Abstract
Summary
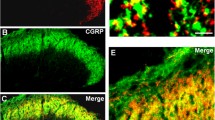
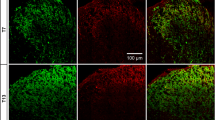
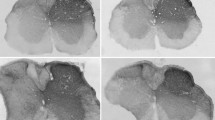
Interferon-γ can facilitate the spinal nociceptive flexor reflex and elicit neuropathic pain-related behavior in rats and mice. Immunoreactivity for the interferon-γ receptor (IFN-γR) occurs in the superficial layers of the dorsal horn and the lateral spinal nucleus in the rat and mouse spinal cord, as well as in subsets of neurons in the dorsal root ganglia. The aim of the present study was to examine the cellular localization and origin of the IFN-γR in the spinal cord. As viewed by confocal microscopy, the immunopositivity for the IFN-γR was co-localized with that of the presynaptic marker synaptophysin and with neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the lateral spinal nucleus, whereas only a minor overlap with these molecules was observed in laminae I and II of the dorsal horn. There was no co-localization of the IFN-γR with markers for astrocytes and microglial cells. Ultrastructurally, the IFN-γR was found predominantly in axon terminals in the lateral spinal nucleus but also at postsynaptic sites in dendrites in laminae I and II. The IFN-γR expressed in neurons in dorsal root ganglia was transported in axons both centrally and peripherally. Hemisection of the spinal cord caused no reduction in immunolabelling of the IFN-γR in the dorsal horn or the lateral spinal nucleus. Since rhizotomy does not effect the immunolabelling in the lateral spinal nucleus, our observation indicates that the presynaptic receptors in this nucleus are derived from intrinsic neurons. The localization of the IFN-γR in the spinal cord differed from that of the AMPA glutamate receptor subunits 2 and 3 and the substance P receptor (NK1). Our results, showing localization of IFN-γR to pre- and postsynaptic sites in the dorsal horn and lateral spinal nucleus indicate that IFN-γ can modulate nociception at the spinal cord level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boehm, U., Klamp, T., Groot, M. & Howard, J.C. (1997) Cellular responses to interferon-γ. Annual Review of Immunology 15, 749-95.
Brown, J.L., Liu, H., Maggio, J.E., Vigna, S.R., Mantyh, P.W. & Basbaum, A.I. (1995) Morphological characterization of substance P receptor-immunoreactive neurons in the rat spinal cord and trigeminal nucleus caudalis. Journal of Comparative Neurology 356, 327-44.
Carlsson, K., Åslund, N., Mossberg, K. & Philip, J. (1994) Simultaneous confocal recording of multiple fluorescent labels with improved channel separation. Journal of Microscopy 176, 287-99.
Carlsson, K. & Ulfhake, B. (1995) Improved fluorophore separation with IMS confocal microscopy. NeuroReport 6, 1169-73.
Carlsson, K. & Liljeborg, A. (1997) Confocal fluorescence microscopy using spectral and lifetime information to simultaneously record four fluorophores with high channel separation. Journal of Microscopy 185, 37-46.
Cliffer, K.D., Urca, G., Elde, R.P. & Giesler Jr, G.J. (1998) Studies of peptidergic input to the lateral spinal nucleus. Brain Research 460, 356-60.
Coggeshall, R.E. & Carlton, S.M. (1997) Receptor localization in the mammalian dorsal horn and primary afferent neurons. Brain Research Reviews 24, 28-66.
Duggan, A.W., Schaible, H.-G., Hope, P.J. & Lang, C.W. (1992) Effect of peptidase inhibition on the pattern of intraspinally released immunoreactive substance P detected with antibody microprobes. Brain Research 579, 261-9.
Dun, N.J., Dun, S.L., Wu, S.Y., FÖrstermann, U., Schmidt, H.H.H.W. & Tseng, L.F. (1993) Nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity in the rat, mouse, cat and squirrel monkey spinal cord. Neuroscience 54, 845-57.
Eneroth, A., Kristensson, K., Ljungdahl, Å. & Olsson T. (1991) Interferon-γ-like immunoreactivity in developing rat spinal ganglia neurons in vivo and in vitro. Journal of Neurocytology 20, 225-31.
Farrar, M.A. & Schreiber, R.D. (1993) The molecular cell biology of interferon-γ and its receptor. Annual Review of Immunology 11, 571-611.
Ferreira, S.H., Lorenzetti, B.B, Bristow, A.F. & Poole, S. (1988) Interleukin-1β as a potent hyperalgesic agent antagonized by a tripeptide analogue. Nature 334, 698-700.
Fuxe, K. & Agnati, L.F. (1991) Two principle models of electrochemical communication in the brain: volume versus wiring transmission. In: Volume Transmission in the Brain (edited by Fuxe, K. & Agnati, L.F.), pp. 1-9. New York: Raven Press.
Hart, B. (1988) Biological basis of the behavior of sick animals. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews 12, 123-37.
Kent, S., BluthÉ, R.-M., Kelley, K.W. & Dantzer, R. (1992) Sickness behavior as a new target for drug development. Trends in Pharmacological Science 13, 24-8.
Kamijo, R., Shapiro, D., Le, J., Huang, S., Aguet, M. & Vilcek, J. (1993) Generation of nitric oxide and induction of major histocompatibility complex class II antigen in macrophages from mice lacking the interferon γ receptor. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 90, 6626-30.
Littlewood, N.K., Todd, A.J., Spike, R.C., Watt, C. & Shehab, S.A.S. (1995) The types of neuron in spinal dorsal horn which possess neurokinin-1 receptors. Neuroscience 66, 597-608.
Liu, H., Brown, J.L., Jasmin, L., Maggio, J.E., Vigna, S.R., Mantyh, P.W. & Basbaum, A. (1994) Synaptic relationship between substance P and the substance P receptor: light and electron microscopic characterization of the mismatch between neuropeptides and their receptors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 91, 1009-13.
Lundkvist, G.B., Robertson, B., Rottenberg, M.E., Mhlanga, J.D.M. & Kristensson, K. (1998) Expression of an oscillating interferon-γ receptor in the suprachiasmatic nuclei. NeuroReport 9, 1059-63.
Maier, S.F., Wiertelak, E.P., Martin, D. & Watkins, L.R. (1993) Interleukin-1 mediates behavioral hyperalgesia produced by lithium chloride and endotoxin. Brain Research 623, 321-4.
Naim, M., Spike, R.C., Watt, C., Shebab, S.A.S. & Todd, A.J. (1997) Cells in laminae III and IV of the rat spinal cord that possess the neurokinin-1 receptor and have dorsally directed dendrites receive a major synaptic input from tachykinin-containing primary afferents. Journal of Neuroscience 17, 5536-48.
Neuhuber, W. (1982) The central projections of visceral primary afferent neurons of the inferior mesenteric plexus and hypogastric nerve and the location of the related sensory and preganglionic sympathetic cell bodies in the rat. Anatomy and Embryology 164, 413-25.
Neumann, H., Schmidt, H., CavaliÉ, A., Jenne, D. & Wekerle, H. (1997a) Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I gene expression in single neurons of the central nervous system: differential regulation by interferon (IFN)-γ and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α. Journal of Experimental Medicine 185, 305-16.
Neumann, H., Schmidt, H., Wilharm, E. Behrens, L. & Wekerle, H. (1997b) Interferon γ gene expression in sensory neurons: evidence for autocrine gene regulation. Journal of Experimental Medicine 186, 2023-31.
Olsson, T., Kelic, S., Edlund, C., Bakhiet, M., HÖjeberg, B., van der Meide, P.H., Ljungdahl, Å. & Kristensson, K. (1994) Neuronal interferon-γ immunoreactive molecule: bioactivities and purification. European Journal of Immunology 24, 308-14.
Popratiloff, A., Weinberg, R.J. & Rustioni, A. (1996) Ampa receptor subunits underlying terminals of fine-caliber primary afferent fibers. Journal of Neuroscience 16, 3363-72.
Robertson, B., Grant, G. & Kristensson, K. (1996) Characterization of neuronal interferon-γ immunoreactive dorsal root ganglion cells and their projections to the spinal cord of the rat. Primary Sensory Neuron 1, 221-30.
Robertson B., Xu, X.-J., Hao, J.-X., Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z., Mhlanga, J., Grant, G. & Kristensson, K. (1997) Interferon-γ receptors in nociceptive pathways: role in neuropathic pain-related behavior. NeuroReport 8, 1311-6.
Rubio, N. & de Felipe, C. (1991) Demonstration of the presence of a specific interferon-γ receptor on murine astrocyte cell surface. Journal of Neuroimmunology 35, 111-7.
Tachibana, M., Wenthold, R.J., Morioka, H. & Petralia, R.S. (1994) Light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical localization of AMPA-selective glutamate receptors in the rat spinal cord. Journal of Comparative Neurology 344, 431-54.
Torres, C., ArÁnguez, I. & Rubio, N. (1995) Expression of interferon-γ receptors on murine oligodendrocytes and its regulation by cytokines and mitogens. Immunology 86, 250-5.
Valente, G., Ozmen, L., Novelli, F., Geuna, M., Palestro, G., Forni, G. & Garotta, G. (1992) Distribution of interferon-γ receptor in human tissues. European Journal of Immunology 22, 2403-12.
Watkins, L.R., Goehler, L.E., Relton, J., Brewer, M.T. & Maier, S.F. (1995a) Mechanisms of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) hyperalgesia. Brain Research 692, 244-50.
Watkins, L.R., Maier, S.F. & Goehler, L.E. (1995b) Immune activation: the role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in inflammation, illness responses and pathological pain states. Pain 63, 289-302.
Xu, X.-J., Hao, J.-X., Olsson, T., Kristensson, K., van der Meide, P.H. & Wiesenfeld-Hallin, H.Z. (1994) Intrathecal interferon-γ facilitates the spinal nociceptive flexor reflex in the rat. Neuroscience Letters 182, 263-6.
Young, H.A. & Hardy, K.J. (1995) Role of interferon-γ in immune cell regulation. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 58, 373-81.
Zhang, X., Verge, V., Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z., Ju, G., Bredt, D., Snyder, S.H. & HÖkfelt, T. (1993) Nitric oxide synthase-like immunoreactivity in lumbar dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord of rat and monkey and effect of peripheral axotomy. Journal of Comparative Neurology 335, 563-75.
Åslund, N. & Carlsson, K. (1993) Confocal scanning microfluorometry of dual-labelled specimens using two excitation wavelengths and lock-in detection technique. Micron 24, 603-9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vikman, K., Robertson, B., Grant, G. et al. Interferon-γ receptors are expressed at synapses in the rat superficial dorsal horn and lateral spinal nucleus. J Neurocytol 27, 749–760 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006903002044
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006903002044