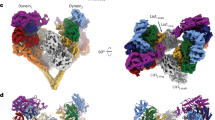
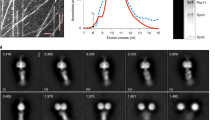
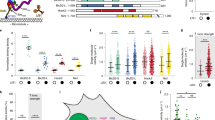
Abstract
CYTOPLASMIC dynein is a microtubule-activated ATPase which produces force towards the minus ends of microtubules1,2. It is thought to be responsible for retrograde axonal transport and other aspects of organelle motility2–6 and may have a role in the poleward movement of mitotic chromosomes7,8. Cytoplasmic dynein is an oligomeric complex of two catalytic heavy chains and a number of accessory subunits1,9,10. We now report the cloning and sequencing of a complementary DNA for one of these species, a cytoplasmic dynein-associated polypeptide of relative molecular mass 150,000 (Mr 150K). A full-length cDNA was found to contain an open reading frame of 4.0 kilobases, which is predicted to encode a polypeptide of Mr 145K11. It has extensive homology with the product of the Drosophila gene Glued, which encodes a poly-peptide of Mr 148K11. The Glued mutation is dominant, with pleiotropic developmental defects in heterozygotes and an em-bryonic lethal phenotype in homozygotes. As dominant mutations may involve disruption of normal protein–protein interactions, the Glued mutation should provide insight into the mode of action of cytoplasmic dynein in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paschal, B. M., Shpetner, H. S. & Vallee, R. B. J. Cell Biol. 105, 1273–1282 (1987).
Paschal, B. M. & Vallee, R. B. Nature 330, 181–183 (1987).
Forman, D. S., Brown, K. J. & Promesberger, M. E. Brain Res. 272, 194–197 (1983).
Schnapp, B. J. & Reese, T. S. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 1548–1552 (1989).
Schroer, T. A., Steuer, E. R. & Sheetz, M. P. Cell 56, 937–946 (1989).
Hirokawa, N. et al. J. Cell Biol. 111, 1027–1037 (1990).
Pfarr, C. M. et al. Nature 345, 263–265 (1990).
Steuer, E. et al. Nature 345, 266–268 (1990).
Vallee, R. B. et al. Nature 332 561–563 (1988).
Collins, C. A. & Vallee, R. B. Cell. Motil. Cytoskel. 14, 491–500 (1989).
Swaroop, A., Swaroop, M. & Garen, A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 6501–6505 (1987).
King, S. M. & Witman, G. B. J. biol. Chem. 265, 19807–19811 (1990).
Holzbaur, E. L. F., Kravit, N. G. & Vallee, R. B. J. Cell Biol. 109, 157a (1988).
Schroer, T. A. & Sheetz, M. P. J. Cell Biol. 111, 294a (1990).
Kozak, M. Cell 44, 283–292 (1986).
Plough, H. H. & Ives, P. T. Genetics 20, 42–69 (1935).
Meyerowitz, E. M. & Kankel, D. R. Devl Biol. 62, 112–142 (1978).
Garen, S. H. & Kankel, D. R. Devl Biol. 96, 445–466 (1983).
Harte, P. J. & Kankel, D. R. Genetics 101, 477–501 (1982).
Swaroop, A. et al. Molec. Cell Biol. 6, 833–841 (1986).
Swaroop, A., Paco-Larson, M. L. & Garen, A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 1751–1755 (1985).
Yoshida, T., Takanzri, H., & Izutsu, K. J. Cell Biol. 111, 296a (1990).
Vallee, R. B. Meth. Enzym. 134, 89–104 (1986).
Sambrook, J., Fritsh, F. & Maniatis, T. in Molecular Cloning (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1989).
Devereux, J., Haeberli, P. & Smithies, O. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 387–395 (1984).
Cleveland, D. W. et al. J. biol. Chem. 252, 1102–1106 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holzbaur , E., Hammarback, J., Paschal, B. et al. Homology of a 150K cytoplasmic dynein-associated polypeptide with the Drosophila gene Glued. Nature 351, 579–583 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/351579a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/351579a0
This article is cited by
-
The impact of cytoskeletal organization on the local regulation of neuronal transport
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2017)
-
Cytoplasmic dynein and early endosome transport
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2015)
-
Dynactin functions as both a dynamic tether and brake during dynein-driven motility
Nature Communications (2014)
-
Autoregulatory mechanism for dynactin control of processive and diffusive dynein transport
Nature Cell Biology (2014)
-
Evolution of the eukaryotic dynactin complex, the activator of cytoplasmic dynein
BMC Evolutionary Biology (2012)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.