Abstract
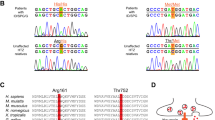
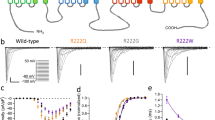
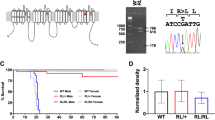
The mutant mouse spastic, which carries a single-locus, recessive mutation1 on chromosome 3 (refs 2, 3), is characterized by hyperexcitability, rapid tremor, rigidity and prolonged righting reflexes1. No anatomical abnormalities have been found in preliminary histological studies of muscle or the central nervous system (CNS)1. Electromyographic studies in spastic mice demonstrate abnormal electrical bursts during activity and abnormal stereotyped reflexes4. Drugs which increase γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)5 or enhance GABA synaptic action6 reduce spastic symptoms, suggesting that they result from an imbalance in excitatory and inhibitory influences in the spastic CNS. Strychnine antagonizes the synaptic action of glycine7, and binds to a membrane site with the characteristics of the postsynaptic glycine receptor8–11. The behavioural and electrophysiological abnormalities of spastic mice are reproduced in normal mice given subconvulsive doses of strychnine4, suggesting that spastic symptoms might result from a deficiency in glycine-mediated inhibition4. We describe here evidence that supports this hypothesis: a decrease in 3H-strychnine binding in membrane fractions prepared from spastic compared with littermate control mice. We also demonstrate an involvement of the benzodiazepine, and possibly the GABA, binding site in the spastic phenotype.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chai, C. K. J. Hered. 52, 241–243 (1961).
Lane, P. W. J. Hered. 63, 135–140 (1972).
Lane, P. W. & Eicher, E. M. J. Hered. 70, 239–244 (1979); 71, 315–318 (1980).
Heller, A. H. & Hallett, M. Brain Res. 234, 299–308 (1982).
Chai, C. K., Roberts, E. & Sidman, R. L. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med. 109, 491–495 (1962).
Biscoe, T. J. & Fry, J. P. Br. J. Pharmac. 75, 23–35 (1982).
Curtis, D. R. & Johnston, G. A. R. Ergebn. Physiol. 69, 97–188 (1974).
Young, A. B. & Snyder, S. H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 70, 2832–2836 (1973).
Mackerer, C. R., Kochman, R. L., Shen, T. F. & Hershensen, F. M. J. Pharmac. exp. Ther. 201, 326–331 (1977).
Young, A. B. & Snyder, S. H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 71, 4002–4005 (1974).
Muller, W. E. & Snyder, S. H. Brain Res. 147, 107–116 (1978).
Biscoe, T. J., Fry, J. P., Martin, I. L. & Rickets, C. J. Physiol., Lond. 317, 32p–33p (1981).
Enna, S. J. & Snyder, S. H. Brain Res. 100, 81–97 (1975).
Speth, R. C. et al. Fedn Proc. 39, 3032–3038 (1980).
Yamamura, H. I. & Snyder, S. H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 71, 1725–1729 (1974).
Tallman, J. F., Thomas, J. W. & Gallager, D. W. Nature 274, 383–385 (1978).
Speth, R. C. & Yamamura, H. I. Eur. J. Pharmac. 54, 397–399 (1979).
Skolnick, P., Syapin, P. J., Paugh, B. & Paul, S. M. Nature 277, 397–398 (1979).
Lippa, A. S., Sano, M. C., Coupet, J., Klepner, C. A. & Beer, B. Life Sci. 23, 2213–2218 (1978).
Chang, R. S. L., Tran, V. T. & Snyder, S. H. Brain Res. 190, 95–110 (1980).
Olsen, R. W. & Mikoshiba, K. J. Neurochem. 30, 1633–1636 (1978).
Palacios, J. M., Wamsley, J. K. & Kuhar, M. J. Brain Res. 222, 285–307 (1981).
Zarbin, M. A., Wamsley, J. K. & Kuhar, M. J. J. Neurosci. 1, 532–547 (1981).
Young, W. S. III & Kuhar, M. J. J. Pharmac. exp. Ther. 212, 337–346 (1980).
Bradford, M. M. Analyt. Biochem. 72, 248–254 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
White, W., Heller, A. Glycine receptor alteration in the mutant mouse spastic. Nature 298, 655–657 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/298655a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/298655a0
This article is cited by
-
Molecular biology of glycinergic neurotransmission
Molecular Neurobiology (1997)
-
A missense mutation in the gene encoding the α1 subunit of the inhibitory glycine receptor in the spasmodic mouse
Nature Genetics (1994)
-
Glycine receptor β–subunit gene mutation in spastic mouse associated with LINE–1 element insertion
Nature Genetics (1994)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.