Abstract
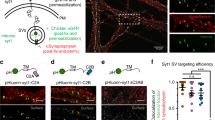
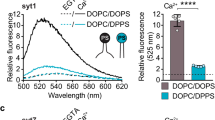
SYNAPTOTAGMINS (Syts) are brain-specific Ca2+/phospholipidbinding proteins1–5. In hippocampal synapses, Syt I is essential for fast Ca2+-dependent synaptic vesicle exocytosis but not for Ca2 +- independent exocytosis3. In vertebrates and invertebrates6–9, Syt may therefore participate in Ca22 +–dependent synaptic membrane fusion, either by serving as the Ca2 + sensor in the last step of fast Ca2 +-triggered neurotransmitter release, or by collaborating with an additional Ca2 + sensor. While Syt I binds Ca2 +(refs 10,11), its phospholipid binding is triggered at lower calcium concentrations (EC50 = 3–6µM) than those required for exocytosis12. Furthermore, Syts bind clathrin–AP2 with high affinity, indicating that they may play a general role in endocytosis4,5 rather than being confined to a specialized function in regulated exocytosis3. Here we resolve this apparent contradiction by describing four Syts, three of which (Syt VI, VII and VIII) are widely expressed in non-neural tissues. All Syts tested share a common domain structure, with a cytoplasmic region composed of two C2 domains that interacts with clathrin–AP2 (Kd = 0.1–1.0nM) and with neural and non-neural syntaxins. The first C2 domains of Syt I, II, III, V and VII, but not of IV, VI or VIII, bind phospholipids with a similar Ca2+–concentration dependence (EC50 = 3–6µM). The same C2 domains also bind syntaxin as a function of Ca2 + but the Ca2 +–concentration dependence of Syt I, II and V (>200 µM) differs from that of Syt III and VII (<10 µM). Syts therefore appear to be ubiquitous proteins with a role in exocytosis mediated by syntaxin binding. The Ca2 +levels needed to trigger syntaxin binding by the different Syts suggest that they play distinct roles in membrane fusion; the level required by Syt I approximates those required for synaptic exocytosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, M. K. & Scheller, R. H. A. Rev. Biochem. 63, 63–100 (1994).
Jahn, R. & Südhof, T. C. A. Rev. Neurosc. 17, 219–246 (1994).
Geppert, M. et al. Cell 79, 717–727 (1994).
Zhang, J. Z., Davletov, B. A., Südhof, T. C. & Anderson, R. G. W. Cell 78, 751–760 (1994).
Ullrich, U. et al. Neuron 13, 1281–1291 (1994).
Bommert, K. et al. Nature 363, 163–165 (1993).
Littleton, J. T., Stern, M., Schulze, K., Perlin, M. & Bellen, H. J. Cell 74, 1125–1134 (1993).
DiAntonio, A. & Schwarz, T. L. Neuron 12, 909–920 (1994).
Nonet, M. L. Grundahl, K., Meyer, B. J. & Rand, J. B. Cell 73, 1291–1305 (1993).
Brose, N., Petrenko, A. G., Südhof, T. C. & Jahn, R. Science 256, 1021–1025 (1992).
Davletov, B. A. & Südhof, T. C. J. biol. Chem. 268, 26386–26390 (1993).
Heidelberger, R., Heinemann, C., Neher, E. & Matthews, G. Nature 371, 513–515 (1994).
Perin, M. S., Fried, V. A., Mignery, G. A., Jahn, R. & Südhof, T. C. Nature 345, 260–261 (1990).
Geppert, M., Archer, B. T. & Südhof, T. C. J. biol. Chem. 266, 13548–13552 (1991).
Mizuta, M. et al. J. biol. Chem. 269, 11675–11678 (1994).
Hilbush, B. S. & Morgan, J. I. Proc. natn. Acad. U.S.A. 91, 8195–8199 (1994).
Hata, Y., Davletov, B., Petrenko, A. G., Jahn, R. & Südhof, T. C. Neuron 10, 307–315 (1993).
Perin, M. S. J. biol. Chem. 266, 623–629 (1994).
Bennett, M. K., Calakos, N. & Scheller, R. H. Science 257, 255–259 (1992).
Yoshida, A. et al. J. biol. Chem. 267, 25925–25928 (1992).
Davletov, B. A. & Südhof, T. C. J. biol. Chem. 269, 28547–28550 (1994).
Söllner, T., Bennett, M. K., Whiteheart, S. W., Scheller, R. H. & Rothman, J. E. Cell 75, 409–418 (1993).
Hayashi, T. et al. EMBO J. 13, 5051–5061 (1994).
McMahon, H. et al. Nature 364, 346–349 (1993).
Bennett, M. et al. Cell 74, 863–873 (1993).
Sutton, R. B., Davletov, B. A., Berghuis, A. M., Südhof, T. C. & Sprang, S. R. Cell 80, 929–938 (1995).
Goda, Y. & Stevens, C. F. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 12942–12946 (1994).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F. & Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual 2nd edn (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1989).
Guan, K. L. & Dixon, J. E. Analyt. Biochem. 192, 262–267 (1991).
Hata, Y., Slaughter, C. A. & Südhof, T. C. Nature 366, 347–351 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Ullrich, B., Zhang, J. et al. Ca2+-dependent and -independent activities of neural and non-neural synaptotagmins. Nature 375, 594–599 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/375594a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/375594a0
This article is cited by
-
Synaptotagmin-7 outperforms synaptotagmin-1 to promote the formation of large, stable fusion pores via robust membrane penetration
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Expression and Neurotransmitter Association of the Synaptic Calcium Sensor Synaptotagmin in the Avian Auditory Brain Stem
Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology (2022)
-
SYT8 promotes pancreatic cancer progression via the TNNI2/ERRα/SIRT1 signaling pathway
Cell Death Discovery (2021)
-
Function of Drosophila Synaptotagmins in membrane trafficking at synapses
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2021)
-
The cell adhesion protein CAR is a negative regulator of synaptic transmission
Scientific Reports (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.