Abstract
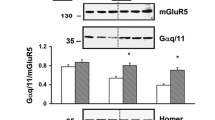
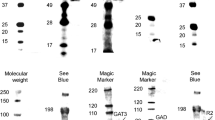
We have shown altered expression of gamma-aminobutyric acid A (GABAA) and gamma-aminobutyric acid B (GABAB) receptors in the brains of subjects with autism. In the current study, we sought to verify our western blotting data for GABBR1 via qRT-PCR and to expand our previous work to measure mRNA and protein levels of 3 GABAA subunits previously associated with autism (GABRα4; GABRα5; GABRβ1). Three GABA receptor subunits demonstrated mRNA and protein level concordance in superior frontal cortex (GABRα4, GABRα5, GABRβ1) and one demonstrated concordance in cerebellum (GABΒR1). These results provide further evidence of impairment of GABAergic signaling in autism.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: APA Press.
Ashley-Koch, A. E., Mei, H., Jaworski, J., Ma, D. Q., Ritchie, M. D., Menold, M. M., et al. (2006). An analysis paradigm for investigating multi-locus effects in complex disease: examination of three GABA receptor subunit genes on 15q11-q13 as risk factors for autistic disorder. Annals of Human Genetics, 70, 281–292.
Blatt, G. J., Fitzgerald, C. M., Guptill, J. T., Booker, A. B., Kemper, T. L., & Bauman, M. L. (2001). Density and distribution of hippocampal neurotransmitter receptors in autism: an autoradiographic study. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 31, 537–544.
Borgatti, R., Piccinelli, P., Passoni, D., Romeo, A., Viri, M., Musumeci, S. A., et al. (2003). Peripheral markers of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic system in Angelman’s syndrome. Journal of Child Neurology, 18, 21–25.
Brandon, N. J., Smart, T. G., & Moss, S. J. (2000). Regulation of GABAA receptors by protein phosphorylation. In D. Martin & R. Olsen (Eds.), GABA in the nervous system: The view at fifty years (pp. 191–206). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins.
Collins, A. L., Ma, D., Whitehead, P. L., Martin, E. R., Wright, H. H., Abramson, R. K., et al. (2006). Investigation of autism and GABA receptor subunit genes in multiple ethnic groups. Neurogenetics, 7, 167–174.
D’Hulst, C., De Geest, N., Reeve, S. P., Van Dam, D., De Deyn, P. P., Hassan, B. A., et al. (2006). Decreased expression of the GABAA receptor in fragile X syndrome. Brain Research, 22(1121), 238–245.
Dhossche, D., Applegate, H., Abraham, A., Maertens, P., Bland, L., Bencsath, A., et al. (2002). Elevated plasma gama-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels in autistic youngsters: Stimulus for GABA hypothesis of autism. Medical Science Monitor, 8, PR1–PR6.
El Idrissi, A., Ding, X. H., Scalia, J., Trenkner, E., Brown, W. T., & Dobkin, C. (2005). Decreased GABA(A) receptor expression in the seizure-prone fragile X mouse. Neuroscience Letters, 377, 141–146.
Fatemi, S. H., Halt, A., Stary, J., Kanodia, R., Schulz, S. C., & Realmuto, G. (2002). Glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 and 67 kDa proteins are reduced in parietal and cerebellar cortices of autistic subjects. Biological Psychiatry, 52, 805–810.
Fatemi, S. H., Stary, J. M., Earle, J. A., Araghi-Niknam, M., & Eagan, E. (2005). GABAergic dysfunction in schizophrenia and mood disorders as reflected by decreased levels of glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 and 67 kDa and Reelin proteins in cerebellum. Schizophrenia Research, 72, 109–122.
Fatemi, S. H., Reutiman, T. J., Folsom, T. D., Huang, H., Oishi, K., Mori, S., et al. (2008). Maternal infection leads to abnormal gene regulation and brain atrophy in mouse offspring: Implications for genesis of neurodevelopmental disorders. Schizophrenia Research, 99, 56–70.
Fatemi, S. H., Reutiman, T. J., Folsom, T. D., & Thuras, P. D. (2009a). GABA(A) receptor downregulation in brains of subjects with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39, 223–230.
Fatemi, S. H., Folsom, T. D., Reutiman, T. J., & Thuras, P. D. (2009b). Expression of GABA(B) receptors is altered in brains of subjects with autism. Cerebellum, 8, 64–69.
Gantois, I., Vandesompele, J., Speleman, F., Reyniers, E., D’Hooge, R., Severijnen, L. A., et al. (2006). Expression profiling suggests underexpression of the GABA(A) receptor subunit delta in the fragile X knockout mouse model. Neurobiology of Diseases, 21, 346–357.
Hauser, J., Rudolph, U., Keist, R., Möhler, H., Feldon, J., & Yee, B. K. (2005). Hippocampal alpha5 subunit-containing GABAA receptors modulate the expression of prepulse inhibition. Molecular Psychiatry, 10, 201–207.
Hogart, A., Nagarajan, R. P., Patzel, K. A., Yasui, D. H., & Lasalle, J. M. (2007). 15q11-13 GABAA receptor genes are normally biallelically expressed in brain yet are subject to epigenetic dysregulation in autism-spectrum disorders. Human Molecular Genetics, 16, 691–703.
Hogart, A., Leung, K. N., Wang, N. J., Wu, D. J., Driscoll, J., Vallero, R. O., et al. (2009). Chromosome 15q11-13 duplication syndrome brain reveals epigenetic alterations in gene expression not predicted from copy number. Journal of Medical Genetics, 46, 86–93.
Inada, T., Koga, M., Ishiguro, H., Horiuchi, Y., Syu, A., Yoshio, T., et al. (2008). Pathway-based association analysis of genome-wide screening data suggest that genes associated with the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor signaling pathway are involved in neuroleptic-induced, treatment-resistant tardive dyskinesia. Pharmacogenetics and Genomics, 18, 317–323.
Jones, K. A., Borowsky, B., Tamm, J. A., Craig, D. A., Durkin, M. M., Dai, M., et al. (1998). GABA(B) receptors function as a heteromeric assembly of the subunits GABA(B)R1 and GABA(B)R2. Nature, 396, 674–679.
Kakinuma, H., Ozaki, M., Sato, H., & Takahashi, H. (2008). Variation in GABA-A subunit gene copy number in an autistic patient with mosaic 4p duplication (p12p16). American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 147B, 973–975.
Kim, S. A., Kim, J. H., Park, M., Cho, I. H., & Yoo, H. J. (2006). Association of GABRB3 polymorphisms with autism spectrum disorders in Korean trios. Neuropsychobiology, 54, 160–165.
Le-Niculescu, H., Balaraman, Y., Patel, S., Tan, J., Sidhu, K., Jerome, R. E., et al. (2007). Towards understanding the schizophrenia code: an expanded convergent functional genomics approach. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 144B, 129–158.
Ma, D. Q., Whitehead, P. L., Menold, M. M., Martin, E. R., Ashley-Koch, A. E., Mei, H., et al. (2005). Identification of significant association and gene–gene interaction of GABA receptor subunit genes in autism. American Journal of Human Genetics, 77, 377–388.
Matsuura, T., Sutcliffe, J. S., Fang, P., Galjaard, R. J., Jiang, Y. H., Benton, C. S., et al. (1997). De novo truncating mutations in E6-AP ubiquitin-protein ligase gene (UBE3A) in Angelman syndrome. Nature Genetics, 15, 74–77.
McCauley, J. L., Olson, L. M., Delahanty, R., Amin, T., Nurmi, E. L., Organ, E. L., et al. (2004). A linkage disequilibrium map of the 1-Mb 15q12 GABA(A) receptor subunit cluster and association to autism. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 131, 51–59.
Olsen, R. W., & Sieghart, W. (2008). International Union of Pharmacology. LXX. Subtypes of gamma-aminobutyric acid (A) receptors: Classification on the basis of subunit composition, pharmacology, and function. Update. Pharmacological Reviews, 60, 243–260.
Princivalle, A. P., Duncan, J. S., Thom, M., & Bowery, N. G. (2003). GABA(B1a), GABA(B1b) AND GABA(B2) mRNA variants expression in hippocampus resected from patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience, 122, 975–984.
Qian, H., & Ripps, H. (2009). Focus on molecules: The GABA(C) receptor. Experimental Eye Research, 88, 1002–1003.
Samaco, R. C., Hogart, A., & LaSalle, J. M. (2005). Epigenetic overlap in autism-spectrum neurodevelopmental disorders: MECP2 deficiency causes reduced expression of UBE3A and GABRB3. Human Molecular Genetics, 14, 483–492.
Schroer, R. J., Phelan, M. C., Michaelis, R. C., Crawford, E. C., Skinner, S. A., Cuccaro, M., et al. (1998). Autism and maternally derived aberrations of chromosome 15q. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 76, 327–336.
Tochigi, M., Kato, C., Koishi, S., Kawakubo, Y., Yamamoto, K., Matsumoto, H., et al. (2007). No evidence for significant association between GABA receptor genes in chromosome. Journal of Human Genetics, 52, 985–989.
Tuchman, R., & Rapin, I. (2002). Epilepsy in autism. Lancet Neurology, 1, 352–358.
Yip, J., Soghomonian, J. J., & Blatt, G. J. (2007). Decreased GAD67 mRNA levels in cerebellar Purkinje cells in autism: Pathophysiological implications. Acta Neuropathologica, 113, 559–568.
Zai, G., Arnold, P., Burroughs, E., Barr, C. L., Richter, M. A., & Kennedy, J. L. (2005a). Evidence for the gamma-amino-butyric acid type B receptor 1 (GABBR1) gene as a susceptibility factor in obsessive-compulsive disorder. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 134, 25–29.
Zai, G., King, N., Wong, G. W., Barr, C. L., & Kennedy, J. L. (2005b). Possible association between the gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptor 1 (GABBR1) gene and schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 15, 347–352.
Acknowledgments
Human tissue was obtained from the NICHD Brain and Tissue Bank for Developmental Disorders; the Harvard Brain Tissue Resource Center, which is supported in part by PHS grant number R24 MH068855; the Brain Endowment Bank, which is funded in part by the National Parkinson Foundation, Inc., Miami, Florida; and the Autism Tissue Program and is gratefully acknowledged. Grant support by National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (#5R01HD052074-01A2) and 3R01HD052074-03S1 to SHF is gratefully acknowledged. Portions of this paper have been presented at the following meetings: Collegium Internationale Neuro-Psychopharmacologicum, Munich, 2008; American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, Scottsdale AZ, 2008; University of Tehran, School of Medicine, 2008; Autism One Conference, Chicago, 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fatemi, S.H., Reutiman, T.J., Folsom, T.D. et al. mRNA and Protein Levels for GABAAα4, α5, β1 and GABABR1 Receptors are Altered in Brains from Subjects with Autism. J Autism Dev Disord 40, 743–750 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-009-0924-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-009-0924-z