Abstract
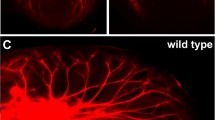
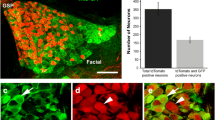
Geniculate ganglion axons arrive in the lingual mesenchyme on embryonic day 13 (E13), 3–4 days before penetrating fungiform papilla epithelium (E17). This latency may result from chemorepulsion by epithelial Sema3A (Dillon et al. (2004) Journal of Comparative Neurology 470, 13–24), or Sema3F, which we report is also expressed in this epithelium. Sema3A and Sema3F repelled or suppressed geniculate neurite outgrowth, respectively, and these effects were stage and neurotrophic factor dependent. BDNF-stimulated outgrowth is repelled by Sema3A until E17, but insensitive to Sema3F from E16. NT-4-stimulated neurite outgrowth is sensitive to Sema3A and Sema3F through E18, but NT-4 has not been detected in E15–18 tongue. E15–18 tongue explants did not exhibit net chemorepulsion of geniculate neurites, but the ability of tongue explants to support geniculate neurite outgrowth fluctuates: E12–13 (Rochlin et al. (2000), Journal of Comparative Neurology, 422, 579–593) and E17–18 explants promote and may attract geniculate neurites, but stages corresponding to intralingual arborization do not. The E18 trophic and tropic effects were evident even in the presence of BDNF or NT-4, suggesting that some other factor is responsible. Intrinsic neurite outgrowth capability (without exogenous neurotrophic factors) fluctuated similarly: ganglia deteriorated at E15, but exhibited moderate outgrowth at E18.
The chemorepulsion studies are consistent with a role for Sema3A, not Sema3F, in restricting geniculate axons from the epithelium until E17, when axons penetrate the epithelium. The transient inability of tongue explants to promote geniculate neurite outgrowth may signify an alternative mechanism for restricting geniculate axons from the epithelium: limiting trophic factor access.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ARIMURA, N., INAGAKI, N., CHIHARA, K., MENAGER, C., NAKAMURA, N., AMANO, M., IWAMATSU, A., GOSHIMA, Y. & KAIBUCHI, K. (2000) Phosphorylation of collapsin response mediator protein-2 by Rho-kinase. Evidence for two separate signaling pathways for growth cone collapse. Journal of Biological Chemistry 275, 23973–23980.
ATWAL, J. K., SINGH, K. K., TESSIER-LAVIGNE, M., MILLER, F. D. & KAPLAN. D. R. (2003) Semaphorin 3F antagonizes neurotrophin-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and mitogenactivated protein kinase kinase signaling: A mechanism for growth cone collapse. Journal of Neuroscience 23, 7602–7609.
BATES, D., TAYLOR, G. I., MINICHIELLO, J., FARLIE, P., CICHOWITZ, A., WATSON, N., KLAGSBRUN, M., MAMLUK, R. & NEWGREEN, D. F. (2003) Neurovascular congruence results from a shared patterning mechanism that utilizes Semaphorin3A and Neuropilin-1. Developmental Biology 255, 77–98.
BOESHORE, K. L., LUCKEY, C. N., ZIGMOND, R. E. & LARGE, T. H. (1999) TrkB isoforms with distinct neurotrophin specificities are expressed in predominantly nonoverlapping populations of avian dorsal root ganglion neurons. Journal of Neuroscience 19, 4739–4747.
CHEN, H., BAGRI, A., ZUPICICH, J. A., ZOU, Y., STOECKLI, E., PLEASURE, S. J., LOWENSTEIN, D. H., SKARNES, W. C., CHEDOTAL, A., SKARNES, W. C. & TESSIER-LAVIGNE, M. (2000) Neuropilin-2 regulates the development of selective cranial and sensory nerves and hippocampal mossy fiber projections. Neuron 25, 43–56.
CHEN, H., CHEDOTAL, A., HE, Z., GOODMAN, C. S. & TESSIER-LAVIGNE, M. (1997) Neuropilin-2, a novel member of the neuropilin family, is a high affinity receptor for the semaphorins Sema E and Sema IV but not Sema III. Neuron 19, 547–559.
CHILTON, J. K. & GUTHRIE, S. (2003) Cranial Expression of Class 3 Secreted Semaphorins and Their Neuropilin Receptors. Developmental Dynamics 228, 726– 733.
DAVIES, A. M. (1998) Developmental changes in the neurotrophic factor survival requirements of peripheral nervous system neurons. Progress in Brain Research 117, 47–56.
DILLON, T. E., SALDANHA, J., GIGER, R., VERHAAGEN, J. & ROCHLIN, M. W. (2004) Sema3A regulates the timing of target contact by cranial sensory axons. Journal of Comparative Neurology 470, 13–24.
DONTCHEV, V. D. & LETOURNEAU, P. C. (2002) Nerve growth factor and semaphorin 3A signaling pathways interact in regulating sensory neuronal growth cone motility. Journal of Neuroscience 22, 6659–6669.
DONTCHEV, V. D. & LETOURNEAU, P. C. (2003) Growth cones integrate signaling from multiple guidance cues. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry 51, 435– 444.
EICKHOLT, B. J., WALSH, F. S. & DOHERTY, P. (2002) An inactive pool of GSK-3 at the leading edge of growth cones is implicated in Semaphorin 3A signaling. Journal of Cell Biology 157, 211–217.
ERNFORS, P. (2001) Local and target-derived actions of neurotrophins during peripheral nervous system development. Cellular & Molecular Life Sciences 58, 1036– 1044.
ERNFORS, P., LEE, K. F. & JAENISCH, R. (1994) Mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor develop with sensory deficits. Nature 368, 147–150.
FARBMAN, A. I., BRANN, J. H., ROZENBLAT, A., ROCHLIN, M. W., WEILER, E. & BHATTACHARYYA, M. (2004) Developmental Expression of Neurotrophin Receptor Genes in Rat Geniculate Ganglion Neurons. Journal of Neurocytology 33, 331–343.
FARBMAN, A. I. & MBIENE, J. P. (1991) Early development and innervation of taste budbearing papillae on the rat tongue. Journal of Comparative Neurology 304, 172–186.
FARINAS, I. (1999) Neurotrophin actions during the development of the peripheral nervous system. Microscopy Research & Technique 45, 233–242.
FU, S. Y., SHARMA, K., LUO, Y. L., RAPER, J. A. & FRANK, E. (2000) Sema3A regulates developing sensory projections in the chicken spinal cord. Journal of Neurobiology 45, 227–236.
GIGER, R. J., CLOUTIER, J. F., SAHAY, A., PRINJHA, R. K., LEVENGOOD, D. V., MOORE, S. E., PICKERING, S., SIMMONS, D., RASTAN, S., WALSH, F. S., KOLODKIN, A. L., GINTY, D. D. & GEPPERT, M. (2000) Neuropilin-2 is required in vivo for selective axon guidance responses to secreted semaphorins. Neuron 25, 29–41.
GIGER, R. J., URQUHART, E. R., GILLESPIE, S. K., LEVENGOOD, D. V., GINTY, D. D. & KOLODKIN, A. L. (1998) Neuropilin-2 is a receptor for semaphorin IV: Insight into the structural basis of receptor function and specificity (see comments). Neuron 21, 1079–1092.
GREGG, J. M. & DIXON, A. D. (1973) Somatotopic organization of the trigeminal ganglion in the rat. Archives of Oral Biology 18, 487–498.
HOGG, I. D. & BRYANT, J. W. (1969) The development of sensory innervation in the mouth and pharynx of the albino Norway rat (Mus norvegicus albinus). Journal of Comparative Neurology 136, 33–56.
KENNEDY, T. E., SERAFINI, T., DE, L. A., TORRE, J. & TESSIER-LAVIGNE, M. (1994) Netrins are diffusible chemotropic factors for commissural axons in the embryonic spinal cord. Cell 78, 425–435.
KOLODKIN, A. L., LEVENGOOD, D. V., ROWE, E. G., TAI, Y. T., GIGER, R. J. & GINTY, D. D. (1997) Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor. Cell 90, 753–762.
KRIMM, R. F., MILLER, K. K., KITZMAN, P. H., DAVIS, B. M. & ALBERS, K. M. (2001) Epithelial overexpression of BDNF or NT4 disrupts targeting of taste neurons that innervate the anterior tongue. Developmental Biology 232, 508–521.
KURUVILLA, R., ZWEIFEL, L. S., GLEBOVA, N. O., LONZE, B. E., VALDEZ, G., YE, H. & GINTY, D. D. (2004) A neurotrophin signaling cascade coordinates sympathetic neuron development through differential control of TrkA trafficking and retrograde signaling. Cell 118, 243–255.
LIEBL, D. J., MBIENE, J. P. & PARADA, L. F. (1999) NT4/5 mutant mice have deficiency in gustatory papillae and taste bud formation. Developmental Biology 213, 378–389.
LIU, X., ERNFORS, P., WU, H. & JAENISCH, R. (1995) Sensory but not motor neuron deficits in mice lacking NT4 and BDNF. Nature 375, 238–241.
MBIENE, J. P. & MISTRETTA, C. M. (1997) Initial innervation of embryonic rat tongue and developing taste papillae: Nerves follow distinctive and spatially restricted pathways. Acta Anatomica 160, 139–158.
MESSERSMITH, E. K., LEONARDO, E. D., SHATZ, C. J., TESSIER-LAVIGNE, M., GOODMAN, C. S. & KOLODKIN, A. L. (1995) Semaphorin III can function as a selective chemorepellent to pattern sensory projections in the spinal cord. Neuron 14, 949–959.
MING, G. L., SONG, H. J., BERNINGER, B., INAGAKI, N., TESSIER-LAVIGNE, M. & POO, M. M. (1999) Phospholipase C-γ and Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Mediate Cytoplasmic Signaling in Nerve Growth Cone Guidance. Neuron 23, 139–148.
MINICHIELLO, L., CASAGR&A, F., TATCHE, R. S., STUCKY, C. L., POSTIGO, A., LEWIN, G. R., DAVIES, A. M. & KLEIN, R. (1998) Point mutation in trkB causes loss of NT4-dependent neurons without major effects on diverse BDNF responses. Neuron 21, 335–345.
MUKOUYAMA, Y. S., SHIN, D., BRITSCH, S., TANIGUCHI, M. & ERSON, D. J. (2002) Sensory nerves determine the pattern of arterial differentiation and blood vessel branching in the skin. Cell 109, 693–705.
NEUFELD, G., COHEN, T., SHRAGA, N., LANGE, T., KESSLER, O. & HERZOG, Y. (2002) The neuropilins: Multifunctional semaphorin and VEGF receptors that modulate axon guidance and angiogenesis. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine 12, 13–19.
NOSRAT, C. A. (1998) Neurotrophic factors in the tongue: Expression patterns, biological activity, relation to innervation and studies of neurotrophin knockout mice. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 855, 28–49.
NOSRAT, C. A., BLOMLOF, J., ELSHAMY, W. M., ERNFORS, P. & OLSON, L. (1997) Lingual Deficits in BDNF and NT3 Mutant Mice Leading to Gustatory and Somatosensory Disturbances, Respectively. Development 124, 1333–1342.
NOSRAT, C. A. & OLSON, L. (1995) Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor Mrna Is Expressed in the Developing Taste Bud-bearing Tongue Papillae of Rat. Journal of Comparative Neurology 360, 698–704.
NOSRAT, I., SEIGER, A., OLSON, L. & NOSRAT, C. A. (2002) Expression patterns of neurotrophic factor mRNAs in developing human teeth. Cell & Tissue Research 310, 177–187.
PFAFFL, M. W. (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT PCR. Nucleic Acids Research 29, e45.
PFAFFL, M. W., HORGAN, G. W. & DEMPFLE, L. (2002) Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Research 30, e36.
POND, A., ROCHE, F. K. & LETOURNEAU, P. C. (2002) Temporal regulation of neuropilin-1 expression and sensitivity to semaphorin 3A in NGF- and NT3-responsive chick sensory neurons. Journal of Neurobiology 51, 43–53.
PUSCHEL, A. W., ADAMS, R. H. & BETZ, H. (1996) The sensory innervation of the mouse spinal cord may be patterned by differential expression of and differential responsiveness to semaphorins. Molecular & Cellular Neurosciences 7, 419–431.
ROCHLIN, M. W. & FARBMAN, A. I. (1998) Trigeminal ganglion axons are repelled by their presumptive targets. Journal of Neuroscience 18, 6840–6852.
ROCHLIN, M. W., O'CONNOR, R., GIGER, R. J., VERHAAGEN, J. & FARBMAN, A. I. (2000) Comparison of neurotrophin and repellent sensitivities of early embryonic geniculate and trigeminal axons. Journal of Comparative Neurology 422, 579–593.
SAHAY, A., MOLLIVER, M. E., GINTY, D. D. & KOLODKIN, A. L. (2003) Semaphorin 3F is critical for development of limbic system circuitry and is required in neurons for selective CNS axon guidance events. Journal of Neuroscience 23, 6671–6680.
SERINI, G., VALDEMBRI, D., ZANIVAN, S., MORTERRA, G., BURKHARDT, C., CACCAVARI, F., ZAMMATARO, L., PRIMO, L., TAMAGNONE, L., LOGAN, M., TESSIERLAVIGNE, M., TANIGUCHI, M., PUSCHEL, A. W. & BUSSOLINO, F. (2003) Class 3 semaphorins control vascular morphogenesis by inhibiting integrin function. Nature 424, 391–397.
SONG, H., MING, G., HE, Z., LEHMANN, M., MCKERRACHER, L., TESSIER-LAVIGNE, M. & POO, M. (1998) Conversion of neuronal growth cone responses from repulsion to attraction by cyclic nucleotides. Science 281, 1515–1518.
STROHMAIER, C., CARTER, B. D., URFER, R., BARDE, Y. A. & DECHANT, G. (1996) A splice variant of the neurotrophin receptor trkB with increased specificity for brain-derived neurotrophic factor. EMBO Journal 15, 3332–3337.
TAKAHASHI, T., NAKAMURA, F., JIN, Z., KALB, R. G. & STRITTMATTER, S. M. (1998) Semaphorins A and E act as antagonists of neuropilin-1 and agonists of neuropilin-2 receptors. Nature Neuroscience 1, 487–493.
TANIGUCHI, M., YUASA, S., FUJISAWA, H., NARUSE, I., SAGA, S., MISHINA, M. & YAGI, T. (1997) Disruption of semaphorin III/ D gene causes severe abnormality in peripheral nerve projection. Neuron 19, 519–530.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by a research grant from the NIDCD, 1 R03 DC04965-01 to MWR.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vilbig, R., Cosmano, J., Giger, R. et al. Distinct roles for Sema3A, Sema3F, and an unidentified trophic factor in controlling the advance of geniculate axons to gustatory lingual epithelium. J Neurocytol 33, 591–606 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11068-005-3329-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11068-005-3329-8