Abstract
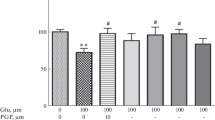
Glutamate excitotoxicity may culminate with neuronal and glial cell death. Glutamate induces apoptosis in vivo and in cell cultures. However, glutamate-induced apoptosis and the signaling pathways related to glutamate-induced cell death in acute hippocampal slices remain elusive. Hippocampal slices exposed to 1 or 10 mM glutamate for 1 h and evaluated after 6 h, showed reduced cell viability, without altering membrane permeability. This action of glutamate was accompanied by cytochrome c release, caspase-3 activation and DNA fragmentation. Glutamate at low concentration (10 μM) induced caspase-3 activation and DNA fragmentation, but it did not cause cytochrome c release and, it did not alter the viability of slices. Glutamate-induced impairment of hippocampal cell viability was completely blocked by MK-801 (non-competitive antagonist of NMDA receptors) and GAMS (antagonist of KA/AMPA glutamate receptors). Regarding intracellular signaling pathways, glutamate-induced cell death was not altered by a MEK1 inhibitor, PD98059. However, the p38MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, prevented glutamate-induced cell damage. In the present study we have shown that glutamate induces apoptosis in hippocampal slices and it causes an impairment of cell viability that was dependent of ionotropic and metabotropic receptors activation and, may involve the activation of p38MAPK pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ERK 1/2:
-
Extracellular-regulated MAP kinase
- Glu:
-
Glutamate
- GAMS:
-
γ-d-glutamylamino-methylsulfonate
- KA:
-
Kainic acid
- MAPKs:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- MK-801:
-
(+)-5-Methyl-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5,10-imine maleate
- NMDA:
-
N-methyl-d-aspartate
- M-CPG:
-
(RS)-α-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
References
Obrenovitch TP, Urenjak J (1997) Altered glutamatergic transmission in neurological disorders: from high extracellular glutamate to excessive synaptic efficacy. Prog Neurobiol 51:39–87
Maragakis NJ, Rothstein JD (2004) Glutamate transporters: animal models to neurological disease. Neurobiol Dis 15:461–473
Meldrum BS (2000) Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the brain: review of physiology and pathology. J Nutr 130:1007S–1015S
Mattson M (2000) Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1:120–129
Olney JW (1981) Kainic acid and other excitotoxins: a comparative analysis. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 27:375–384
Chen TA, Yang F, Cole GM, Chan SO (2001) Inhibition of caspase-3-like activity reduces glutamate induced cell death in the adult retina. Brain Res 1:1–12
Matute C, Domercq C, Sanchez-Gomez MV (2006) Glutamate-mediated glial injury: mechanisms and clinical importance. Glia 15:212–24
Ankarcrona M, Dypburkt JM, Bonfoco E, Zhyvotovsky B, Orrenius S, Lipton SA, Nicotera P (1995) Glutamate-induced neuronal death: a succession of necrosis or apoptosis depending on mitochondrial function. Neuron 15:961–973
Portera-Cailliau C, Price DL, Martin LJ (1997) Non-NMDA and NMDA receptor-mediated excitotoxic neuronal deaths in adult brain are morphologically distinct: further evidence for an apoptosis-necrosis continuum. J Comp Neurol 378:88–104
Cheung NS, Pascoe CJ, Giardina SF, John CA (1998) Micromolar l-glutamate induces extensive apoptosis in an apoptotic-necrotic continuum of insult-dependent, excitotoxic injury in cultured cortical neurones. Neuropharmacology 37:1419–1429
Sastry PS, Rao KS (2000) Apoptosis and the nervous system. J Neurochem 74:1–20
Olson M, Kornbluth S (2001) Mitochondria in apoptosis and human disease. Curr Mol Med 1:91–122
Hirashima Y, Kurimoto M, Nogami K, Endo S, Saitoh M, Ohtani O, Nagata T, Muraguchi A, Takaku A (1999) Correlation of glutamate-induced apoptosis with caspase activities in cultured rat cerebral neurons. Brain Res 849(1–2):109–118
Thomas CE, Mayle DA (2000) NMDA-sensitive neurons profoundly influence delayed staurosporine-induced apoptosis in rat mixed cortical neuronal cultures. Brain Res 889:163–173
Yu X, Sun L, Luo X, Xu Z, An L (2003) Investigation of the neuronal death mode induced by glutamate treatment in serum-, antioxidant-free primary cultures cortical neurons. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 145:263–268
Leal RB, Gonçalves CA, Rodnight R (1997) Calcium-dependent phosphorylation acidic protein (GFAP) in the rat hippocampus: a comparison of de kinase/phosphatase balance in immature and mature slices using tryptic phosphopeptide mapping. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 104:1–10
Vanhoutte P, Barnier JV, Guibert N, Pagès C, Besson M, Hipskind RA, Caboche J (1999) Glutamate induces phosphorylation of ElK-1 and CREB, along with c-fos activation, via an extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent pathway in brain slices. Mol Cell Biol 19:136–146
Banko JL, Hou L, Klann E (2004) NMDA receptor activation in PKA- and ERK-dependent MnK1 activation and increase in eIF4E phosphorylation in hippocampal area CA1. J Neurochem 91:462–470
Corvol JC, Valjent E, Toutant M, Enslet H, Irinopoulot T, Lev S, Hervé D, Girault JA (2005) Depolarization activates ERK and praline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (PYK2) independently in different cellular compartments in hippocampal slices. J Biol Chem 1:660–668
Collingridge GL, Bliss TW (1995) Memories of NMDA receptors and LTP. Trends Neurosci 18:54–56
Gong CX, Lidsky T, Wegiel J, Grundke-Igbal I, Igbal K (2001) Metabolically active rat brain slices as a model to study the regulation of protein phosphorylation in mammalian brain. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 6:134–140
Cordova FM, Rodrigues ALS, Giacomelli MBO, Oliveira CS, Posser T, Dunkley PR, Leal RB (2004) Lead stimulates ERK 1/2 and p38MAPK phosphorylation in the hippocampus of immature rats. Brain Res 998:65–72
Molz S, Oliveira IJL, Decker H, Souza DO, Tasca CI (2005) Neurotoxicity induced by glutamate in glucose-deprived rat hippocampal slices is prevented by GMP. Neurochem Res 30:83–89
Niswander JM, Dokas LA (2006) Phosphorylation of HSP27 and synthesis of 14-3-3 epsilon are parallel responses to hyperosmotic stress in the hippocampus. Brain Res 1116:19–30
Oliveira IJL, Molz S, Souza DO, Tasca CI (2002) Neuroprotective effect of GMP in hippocampal slices submitted to an in vitro model of ischemia. Cell Mol Neurobiol 22:335–344
Brongholi K, Sousa DG, Bainy AC, Dafré AL, Tasca CI (2006) Oxygen–glucose deprivation decreases glutathione levels and glutamate uptake in rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res 1083:211–218
Camacho A, Massieu L (2006) Role of glutamate transporters in the clearance and release of glutamate during ischemia and its relation to neuronal death. Arch Med Res 37:11–18
Chen Z, Gibson TB, Robinson F, Silvestro L, Pearson G, Xu B, Wright A, Vanderbilt C, Cobb M (2001) MAP kinases. Chem Rev 101:2449–2476
Chang L, Karin M (2001) Mammalian MAP kinase signaling cascades. Nature 410:37–40
Gallagher SM, Daly CA, Bear MF, Huber KM (2004) Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases activation is required for metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term depression in hippocampal area CA1. J Neurosci 24:4864–4859
Sweatt JD (2004) Mitogen-activated protein kinases in synaptic plasticity and memory. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14:311–317
Jiang Q, Zhengling G, Zhang G, Guozhang J (2000) Diphosphorylation and involvement of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2) in glutamate-induced apoptotic-like death in cultured rat cortical neurons. Brain Res 857:71–77
Grant ER, Errico MA, Emanuel SL, Benjamin D, McMillian MK, Wadsworth SA, Zivin RA, Zhong Z (2001) Protection against glutamate toxicity through inhibition of the p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in neuronally differentiated P19 cells. Biochem Pharmacol 62:283–296
Legos JJ, McLaughlin B, Skaper SD, Strijbos PJ, Parsons AA, Aizenman E, Herin GA, Barone FC, Erhardt JA (2002) The selective p38 inhibitor SB-239063 protects primary neurons from mild to moderate excitotoxic injury. Eur J Pharmacol 447:37–42
Park JE, Kim EJ, Kwon KJ, Jung YS, Moon CH, Lee SH, Baik EJ (2004) Neuroprotection by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate involves ROS alterations via p38 MAPK/ERK. Brain Res 1026:295–301
Munemasa Y, Ohtani-Kaneko R, Kitaoka Y, Kuribayashi K, Isenoumi K, Kogo J, Yamashita K, Kumai T, Kobayashi S, Hirata K, Ueno K (2005) Contribution of mitogen-activated protein kinases to NMDA-induced neurotoxicity in the rat retina. Brain Res 1044:227–240
Sugino T, Nozaki K, Tagaki Y, Hattori I, Hashimoto N, Moriguchi T, Nishida E (2000) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases after transient forebrain ischemia in gerbil and hippocampus. J Neurosci 20:4506–4514
Namura S, Iihara K, Takami S, Nagata I, Kikuchi H, Matsushita K, Moskowitz MA, Bonventre JV, Alessandrini A (2001) Intravenous administration of MEK inhibitor UO126 affords brain protection against forebrain ischemia and focal cerebral ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11569–11574
Gähwiller BH, Capogna M, Debanne D, Mckinney RA, Thompson SM (1997) Organotypic slices cultures: a technique has come of age. Trends Neurosci 20:471–477
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Leist M, Single B, Naumann H, Fava E, Simon B, Kühnle S, Nicotera P (1999) Nitric oxide inhibits execution of apoptosis at two distinct ATP-dependent and downstream of mitochondrial cytochrome c release. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 258:215–221
Leal R, Cordova FM, Lynn H, Dunkley PR (2002) Lead-stimulate p38MAPK-dependent Hsp27 phosphorylation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 178:44–51
Yang G-M, Paul SM (1997) Cultured cerebellar granule neurons as a model of neuronal apoptosis. In: Poirier J (ed) Neuromethods, vol 29. Humana Press Inc, Totowa, pp 47–66
Lowry OH, Rosembrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Peterson GL (1977) A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem 83:346–356
Ientile R, Macaione V, Teletta M, Torre V, Macaione S (2001) Apoptosis and necrosis occurring in excitotoxic cell death in isolated chick embryo retina. J Neurochem 79:71–78
Zhang Y, Bhavnani BR (2005) Glutamate-induced apoptosis in primary cortical neurons is inhibited by equine estrogen via down-regulation of caspase-3 and prevention of mitochondrial cytochrome c release. BMC Neurosci 6:1–23
Tenneti L, Lipton SA (2000) Involvement of activated caspase-3-like proteases in N-methyl-d-aspartate-induced apoptosis in cerebrocortical neurons. J Neurochem 74:134–142
Brewer GJ, Lim A, Capps NG, Torricelli JR (2005) Age-related calcium changes, oxyradical damage, caspase activation and nuclear condensation in hippocampal neurons in response to glutamate and beta-amyloid. Exp Gerontol 40:426–437
Ventura R, Harris KM (1999) Three-dimensional relationships between hippocampal synapses and astrocytes. J Neurosci 19:6897–6906
Garrido R, Mattson M, Hennig B, Toborek M (2000) Nicotine protects against arachidonic-acid-induced caspase activation, cytochrome c release and apoptosis of cultured spinal cord neurons. J Neurochem 76:1395–1403
Hirai K, Sugawara T, Chan PK, Basus VJ, James TL, Litt L (2002) Cytochrome c associated apoptosis during ATP recovery after hypoxia in neonatal rat cerebrocortical slices. J Neurochem 83:309–319
Cho S, Liu D, Fairman D, Li P, Jenkins L, McGonigle P, Wood A (2004) Spatiotemporal evidence of apoptosis-mediated ischemic injury in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. Neurochem Int 45:117–127
Bonfoco E, Krainc D, Ankarcrona M, Nicotera P, Lipton SP (1995) Apoptosis and necrosis: two distinct events induced, respectively, by mild and intense insult with N-methyl-d-aspartate or nitric oxide in cortical cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7162–7166
Du Y, Bales KR, Dodel RC, Hamilton-Byrd E, Horn JW, Czilli DL, Simmons LK, Ni B, Paul SM (1997) Activation of a caspase 3-related cysteine protease is required for glutamate-mediated apoptosis of cultured cerebellar granule neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(21):11657–11662
Baskys A, Fang L, Bayazitov I (2005) Activation of neuroprotective pathways by metabotropic group I glutamate receptors: a potential target for drug discovery? Ann NY Acad Sci 1053:55–73
Rivera-Cervantes MC, Torres JS, Faria-Velasco A, Armendariz-Borunda J, Beas-Zarate C (2004) NMDA and AMPA expression and cortical neuronal death are associated with p38 in glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in vivo. J Neurosci Res 1:678–687
Torres JES, Chaparro-Huerta V, Rivera-Cervantes MC, Montez-González R, Flores Soto ME, Beas-Zárate C (2006) Neuronal cell death due to glutamate excitotoxicity is mediated by P38 activation in the rat cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett 403:133–238
Chen J, Errico SL, Freed WJ (2005) Reactive oxygen species and p38 phosphorylation regulate the protective effect of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol in the apoptotic response to NMDA. Neurosci Lett 389:99–103
Kawasaki H, Morooka T, Shimohama S, Kimura J, Hirama T, Gotoh Y, Nishida E (1997) Activation and involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in glutamate-induced apoptosis in rat cerebellar granule cells. J Biol Chem 272:18518–18521
Alessandrini A, Namura S, Moskowitz MA, Bonventre JV (1999) MEK1 protein kinase inhibition protects against damage resulting from focal cerebral ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:12866–12869
Jiang Q, Gu Z, Zhang G, Jing J (2000) N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptor activation results in regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases by protein kinases and phosphatases in glutamate-induced neuronal apoptotic-like death. Brain Res 887:285–292
Giardina SF, Beart PM (2002) Kainate receptor-mediated apoptosis in primary culture of cerebellar granule cells is attenuated by mitogen-activated protein and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Br J Pharmacol 135:1733–1742
Seo SR, Chong SA, Lee SI, Sung J, Ahn YS, Chung KC, Seo JT (2001) Zn2+-induced ERK activation mediated by reactive oxygen species causes cell death in differentiated PC12 cells. J Neurochem 78:600–610
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molz, S., Decker, H., Dal-Cim, T. et al. Glutamate-induced Toxicity in Hippocampal Slices Involves Apoptotic Features and p38MAPK Signaling. Neurochem Res 33, 27–36 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9402-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9402-1