Abstract
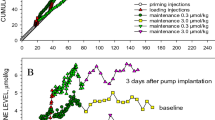
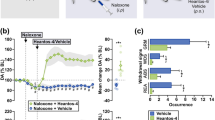
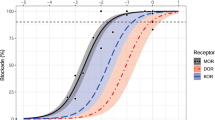
THE biochemical basis of the development of tolerance for and dependence on narcotic analgesics has been the subject of much speculation and experiment1–6. Theories which try to account for these closely related4,7 phenomena can be grouped into three main classes: (1) the body reacts to narcotic drugs by increasing the rate at which they are destroyed or neutralised (by antibodies, for example) so that a smaller proportion of the total dose reaches the brain receptors2; (2) processes which are directly affected by the narcotic analgesics are circumvented or otherwise accommodated through an indirect physiological adaptation6; (3) a direct adaptation takes place in which the number of receptor sites for the narcotics is greatly increased, or their affinities greatly reduced so that large amounts of drugs are needed to fill the available sites and thus effect a response5. We wish to present data which effectively rule out this third possibility as a major factor in narcotic drug dependence and tolerance. We show that neither the number, nor the binding affinity, nor the specificity of narcotic receptor sites8–10 is changed in the morphine-dependent (and therefore also tolerant7) rat brain when compared with that of the normal animal.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dole, V. P., A. Rev. Biochem., 39, 821 (1970).
Cochin, J., Fed. Proc., 29, 19 (1970).
Martin, W. R., Fed. Proc., 29, 13 (1970).
Shuster, L., in Narcotic Drugs, Biochemical Pharmacology (edit. by Clouet, D. H.), 408 (Plenum, New York, 1971).
Collier, H. O. J., Nature, 220, 228 (1968).
Schulz, R., and Goldstein, A., Nature, 244, 168 (1973).
Way, E. L., Loh, H. H., and Shen, F. H., J. pharmac. exp. Ther., 167, 18 (1969).
Pert, C. B., and Snyder, S. H., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 70, 2243 (1973).
Simon, E. J., Hiller, J. M., and Edelman, I., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 70, 1947 (1973).
Terenius, L., Acta Pharmac. Toxic., 32, 317 (1973).
Bison, R. D., and Tingstad, J. E., J. pharm. Sci., 59, 426 (1970).
Cicero, T. J., and Meyer, E. R., J. pharmac. exp. Ther., 184, 404 (1973).
Dewey, W. L., in Chemical and Biological Aspects of Drug Dependence (edit. by Mulé, S. J., and Brill, H.), 25 (CRC Press, Cleveland, 1972).
Whittaker, V. P., Biochem. J., 72, 694 (1959).
Mulé, S. J., in Chemical and Biological Aspects of Drug Dependence (edit. by Mulé, S. J., and Brill, H.), 277 (CRC Press, Cleveland, 1972).
Mulé, S. J., Redman, C. M., and Flesher, J. W., J. pharmac. exp. Ther., 157, 459 (1967).
Mulé, S. J., in Narcotic Drugs, Biochemical Pharmacology (edit. by Clouet, D. H.), 117 (Plenum, New York, 1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KLEE, W., STREATY, R. Narcotic Receptor Sites in Morphine-dependent Rats. Nature 248, 61–63 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1038/248061a0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/248061a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.