196/annals.1344.008
Wang KC, Koprivica V, Kim JA, Sivasankaran R, Guo Y, Neve RL et al (2002) Oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein is a Nogo receptor ligand that inhibits neurite outgrowth. Nature 417:941–944. doi:10.1038/nature00867
Wieloch T, Nikolich K (2006) Mechanisms of neural plasticity following brain injury. Curr Opin Neurobiol 16:258–264. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2006.05.011
Wiessner C, Bareyre FM, Allegrini PR, Mir AK, Frentzel S, Zurini M et al (2003) Anti-Nogo-A antibody infusion 24 hours after experimental stroke improved behavioral outcome and corticospinal plasticity in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:154–165. doi:10.1097/00004647-200302000-00003
Wu Y, Shang Y, Sun S, Liu RG, Yang WQ (2007) Protective effect of erythropoietin against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced neurodegenaration in PC12 cells. Neurosci Bull 23:156–164. doi:10.1007/s12264-007-0023-0
Yin W, Cao G, Johnnides MJ, Signore AP, Luo Y, Hickey RW et al (2006) TAT-mediated delivery of Bcl-xL protein is neuroprotective against neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury via inhibition of caspases and AIF. Neurobiol Dis 21:358–371. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2005.07.015
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 30371763), and in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (Grant 2006C254). Nogo-A cDNA (KIAA0886) was generously provided by the Kazusa DNA Research Institute. We wish to thank Dr. Steven F. Dowdy (Ph.D., Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, University of California San Diego, School of Medicine, La Jolla, CA 92093-0686, USA) for providing the pTAT-HA vector and pTAT-HA-β-galactosidase plasmids; and Dr. Yan Lu for his critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Qiang Wang and Xingchun Gou contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Gou, X., Jin, W. et al. TAT-Mediated Protein Transduction of Nogo Extracellular Peptide 1-40 and its Biological Activity. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29, 97–108 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-008-9301-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-008-9301-2