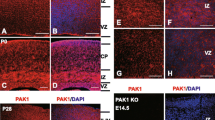
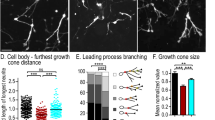
Abstract
The mammalian central nervous system (CNS) represents a highly complex unit, the correct function of which relies on the appropriate differentiation and survival of its neurones. It is becoming apparent that the Rho family of small GTPases and their downstream targets have a major function in regulating CNS development. Among the effectors, the role of the Pak family of kinases, especially Pak1, is becoming increasingly evident. Although highest levels of Pak1 expression and activation are detected in the developing nervous system, much remains undiscovered concerning its function in neurones. This review summarises what is currently known regarding the biological and molecular role of Pak1 in the mammalian forebrain. It emphasises the importance of Pak1 in regulating neuronal polarity, morphology, migration and synaptic function. Consequently, there are also strong indications that Pak1 is required for normal cognitive function. Furthermore, loss of Pak1 has been associated with the progression of neurodegenerative disorders, particularly Alzheimer’s disease, while up-regulation and de-regulation may be responsible for oncogenic transformation of support cells within the CNS, especially astrocyte progenitors. Together, these new and exciting findings encourage the future exploration into the function of Pak1 in the nervous system, thus, paving the way for novel strategies towards improved diagnosis and therapeutic treatment of diseases that affect the CNS.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Linseman DA, Loucks FA (2008) Diverse roles of Rho family GTPases in neuronal development, survival, and death. Front Biosci 13:657–676
Bokoch GM (2003) Biology of the p21-activated kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 72:743–781
Jaffer ZM, Chernoff J (2002) p21-activated kinases: three more join the Pak. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 34:713–717
Lei M, Lu W, Meng W, Parrini MC, Eck MJ, Mayer BJ, Harrison SC (2000) Structure of PAK1 in an autoinhibited conformation reveals a multistage activation switch. Cell 102:387–397
Pirruccello M, Sondermann H, Pelton JG, Pellicena P, Hoelz A, Chernoff J, Wemmer DE, Kuriyan J (2006) A dimeric kinase assembly underlying autophosphorylation in the p21 activated kinases. J Mol Biol 361:312–326
Parrini MC, Lei M, Harrison SC, Mayer BJ (2002) Pak1 kinase homodimers are autoinhibited in trans and dissociated upon activation by Cdc42 and Rac1. Mol Cell 9:73–83
Sells MA, Pfaff A, Chernoff J (2000) Temporal and spatial distribution of activated Pak1 in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 151:1449–1458
Zhao ZS, Lim JP, Ng YW, Lim L, Manser E (2005) The GIT-associated kinase PAK targets to the centrosome and regulates Aurora-A. Mol Cell 20:237–249
Loo TH, Ng YW, Lim L, Manser E (2004) GIT1 activates p21-activated kinase through a mechanism independent of p21 binding. Mol Cell Biol 24:3849–3859
King CC, Gardiner EM, Zenke FT, Bohl BP, Newton AC, Hemmings BA, Bokoch GM (2000) p21-activated kinase (PAK1) is phosphorylated and activated by 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 (PDK1). J Biol Chem 275:41201–41209
Chong C, Tan L, Lim L, Manser E (2001) The mechanism of PAK activation. Autophosphorylation events in both regulatory and kinase domains control activity. J Biol Chem 276:17347–17353
Arias-Romero LE, Chernoff J (2008) A tale of two Paks. Biol Cell 100:97–108
Allen KM, Gleeson JG, Bagrodia S, Partington MW, MacMillan JC, Cerione RA, Mulley JC, Walsh CA (1998) PAK3 mutation in nonsyndromic X-linked mental retardation. Nat Genet 20:25–30
Boda B, Alberi S, Nikonenko I, Node-Langlois R, Jourdain P, Moosmayer M, Parisi-Jourdain L, Muller D (2004) The mental retardation protein PAK3 contributes to synapse formation and plasticity in hippocampus. J Neurosci 24:10816–10825
Boda B, Nikonenko I, Alberi S, Muller D (2006) Central Nervous System Functions of PAK Protein Family: From Spine Morphogenesis to Mental Retardation. Mol Neurobiol 34:67–80
Meng J, Meng Y, Hanna A, Janus C, Jia Z (2005) Abnormal long-lasting synaptic plasticity and cognition in mice lacking the mental retardation gene Pak3. J Neurosci 25:6641–6650
Li X, Minden A (2003) Targeted disruption of the gene for the PAK5 kinase in mice. Mol Cell Biol 23:7134–7142
Qu J, Li X, Novitch BG, Zheng Y, Kohn M, Xie JM, Kozinn S, Bronson R, Beg AA, Minden A (2003) PAK4 kinase is essential for embryonic viability and for proper neuronal development. Mol Cell Biol 23:7122–7133
Manser E, Leung T, Salihuddin H, Zhao ZS, Lim L (1994) A brain serine/threonine protein kinase activated by Cdc42 and Rac1. Nature 367:40–46
Hofmann C, Shepelev M, Chernoff J (2004) The genetics of Pak. J Cell Sci 117:4343–4354
Kumar R, Gururaj AE, Barnes CJ (2006) p21-activated kinases in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:459–471
Settleman J (2007) PAK-in’ up cGMP for the move. Cell 128:237–238
Burbelo PD, Kozak CA, Finegold AA, Hall A, Pirone DM (1999) Cloning, central nervous system expression and chromosomal mapping of the mouse PAK-1 and PAK-3 genes. Gene 232:209–215
Zhong JL, Banerjee MD, Nikolic M (2003) Pak1 and its T212 phosphorylated form accumulate in neurones and epithelial cells of the developing rodent. Dev Dyn 228:121–127
Hayashi K, Ohshima T, Mikoshiba K (2002) Pak1 is involved in dendrite initiation as a downstream effector of Rac1 in cortical neurones. Mol Cell Neurosci 20:579–594
Jacobs T, Causeret F, Nishimura YV, Terao M, Norman A, Hoshino M, Nikolic M (2007) Localized activation of p21-activated kinase controls neuronal polarity and morphology. J Neurosci 27:8604–8615
Thiel DA, Reeder MK, Pfaff A, Coleman TR, Sells MA, Chernoff J (2002) Cell cycle-regulated phosphorylation of p21-activated kinase 1. Curr Biol 12:1227–1232
Banerjee M, Worth D, Prowse DM, Nikolic M (2002) Pak1 phosphorylation on t212 affects microtubules in cells undergoing mitosis. Curr Biol 12:1233–1239
Buchman JJ, Tsai LH (2007) Spindle regulation in neural precursors of flies and mammals. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:89–100
Gotz M, Huttner WB (2005) The cell biology of neurogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:777–788
Petersen PH, Zou K, Krauss S, Zhong W (2004) Continuing role for mouse Numb and Numbl in maintaining progenitor cells during cortical neurogenesis. Nat Neurosci 7:803–811
Petersen PH, Zou K, Hwang JK, Jan YN, Zhong W (2002) Progenitor cell maintenance requires numb and numblike during mouse neurogenesis. Nature 419:929–934
Chenn A, Walsh CA (2002) Regulation of cerebral cortical size by control of cell cycle exit in neural precursors. Science 297:365–369
Li HS, Wang D, Shen Q, Schonemann MD, Gorski JA, Jones KR, Temple S, Jan LY, Jan YN (2003) Inactivation of Numb and Numblike in embryonic dorsal forebrain impairs neurogenesis and disrupts cortical morphogenesis. Neuron 40:1105–1118
Cappello S, Attardo A, Wu X, Iwasato T, Itohara S, Wilsch-Brauninger M, Eilken HM, Rieger MA, Schroeder TT, Huttner WB et al (2006) The Rho-GTPase cdc42 regulates neural progenitor fate at the apical surface. Nat Neurosci 9:1099–1107
Ong WY, Wang XS, Manser E (2002) Differential distribution of alpha and beta isoforms of p21-activated kinase in the monkey cerebral neocortex and hippocampus. Exp Brain Res 144:189–199
Rashid T, Banerjee M, Nikolic M (2001) Phosphorylation of Pak1 by the p35/Cdk5 kinase affects neuronal morphology. J Biol Chem 276:49043–49052
Hayashi K, Ohshima T, Hashimoto M, Mikoshiba K (2007) Pak1 regulates dendritic branching and spine formation. Dev Neurobiol 67:655–669
Cheung ZH, Fu AK, Ip NY (2006) Synaptic roles of Cdk5: implications in higher cognitive functions and neurodegenerative diseases. Neuron 50:13–18
Xie Z, Samuels BA, Tsai LH (2006) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 permits efficient cytoskeletal remodeling–a hypothesis on neuronal migration. Cereb Cortex 16 Suppl 1:i64–i68
Charest PG, Firtel RA (2007) Big roles for small GTPases in the control of directed cell movement. Biochem J 401:377–390
Wittmann T, Bokoch GM, Waterman-Storer CM (2003) Regulation of leading edge microtubule and actin dynamics downstream of Rac1. J Cell Biol 161:845–851
Ang LH, Chen W, Yao Y, Ozawa R, Tao E, Yonekura J, Uemura T, Keshishian H, Hing H (2006) Lim kinase regulates the development of olfactory and neuromuscular synapses. Dev Biol 293:178–190
Hing H, Xiao J, Harden N, Lim L, Zipursky SL (1999) Pak functions downstream of Dock to regulate photoreceptor axon guidance in Drosophila. Cell 97:853–863
Fan X, Labrador JP, Hing H, Bashaw GJ (2003) Slit stimulation recruits Dock and Pak to the roundabout receptor and increases Rac activity to regulate axon repulsion at the CNS midline. Neuron 40:113–127
Newsome TP, Schmidt S, Dietzl G, Keleman K, Asling B, Debant A, Dickson BJ (2000) Trio combines with dock to regulate Pak activity during photoreceptor axon pathfinding in Drosophila. Cell 101:283–294
Vikis HG, Li W, Guan KL (2002) The plexin-B1/Rac interaction inhibits PAK activation and enhances Sema4D ligand binding. Genes Dev 16:836–845
Dotti CG, Sullivan CA, Banker GA (1988) The establishment of polarity by hippocampal neurones in culture. J Neurosci 8:1454–1468
Arimura N, Kaibuchi K (2007) Neuronal polarity: from extracellular signals to intracellular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:194–205
Zhou GL, Zhuo Y, King CC, Fryer BH, Bokoch GM, Field J (2003) Akt phosphorylation of serine 21 on Pak1 modulates Nck binding and cell migration. Mol Cell Biol 23:8058–8069
Johnson K, D’Mello SR (2005) p21-Activated kinase-1 is necessary for depolarization-mediated neuronal survival. J Neurosci Res 79:809–815
Welch HC, Coadwell WJ, Stephens LR, Hawkins PT (2003) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent activation of Rac. FEBS Lett 546:93–97
Obermeier A, Ahmed S, Manser E, Yen SC, Hall C, Lim L (1998) PAK promotes morphological changes by acting upstream of Rac. Embo J 17:4328–4339
Mao K, Kobayashi S, Jaffer ZM, Huang Y, Volden P, Chernoff J, Liang Q (2008) Regulation of Akt/PKB activity by P21-activated kinase in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 44:429–434
Daniels RH, Hall PS, Bokoch GM (1998) Membrane targeting of p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) induces neurite outgrowth from PC12 cells. Embo J 17:754–764
Holly SP, Blumer KJ (1999) PAK-family kinases regulate cell and actin polarization throughout the cell cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol 147:845–856
Lee S, Rivero F, Park KC, Huang E, Funamoto S, Firtel RA (2004) Dictyostelium PAKc is required for proper chemotaxis. Mol Biol Cell 15:5456–5469
Nichols CB, Fraser JA, Heitman J (2004) PAK kinases Ste20 and Pak1 govern cell polarity at different stages of mating in Cryptococcus neoformans. Mol Biol Cell 15:4476–4489
Ottilie S, Miller PJ, Johnson DI, Creasy CL, Sells MA, Bagrodia S, Forsburg SL, Chernoff J (1995) Fission yeast pak1 + encodes a protein kinase that interacts with Cdc42p and is involved in the control of cell polarity and mating. Embo J 14:5908–5919
Edwards DC, Sanders LC, Bokoch GM, Gill GN (1999) Activation of LIM-kinase by Pak1 couples Rac/Cdc42 GTPase signalling to actin cytoskeletal dynamics. Nat Cell Biol 1:253–259
Delorme V, Machacek M, DerMardirossian C, Anderson KL, Wittmann T, Hanein D, Waterman-Storer C, Danuser G, Bokoch GM (2007) Cofilin activity downstream of Pak1 regulates cell protrusion efficiency by organizing lamellipodium and lamella actin networks. Dev Cell 13:646–662
Kawauchi T, Chihama K, Nabeshima Y, Hoshino M (2006) Cdk5 phosphorylates and stabilizes p27kip1 contributing to actin organization and cortical neuronal migration. Nat Cell Biol 8:17–26
Gurniak CB, Perlas E, Witke W (2005) The actin depolymerizing factor n-cofilin is essential for neural tube morphogenesis and neural crest cell migration. Dev Biol 278:231–241
Meng Y, Zhang Y, Tregoubov V, Falls DL, Jia Z (2003) Regulation of spine morphology and synaptic function by LIMK and the actin cytoskeleton. Rev Neurosci 14:233–240
Bernard O (2007) Lim kinases, regulators of actin dynamics. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:1071–1076
Wittmann T, Bokoch GM, Waterman-Storer CM (2004) Regulation of microtubule destabilizing activity of Op18/stathmin downstream of Rac1. J Biol Chem 279:6196–6203
Poulain FE, Sobel A (2007) The “SCG10-LIke Protein” SCLIP is a novel regulator of axonal branching in hippocampal neurones, unlike SCG10. Mol Cell Neurosci 34:137–146
Shekarabi M, Moore SW, Tritsch NX, Morris SJ, Bouchard JF, Kennedy TE (2005) Deleted in colorectal cancer binding netrin-1 mediates cell substrate adhesion and recruits Cdc42, Rac1, Pak1, and N-WASP into an intracellular signaling complex that promotes growth cone expansion. J Neurosci 25:3132–3141
Cobos I, Borello U, Rubenstein JL (2007) Dlx transcription factors promote migration through repression of axon and dendrite growth. Neuron 54:873–888
Nakajima K (2007) Control of tangential/non-radial migration of neurones in the developing cerebral cortex. Neurochem Int 51:121–131
Wonders C, Anderson SA (2005) Cortical interneurones and their origins. Neuroscientist 11:199–205
Sakakibara A, Horwitz AF (2006) Mechanism of polarized protrusion formation on neuronal precursors migrating in the developing chicken cerebellum. J Cell Sci 119:3583–3592
Matsuzaki M (2007) Factors critical for the plasticity of dendritic spines and memory storage. Neurosci Res 57:1–9
Luo L, Hensch TK, Ackerman L, Barbel S, Jan LY, Jan YN (1996) Differential effects of the Rac GTPase on Purkinje cell axons and dendritic trunks and spines. Nature 379:837–840
Nakayama AY, Harms MB, Luo L (2000) Small GTPases Rac and Rho in the maintenance of dendritic spines and branches in hippocampal pyramidal neurones. J Neurosci 20:5329–5338
Tashiro A, Minden A, Yuste R (2000) Regulation of dendritic spine morphology by the rho family of small GTPases: antagonistic roles of Rac and Rho. Cereb Cortex 10:927–938
Tashiro A, Yuste R (2004) Regulation of dendritic spine motility and stability by Rac1 and Rho kinase: evidence for two forms of spine motility. Mol Cell Neurosci 26:429–440
Penzes P, Beeser A, Chernoff J, Schiller MR, Eipper BA, Mains RE, Huganir RL (2003) Rapid induction of dendritic spine morphogenesis by trans-synaptic ephrinB-EphB receptor activation of the Rho-GEF kalirin. Neuron 37:263–274
Zhang H, Webb DJ, Asmussen H, Horwitz AF (2003) Synapse formation is regulated by the signaling adaptor GIT1. J Cell Biol 161:131–142
Zhang H, Webb DJ, Asmussen H, Niu S, Horwitz AF (2005) A GIT1/PIX/Rac/PAK signaling module regulates spine morphogenesis and synapse formation through MLC. J Neurosci 25:3379–3388
Park E, Na M, Choi J, Kim S, Lee JR, Yoon J, Park D, Sheng M, Kim E (2003) The Shank family of postsynaptic density proteins interacts with and promotes synaptic accumulation of the beta PIX guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rac1 and Cdc42. J Biol Chem 278:19220–19229
Hayashi ML, Choi SY, Rao BS, Jung HY, Lee HK, Zhang D, Chattarji S, Kirkwood A, Tonegawa S (2004) Altered cortical synaptic morphology and impaired memory consolidation in forebrain- specific dominant-negative PAK transgenic mice. Neuron 42:773–787
Carlisle HJ, Kennedy MB (2005) Spine architecture and synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci 28:182–187
Goda Y, Davis GW (2003) Mechanisms of synapse assembly and disassembly. Neuron 40:243–264
Sakurada K, Kato H, Nagumo H, Hiraoka H, Furuya K, Ikuhara T, Yamakita Y, Fukunaga K, Miyamoto E, Matsumura F et al (2002) Synapsin I is phosphorylated at Ser603 by p21-activated kinases (PAKs) in vitro and in PC12 cells stimulated with bradykinin. J Biol Chem 277:45473–45479
Hayashi ML, Rao BS, Seo JS, Choi HS, Dolan BM, Choi SY, Chattarji S, Tonegawa S (2007) Inhibition of p21-activated kinase rescues symptoms of fragile X syndrome in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:11489–11494
Comery TA, Harris JB, Willems PJ, Oostra BA, Irwin SA, Weiler IJ, Greenough WT (1997) Abnormal dendritic spines in fragile X knockout mice: maturation and pruning deficits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:5401–5404
Nimchinsky EA, Oberlander AM, Svoboda K (2001) Abnormal development of dendritic spines in FMR1 knock-out mice. J Neurosci 21:5139–5146
Sananbenesi F, Fischer A, Wang X, Schrick C, Neve R, Radulovic J, Tsai LH (2007) A hippocampal Cdk5 pathway regulates extinction of contextual fear. Nat Neurosci 10:1012–1019
Zhao L, Ma QL, Calon F, Harris-White ME, Yang F, Lim GP, Morihara T, Ubeda OJ, Ambegaokar S, Hansen JE et al (2006) Role of p21-activated kinase pathway defects in the cognitive deficits of Alzheimer disease. Nat Neurosci 9:234–242
Benavides-Piccione R, Ballesteros-Yanez I, de Lagran MM, Elston G, Estivill X, Fillat C, Defelipe J, Dierssen M (2004) On dendrites in Down syndrome and DS murine models: a spiny way to learn. Prog Neurobiol 74:111–126
Gao FB (2007) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of dendritic morphogenesis. Curr Opin Neurobiol 17:525–532
Schmucker D (2007) Molecular diversity of Dscam: recognition of molecular identity in neuronal wiring. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:915–920
Yamakawa K, Huot YK, Haendelt MA, Hubert R, Chen XN, Lyons GE, Korenberg JR (1998) DSCAM: a novel member of the immunoglobulin superfamily maps in a Down syndrome region and is involved in the development of the nervous system. Hum Mol Genet 7:227–237
Li W, Guan KL (2004) The Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule (DSCAM) interacts with and activates Pak. J Biol Chem 279:32824–32831
Schmucker D, Clemens JC, Shu H, Worby CA, Xiao J, Muda M, Dixon JE, Zipursky SL (2000) Drosophila Dscam is an axon guidance receptor exhibiting extraordinary molecular diversity. Cell 101:671–684
Sen A, Thom M, Martinian L, Harding B, Cross JH, Nikolic M, Sisodiya SM (2007) Pathological tau tangles localize to focal cortical dysplasia in older patients. Epilepsia 48:1447–1454
Sen A, Thom M, Nikolic M, Sisodiya SM (2008) The potential role of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 in focal cortical dysplasia. Dev Neurosci 30:96–104
Teipel SJ, Hampel H (2006) Neuroanatomy of Down syndrome in vivo: a model of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Behav Genet 36:405–415
Kojima N, Shirao T (2007) Synaptic dysfunction and disruption of postsynaptic drebrin-actin complex: a study of neurological disorders accompanied by cognitive deficits. Neurosci Res 58:1–5
Bell KF, Claudio Cuello A (2006) Altered synaptic function in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Pharmacol 545:11–21
Scheff SW, Price DA (2006) Alzheimer’s disease-related alterations in synaptic density: neocortex and hippocampus. J Alzheimers Dis 9:101–115
Nguyen TV, Galvan V, Huang W, Banwait S, Tang H, Zhang J, Bredesen DE (2008) Signal transduction in Alzheimer disease: p21-activated kinase signaling requires C-terminal cleavage of APP at Asp664. J Neurochem 104:1065–1080
McPhie DL, Coopersmith R, Hines-Peralta A, Chen Y, Ivins KJ, Manly SP, Kozlowski MR, Neve KA, Neve RL (2003) DNA synthesis and neuronal apoptosis caused by familial Alzheimer disease mutants of the amyloid precursor protein are mediated by the p21 activated kinase PAK3. J Neurosci 23:6914–6927
Chandran J, Ding J, Cai H (2007) Alsin and the molecular pathways of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol Neurobiol 36:224–231
Pasinelli P, Brown RH (2006) Molecular biology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: insights from genetics. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:710–723
Tudor EL, Perkinton MS, Schmidt A, Ackerley S, Brownlees J, Jacobsen NJ, Byers HL, Ward M, Hall A, Leigh PN et al (2005) ALS2/Alsin regulates Rac-PAK signaling and neurite outgrowth. J Biol Chem 280:34735–34740
Aoki H, Yokoyama T, Fujiwara K, Tari AM, Sawaya R, Suki D, Hess KR, Aldape KD, Kondo S, Kumar R et al (2007) Phosphorylated Pak1 level in the cytoplasm correlates with shorter survival time in patients with glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 13:6603–6609
Puto LA, Pestonjamasp K, King CC, Bokoch GM (2003) p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) interacts with the Grb2 adapter protein to couple to growth factor signaling. J Biol Chem 278:9388–9393
Lu W, Katz S, Gupta R, Mayer BJ (1997) Activation of Pak by membrane localization mediated by an SH3 domain from the adaptor protein Nck. Curr Biol 7:85–94
Xia C, Ma W, Stafford LJ, Marcus S, Xiong WC, Liu M (2001) Regulation of the p21-activated kinase (PAK) by a human Gbeta -like WD-repeat protein, hPIP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6174–6179
Aronheim A, Broder YC, Cohen A, Fritsch A, Belisle B, Abo A (1998) Chp, a homologue of the GTPase Cdc42Hs, activates the JNK pathway and is implicated in reorganizing the actin cytoskeleton. Curr Biol 8:1125–1128
Tao W, Pennica D, Xu L, Kalejta RF, Levine AJ (2001) Wrch-1, a novel member of the Rho gene family that is regulated by Wnt-1. Genes Dev 15:1796–1807
Neudauer CL, Joberty G, Tatsis N, Macara IG (1998) Distinct cellular effects and interactions of the Rho-family GTPase TC10. Curr Biol 8:1151–1160
Talukder AH, Meng Q, Kumar R (2006) CRIPak, a novel endogenous Pak1 inhibitor. Oncogene 25:1311–1319
Manser E, Loo TH, Koh CG, Zhao ZS, Chen XQ, Tan L, Tan I, Leung T, Lim L (1998) PAK kinases are directly coupled to the PIX family of nucleotide exchange factors. Mol Cell 1:183–192
Leeuw T, Wu C, Schrag JD, Whiteway M, Thomas DY, Leberer E (1998) Interaction of a G-protein beta-subunit with a conserved sequence in Ste20/PAK family protein kinases. Nature 391:191–195
Menard RE, Mattingly RR (2004) Gbetagamma subunits stimulate p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) through activation of PI3-kinase and Akt but act independently of Rac1/Cdc42. FEBS Lett 556:187–192
Mayhew MW, Jeffery ED, Sherman NE, Nelson K, Polefrone JM, Pratt SJ, Shabanowitz J, Parsons JT, Fox JW, Hunt DF et al (2007) Identification of phosphorylation sites in betaPIX and PAK1. J Cell Sci 120:3911–3918
Zhao ZS, Manser E, Lim L (2000) Interaction between PAK and nck: a template for Nck targets and role of PAK autophosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol 20:3906–3917
Sundberg-Smith LJ, Doherty JT, Mack CP, Taylor JM (2005) Adhesion stimulates direct PAK1/ERK2 association and leads to ERK-dependent PAK1 Thr212 phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 280:2055–2064
Fryer BH, Wang C, Vedantam S, Zhou GL, Jin S, Fletcher L, Simon MC, Field J (2006) cGMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates p21-activated kinase (Pak) 1, inhibiting Pak/Nck binding and stimulating Pak/vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein association. J Biol Chem 281:11487–11495
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Deanna Taylor and Magdalena Sastre for critically reading the manuscript and to Frédéric Causeret and Tom Jacobs for several years of successful research into the functional role of Pak1 in primary neurones
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikolić, M. The Pak1 Kinase: An Important Regulator of Neuronal Morphology and Function in the Developing Forebrain. Mol Neurobiol 37, 187–202 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-008-8032-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-008-8032-1