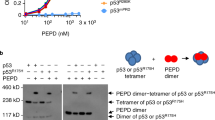
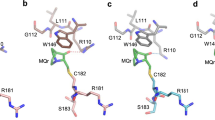
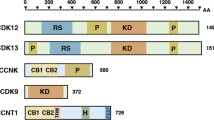
Abstract
CENTRAL to the role of p53 in cell regulation are its sequence-specific interactions with genes that control the cell cycle and apoptosis1,2. p53 response elements contain two or more copies of a somewhat promiscuous consensus sequence: 5′-XXXC(A,T)(T,A)GYYY-3′ (where X is a purine and Y is a pyrimidine) (ref. 3). The sequence-specific DNA-binding region of p53 resides in its central conserved region4. Although this region itself is not known to be phosphorylated, the amino and carboxy termini of human p53 contain sites for phosphorylation by several protein kinases. We have examined the role of cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) shown previously to phosphorylate human p53 at serine 315 (ref. 5). We report here that p53 is efficiently and selectively phosphor-ylated by S and G2/M Cdks. Such phosphorylation markedly stimulates sequence-specific DNA binding by p53 and also causes a distinctive conformational change in p53 as revealed by partial protease analysis. Strikingly, Cdk phosphorylation also confers binding-site preference on p53. These data suggest a potential regulatory mechanism of p53 activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levine, A. J. A. Rev. Biochem. 62, 623–651 (1993).
Donehower, L. A. & Bradley, A. Biochim. biophys. Acta 1155, 181–205 (1993).
Vogelstein, B. & Kinzler, K. W. Cell 70, 523–526 (1992).
Prives, C. Cell 78, 543–546 (1994).
Bischoff, J. R., Friedman, P. N., Marshak, D. R., Prives, C. & Beach, D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 4766–4770 (1990).
Meek, D. W., Simon, S., Kikkawa, U. & Eckhart, W. EMBO J. 9, 3253–3260 (1990).
Hupp, T. R., Meek, D. W., Midgley, C. A. & Lane, D. P. Cell 71, 875–886 (1992).
Nigro, J. M., Sikorski, R., Reed, S. I. & Vogelstein, B. Molec. cell. Biol. 12, 1357–1365 (1992).
Slingerland, J. M., Jenkins, J. R. & Benchimol, S. EMBO J. 12, 1029–1037 (1993).
Marston, N. J., Crook, T. & Vousden, K. H. Oncogene 9, 2707–2716 (1994).
Fiscella, M. et al. Oncogene 9, 3249–3257 (1994).
Lin, W. C. & Desiderio, S. Science 260, 953–959 (1993).
Sherr, C. J. Cell 79, 551–555 (1994).
Heichmann, K. A. & Roberts, J. M. Cell 79, 557–562 (1994).
King, R. W., Jackson, P. K. & Kirschner, M. W. Cell 79, 563–571 (1994).
Dynlacht, B. D., Flore, O., Lees, J. A. & Harlow, E. Genes Dev. 8, 1772–1786 (1994).
Sturzbecher, H. W. et al. Oncogene 5, 795–801 (1990).
Kastan, M. B. et al. Cell 71, 587–597 (1992).
Lu, X. & Lane, D. P. Cell 75, 765–778 (1993).
Okamoto, K. & Beach, D. EMBO J. 13, 4816–4822 (1994).
Michalovitz, D., Halevy, O. & Oren, M. Cell 62, 671–680 (1990).
Stewart, N., Hicks, G. G., Paraskevas, F. & Mowat, M. Oncogene 10, 109–115 (1995).
Cross, S. M. et al. Science 267, 1353–1356 (1995).
Xiong, Y., Zhang, H. & Beach, D. Cell 71, 505–514 (1992).
Hunter, T. & Karin, M. Cell 70, 375–387 (1992).
Friedman, P. N., Scott, S. E., Vogelstein, B. & Prives, C. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 9275–9279 (1990).
Dowdy, S. F. et al. Cell 79, 499–511 (1993).
Boyle, W. J., van der Geer, P. & Hunter, T. Meth. Enzym. 201, 110–148 (1991).
Bargonetti, J., Reynisdottir, I., Friedman, P. N. & Prives, C. Genes Dev. 6, 1886–1898 (1992).
el-Deiry, W. S. et al. Cell 75, 817–825 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Prives, C. Increased and altered DNA binding of human p53 by S and G2/M but not Gl cyclin-dependent kinases. Nature 376, 88–91 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/376088a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/376088a0
This article is cited by
-
Hybrid-DIA: intelligent data acquisition integrates targeted and discovery proteomics to analyze phospho-signaling in single spheroids
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Coordination between cell proliferation and apoptosis after DNA damage in Drosophila
Cell Death & Differentiation (2022)
-
Upregulated cyclins may be novel genes for triple-negative breast cancer based on bioinformatic analysis
Breast Cancer (2020)
-
TC2N, a novel oncogene, accelerates tumor progression by suppressing p53 signaling pathway in lung cancer
Cell Death & Differentiation (2019)
-
CDK4 inhibition diminishes p53 activation by MDM2 antagonists
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.