Abstract
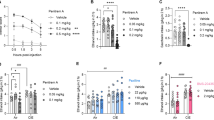
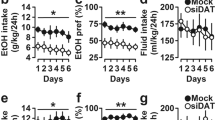
P2X receptors (P2XRs) are a family of cation-permeable ligand-gated ion channels activated by synaptically released extracellular adenosine 5′-triphosphate. The P2X4 subtype is abundantly expressed in the central nervous system and is sensitive to low intoxicating ethanol concentrations. Genetic meta-analyses identified the p2rx4 gene as a candidate gene for innate alcohol intake and/or preference. The current study used mice lacking the p2rx4 gene (knockout, KO) and wildtype (WT) C57BL/6 controls to test the hypothesis that P2X4Rs contribute to ethanol intake. The early acquisition and early maintenance phases of ethanol intake were measured with three different drinking procedures. Further, we tested the effects of ivermectin (IVM), a drug previously shown to reduce ethanol’s effects on P2X4Rs and to reduce ethanol intake and preference, for its ability to differentially alter stable ethanol intake in KO and WT mice. Depending on the procedure and the concentration of the ethanol solution, ethanol intake was transiently increased in P2X4R KO versus WT mice during the acquisition of 24-h and limited access ethanol intake. IVM significantly reduced ethanol intake in P2X4R KO and WT mice, but the degree of reduction was 50 % less in the P2X4R KO mice. Western blot analysis identified significant changes in γ-aminobutyric acidA receptor α1 subunit expression in brain regions associated with the regulation of ethanol behaviors in P2X4R KO mice. These findings add to evidence that P2X4Rs contribute to ethanol intake and indicate that there is a complex interaction between P2X4Rs, ethanol, and other neurotransmitter receptor systems.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deitrich R, Dunwiddie T, Harris RA, Erwin VG (1989) Mechanism of action of ethanol: initial central nervous system actions. Pharmacol Rev 41:489–537
Weight FF, Aguayo LG, White G, Lovinger DM, Peoples RW (1992) GABA- and glutamate-gated ion channels as molecular sites of alcohol and anesthetic action. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 47:335–347
Dildy-Mayfield JE, Mihic SJ, Liu Y, Deitrich RA, Harris RA (1996) Actions of long chain alcohols on GABA A and glutamate receptors: relation to in vivo effects. Br J Pharmacol 118:378–384
Mihic SJ, Ye Q, Wick MJ, Koltchine VV, Krasowski MD et al (1997) Sites of alcohol and volatile anaesthetic action on GABA A and glycine receptors. Nature 389:385–389
Harris RA (1999) Ethanol actions on multiple ion channels: which are important? Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23:1563–1570
Cardoso RA, Brozowski SJ, Chavez-Noriega LE, Harpold M, Valenzuela CF, Harris RA (1999) Effects of ethanol on recombinant human neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289:774–780
Woodward JJ (2000) Ethanol and NMDA receptor signaling. Crit Rev Neurobiol 14:69–89
Davies DL, Alkana RL (2001) Direct evidence for a cause effect link between ethanol potentiation of GABA A receptor function and intoxication from hyperbaric studies in C57, LS and SS mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:1098–1106
Betz H (1990) Ligand-gated ion channels in the brain: the amino acid receptor superfamily. Neuron 5:383–392
Ortells MO, Lunt GG (1995) Evolutionary history of the ligand-gated ion-channel superfamily of receptors. Trends Neurosci 18:121–127
Monaghan DT, Bridges RJ, Cotman CW (1989) The excitatory amino acid receptors: their classes, pharmacology, and distinct properties in the function of the central nervous system. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 29:365–402
Sommer B, Seeburg P (1992) Glutamate receptor channels: novel properties and new clones. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13:291–296
Burnstock G (2008) Purinergic signalling and disorders of the central nervous system. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 7:575–590
Gum RJ, Wakefield B, Jarvis MF (2012) P2X receptor antagonists for pain management: examination of binding and physicochemical properties. Purinergic Signal 8:41–56
Asatryan L, Nam HW, Lee MR, Thakkar MM, Dar MS et al (2011) Implication of the purinergic system in alcohol use disorders. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 35:584–594
Litten RZ, Egli M, Heilig M, Cui C, Fertig JB et al (2012) Medications development to treat alcohol dependence: a vision for the next decade. Addict Biol 17:513–527
Bortolato M, Yardley M, Khoja S, Godar SC, Asatryan L et al (2013) Pharmacological insights into the role of P2X4 receptors in behavioral regulation: lessons from ivermectin. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 16:1059–1070
Chizh BA, Illes P (2001) P2X receptors and nociception. Pharmacol Rev 53:553–568
Khakh BS (2001) Molecular physiology of P2X receptors and ATP signalling at synapses. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:165–174
North RA (2002) Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol Rev 82:1013–1067
Jo YH, Schlichter R (1999) Synaptic corelease of ATP and GABA in cultured spinal neurons. Nat Neurosci 2:241–245
Deuchars SA, Atkinson L, Brooke RE, Musa H, Milligan CJ et al (2001) Neuronal P2X7 receptors are targeted to presynaptic terminals in the central and peripheral nervous systems. J Neurosci 21:7143–7152
Baxter AW, Choi SJ, Sim JA, North RA (2011) Role of P2X4 receptors in synaptic strengthening in mouse CA1 hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 34:213–220
Buell G, Lewis C, Collo G, North RA, Suprenant A (1996) An antagonist insensitive P2X receptor expressed in epithelia and brain. EMBO J 15:55–62
Soto F, Garcia-Guzman M, Gomez-Hernandez JM, Hollmann M, Karschin C, Stuhmer W (1996) P2X4: an ATP-activated ionotropic receptor cloned from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:3684–3688
Li C, Peoples RW, Weight FF (1994) Alcohol action on a neuronal membrane receptor: evidence for a direct interaction with the receptor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8200–8204
Li C, Peoples RW, Weight FF (1998) Ethanol-induced inhibition of a neuronal P2X purinoceptor by an allosteric mechanism. Br J Pharmacol 123:1–3
Li C, Peoples RW, Weight FF (1993) Ethanol inhibits a neuronal ATP-gated ion channel. Mol Pharmacol 44:871–875
Weight FF, Li C, Peoples RW (1999) Alcohol action on membrane ion channels gated by extracellular ATP (P2X receptors). Neurochem Int 35:143–152
Xiao C, Zhou C, Li K, Davies DL, Ye JH (2008) Purinergic type 2 receptors at GABAergic synapses on ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons are targets for ethanol action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 327:196–205
Xiong K, Li C, Weight FF (2000) Inhibition by ethanol of rat P2X 4 receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Br J Pharmacol 130:1394–1398
Xiong KM, Li C, Weight FF (2001) Differential modulation by short chain and long chain n-alcohols of rat P2X4 receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:7A
Davies DL, Machu TK, Guo Y, Alkana RL (2002) Ethanol sensitivity in ATP-gated P2X receptors is subunit dependent. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:773–778
Davies DL, Kochegarov AA, Kuo ST, Kulkarni AA, Woodward JJ et al (2005) Ethanol differentially affects ATP-gated P2X(3) and P2X(4) receptor subtypes expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neuropharmacology 49:243–253
Asatryan L, Popova M, Woodward JJ, King BF, Alkana RL, Davies DL (2008) Roles of ectodomain and transmembrane regions in ethanol and agonist action in purinergic P2X2 and P2X3 receptors. Neuropharmacology 55:835–843
Asatryan L, Popova M, Perkins DI, Trudell JR, Alkana RL, Davies DL (2010) Ivermectin antagonizes ethanol inhibition in P2X4 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 334:720–728
Pankratov Y, Lalo U, Krishtal OA, Verkhratsky A (2009) P2X receptors and synaptic plasticity. Neuroscience 158:137–148
Sim JA, Chaumont S, Jo J, Ulmann L, Young MT et al (2006) Altered hippocampal synaptic potentiation in P2X4 knock-out mice. J Neurosci 26:9006–9009
Gonzales RA, Job MO, Doyon WM (2004) The role of mesolimbic dopamine in the development and maintenance of ethanol reinforcement. Pharmacol Ther 103:121–146
McCool BA (2011) Ethanol modulation of synaptic plasticity. Neuropharmacology 61:1097–1108
Tsuda M, Koizumi S, Kita A, Shigemoto Y, Ueno S, Inoue K (2000) Mechanical allodynia caused by intraplantar injection of P2X receptor agonist in rats: involvement of heteromeric P2X2/3 receptor signaling in capsaicin-insensitive primary afferent neurons. J Neurosci 20:RC90
Ulmann L, Hatcher JP, Hughes JP, Chaumont S, Green PJ et al (2008) Up-regulation of P2X4 receptors in spinal microglia after peripheral nerve injury mediates BDNF release and neuropathic pain. J Neurosci 28:11263–11268
Zemkova H, Kucka M, Li S, Gonzalez-Iglesias AE, Tomic M, Stojilkovic SS (2010) Characterization of purinergic P2X4 receptor channels expressed in anterior pituitary cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metabol 298:E644–E651
Lorca RA, Rozas C, Loyola S, Moreira-Ramos S, Zeise ML et al (2011) Zinc enhances long-term potentiation through P2X receptor modulation in the hippocampal CA1 region. Eur J Neurosci 33:1175–1185
Jo YH, Donier E, Martinez A, Garret M, Toulme E, Boue-Grabot E (2011) Cross-talk between P2X4 and gamma-aminobutyric acid, type A receptors determines synaptic efficacy at a central synapse. J Biol Chem 286:19993–20004
Kimpel MW, Strother WN, McClintick JN, Carr LG, Liang T et al (2007) Functional gene expression differences between inbred alcohol-preferring and -non-preferring rats in five brain regions. Alcohol 41:95–132
Tabakoff B, Saba L, Printz M, Flodman P, Hodgkinson C et al (2009) Genetical genomic determinants of alcohol consumption in rats and humans. BMC Biol 7:70
Popova M, Trudell J, Li K, Alkana R, Davies D, Asatryan L (2013) Tryptophan 46 is a site for ethanol and ivermectin action in P2X4 receptors. Purinergic Signal 9:621–632
Asatryan L, Yardley MM, Khoja S, Trudell JR, Hyunh N et al (2014) Avermectins differentially affect ethanol intake and receptor function: Implications for developing new therapeutics for alcohol use disorders. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. doi:10.1017/S1461145713001703
Yardley M, Wyatt L, Khoja S, Asatryan L, Ramaker MJ et al (2012) Ivermectin reduces alcohol intake and preference in mice. Neuropharmacology 63:190–201
Kralic JE, Sidler C, Parpan F, Homanics GE, Morrow AL, Fritschy JM (2006) Compensatory alteration of inhibitory synaptic circuits in cerebellum and thalamus of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor alpha1 subunit knockout mice. J Comp Neurol 495:408–421
Crabbe JC, Phillips TJ, Harris RA, Arends MA, Koob GF (2006) Alcohol-related genes: contributions from studies with genetically engineered mice. Addict Biol 11:195–269
Blednov YA, Walker D, Alva H, Creech K, Findlay G, Harris RA (2003) GABAA receptor alpha 1 and beta 2 subunit null mutant mice: behavioral responses to ethanol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:854–863
Kralic JE, Wheeler M, Renzi K, Ferguson C, O’Buckley TK et al (2003) Deletion of GABAA receptor alpha 1 subunit-containing receptors alters responses to ethanol and other anesthetics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:600–607
June HL Sr, Foster KL, Eiler WJ II, Goergen J, Cook JB et al (2007) Dopamine and benzodiazepine-dependent mechanisms regulate the EtOH-enhanced locomotor stimulation in the GABAA alpha1 subunit null mutant mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:137–152
Koob GF, Volkow ND (2010) Neurocircuitry of addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:217–238
Saeed Dar M (2006) Co-modulation of acute ethanol-induced motor impairment by mouse cerebellar adenosinergic A1 and GABA(A) receptor systems. Brain Res Bull 71:287–295
McClearn GE (1959) The genetics of mouse behavior in novel situations. J Comp Physiol Psychol 52:62–67
Rodgers DA (1966) Research activities related to treatment of alcoholism. Compr Psychiatry 7:57–67
Belknap JK, Crabbe JC, Young ER (1993) Voluntary consumption of ethanol in 15 inbred mouse strains. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 112:503–510
Middaugh LD, Kelley BM, Bandy AL, McGroarty KK (1999) Ethanol consumption by C57BL/6 mice: influence of gender and procedural variables. Alcohol 17:175–183
Yoneyama N, Crabbe JC, Ford MM, Murillo A, Finn DA (2008) Voluntary ethanol consumption in 22 inbred mouse strains. Alcohol 42:149–160
Blednov YA, Ozburn AR, Walker D, Ahmed S, Belknap JK, Harris RA (2010) Hybrid mice as genetic models of high alcohol consumption. Behav Genet 40:93–110
Priel A, Silberberg SD (2004) Mechanism of ivermectin facilitation of human P2X4 receptor channels. J Gen Physiol 123:281–293
Rhodes JS, Best K, Belknap JK, Finn DA, Crabbe JC (2005) Evaluation of a simple model of ethanol drinking to intoxication in C57BL/6J mice. Physiol Behav 84:53–63
Rhodes JS, Ford MM, Yu CH, Brown LL, Finn DA et al (2007) Mouse inbred strain differences in ethanol drinking to intoxication. Genes Brain Behav 6:1–18
Neasta J, Hamida S, Yowell Q, Carnicella S, Ron D (2010) Role for mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 signaling in neuroadaptations underlying alcohol-related disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:20093–20098
Hwa LS, Chu A, Levinson SA, Kayyali TM, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2011) Persistent escalation of alcohol drinking in C57BL/6J mice with intermittent access to 20 % ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 35:1938–1947
Alkana RL, Finn DA, Bejanian M, Crabbe JC (1988) Genetically determined differences in ethanol sensitivity influenced by body temperature during intoxication. Life Sci 43:1973–1982
Finn DA, Snelling C, Fretwell AM, Tanchuck MA (2007) Increased drinking during withdrawal from intermittent ethanol exposure is blocked by the CRF receptor antagonist D-Phe-CRF(12–41). Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:939–949
Parker CC, Ponicsan H, Spencer RL, Holmes A, Johnson TE (2008) Restraint stress and exogenous corticosterone differentially alter sensitivity to the sedative-hypnotic effects of ethanol in inbred long-sleep and inbred short-sleep mice. Alcohol 42:477–485
Radcliffe RA, Floyd KL, Drahnak JA, Deitrich RA (2005) Genetic dissociation between ethanol sensitivity and rapid tolerance in mouse and rat strains selectively bred for differential ethanol sensitivity. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:1580–1589
Popova M, Asatryan L, Ostrovskaya O, Wyatt RL, Li K et al (2010) A point mutation in the ectodomain-transmembrane 2 interface eliminates the inhibitory effects of ethanol in P2X4 receptors. J Neurochem 112:307–317
Ostrovskaya O, Asatryan L, Wyatt L, Popova M, Li K et al (2011) Ethanol is a fast channel inhibitor of purinergic P2X4 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 337:171–179
Xiong K, Hu XQ, Stewart RR, Weight FF, Li C (2005) The mechanism by which ethanol inhibits rat P2X4 receptors is altered by mutation of histidine 241. Br J Pharmacol 145:576–586
Yi CL, Liu YW, Xiong KM, Stewart RR, Peoples RW et al (2009) Conserved extracellular cysteines differentially regulate the inhibitory effect of ethanol in rat P2X4 receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 381:102–106
Blednov YA, Mayfield RD, Belknap J, Harris RA (2012) Behavioral actions of alcohol: phenotypic relations from multivariate analysis of mutant mouse data. Genes Brain Behav 11:424–435
Khakh BS, Bao XR, Labarca C, Lester HA (1999) Neuronal P2X transmitter-gated cation channels change their ion selectivity in seconds. Nat Neurosci 2:322–330
Toulme E, Soto F, Garret M, Boue-Grabot E (2006) Functional properties of internalization-deficient P2X4 receptors reveal a novel mechanism of ligand-gated channel facilitation by ivermectin. Mol Pharmacol 69:576–587
Krause RM, Buisson B, Bertrand S, Corringer PJ, Galzi JL et al (1998) Ivermectin: a positive allosteric effector of the alpha 7 meuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Mol Pharmacol 53:283–294
Dawson GR, Wafford KA, Smith A, Marshall GR, Bayley PJ et al (2000) Anticonvulsant and adverse effects of avermectin analogs in mice are mediated through the gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:1051–1060
Shan Q, Haddrill JL, Lynch JW (2001) Ivermectin, an unconventional agonist of the glycine receptor chloride channel. J Biol Chem 276:12556–12564
Spinosa HS, Stilck SRAN, Bernardi MM (2002) Possible anxiolytic effects of ivermectin in rats. Vet Res Commun 26:309–321
Sattelle DB, Buckingham SD, Akamatsu M, Matsuda K, Pienaar I et al (2009) Comparative pharmacology and computational modelling yield insights into allosteric modulation of human alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 78:836–843
Wyatt LR, Godar SC, Khoja S, Jakowec MW, Alkana RL et al (2013) Sociocommunicative and sensorimotor impairments in male P2X4-deficient mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:1993–2002
Acknowledgments
This work was conducted as part of fulfillment of the requirements for the Ph.D. degree in Molecular Pharmacology and Toxicology, University of Southern California (L.R.W.). We thank Miriam Fine for technical assistance and USC Undergraduates (Ayee Azah, Christina Minh, Vanessa Fimreite, and Megan Won) and STAR students for laboratorial assistance. We also want to thank Chris Snelling at OHSU for conducting the analysis of BECRRs. This work was supported (in part or in full) by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), NIAAA, Grants F31AA018926 (L.R.W), KO-1-AA017243 (L.A.), AA016981 (D.A.F), AA03972 (R.L.A.), AA13992 and AA022448 (D.L.D); the American Foundation for Pharmaceutical Education (M.Y.); the Dept of Veterans Affairs (D.A.F); USC Undergraduate Provosts Fellowship (D.L.D. and V.F.), USC Summer Undergraduate Research Fund (D.L.D. and C.M.); and the USC School of Pharmacy (R.L.A and D.L.D).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wyatt, L.R., Finn, D.A., Khoja, S. et al. Contribution of P2X4 Receptors to Ethanol Intake in Male C57BL/6 Mice. Neurochem Res 39, 1127–1139 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1271-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1271-9