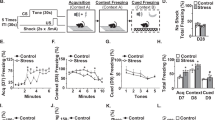
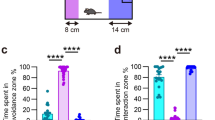
Abstract
Psychosocial stress contributes to the development of anxiety and depression. Recent clinical studies have reported increased inflammatory leukocytes in circulation of individuals with stress-related psychiatric disorders. Parallel to this, our work in mice shows that social stress causes release of inflammatory monocytes into circulation. In addition, social stress caused the development of prolonged anxiety that was dependent on inflammatory monocytes in the brain. Therefore, we hypothesize that chronic stress drives the production of inflammatory monocytes that are actively recruited to the brain by microglia, and these monocytes augment neuroinflammatory signaling and prolong anxiety. Here we show that repeated social defeat stress in mice activated threat appraisal centers in the brain that spatially coincided with microglial activation and endothelial facilitation of monocyte recruitment. Moreover, microglial depletion with a CSF1R antagonist prior to stress prevented the recruitment of monocytes to the brain and abrogated the development of anxiety. Cell-specific transcriptional profiling revealed that microglia selectively enhanced CCL2 expression, while monocytes expressed the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1β (IL-1β). Consistent with these profiles, the recruited inflammatory monocytes with stress adhered to IL-1R1+ neurovascular endothelial cells and this interaction was blocked by microglial depletion. Furthermore, disruption of IL-1β signaling by caspase-1KO specifically within bone marrow-derived cells revealed that monocytes promoted anxiogenesis through stimulation of neurovascular IL-1R1 by IL-1β. Collectively, the development of anxiety during stress was caused by microglial recruitment of IL-1β-producing monocytes, which stimulated brain endothelial IL-1R1. Thus, monocyte IL-1β production represents a novel mechanism that underlies behavioral complications associated with stress-related psychiatric disorders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kendler KS, Hettema JM, Butera F, Gardner CO, Prescott CA . Life event dimensions of loss, humiliation, entrapment, and danger in the prediction of onsets of major depression and generalized anxiety. Arch Gen Psychiat 2003; 60: 789–796.
Kendler KS, Karkowski LM, Prescott CA . Stressful life events and major depression: risk period, long-term contextual threat, and diagnostic specificity. J Nerv Ment Dis 1998; 186: 661–669.
Dantzer R, O'Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW . From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 2008; 9: 46–56.
Haroon E, Raison CL, Miller AH . Psychoneuroimmunology meets neuropsychopharmacology: translational implications of the impact of inflammation on behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012; 37: 137–162.
Beumer W, Gibney SM, Drexhage RC, Pont-Lezica L, Doorduin J, Klein HC et al. The immune theory of psychiatric diseases: a key role for activated microglia and circulating monocytes. J Leukoc Biol 2012; 92: 959–975.
Setiawan E, Wilson AA, Mizrahi R, Rusjan PM, Miler L, Rajkowska G et al. Role of translocator protein density, a marker of neuroinflammation, in the brain during major depressive episodes. JAMA Psychiatry 2015; 72: 268–275.
Castillo-Richmond A, Schneider RH, Alexander CN, Cook R, Myers H, Nidich S et al. Effects of stress reduction on carotid atherosclerosis in hypertensive African Americans. Stroke 2000; 31: 568–573.
Jakobsson J, Bjerke M, Sahebi S, Isgren A, Ekman CJ, Sellgren C et al. Monocyte and microglial activation in patients with mood-stabilized bipolar disorder. J Psychiatry Neurosci 2015; 40: 250–258.
Heidt T, Sager HB, Courties G, Dutta P, Iwamoto Y, Zaltsman A et al. Chronic variable stress activates hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Med 2014; 20: 754–758.
Cole SW, Hawkley LC, Arevalo JM, Cacioppo JT . Transcript origin analysis identifies antigen-presenting cells as primary targets of socially regulated gene expression in leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 3080–3085.
Hickey WF, Kimura H . Perivascular microglial cells of the CNS are bone marrow-derived and present antigen in vivo. Science 1988; 239: 290–292.
Mildner A, Schmidt H, Nitsche M, Merkler D, Hanisch UK, Mack M et al. Microglia in the adult brain arise from Ly-6ChiCCR2+ monocytes only under defined host conditions. Nat Neurosci 2007; 10: 1544–1553.
Raison CL, Capuron L, Miller AH . Cytokines sing the blues: inflammation and the pathogenesis of depression. Trends Immunol 2006; 27: 24–31.
Raison CL, Rutherford RE, Woolwine BJ, Shuo C, Schettler P, Drake DF et al. A randomized controlled trial of the tumor necrosis factor antagonist infliximab for treatment-resistant depression: the role of baseline inflammatory biomarkers. JAMA Psychiatry 2013; 70: 31–41.
Weinberger JF, Raison CL, Rye DB, Montague AR, Woolwine BJ, Felger JC et al. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor improves sleep continuity in patients with treatment resistant depression and high inflammation. Brain Behav Immun 2015; 47: 193–200.
Wohleb ES, McKim DB, Sheridan JF, Godbout JP . Monocyte trafficking to the brain with stress and inflammation: a novel axis of immune-to-brain communication that influences mood and behavior. Front Neurosci 2014; 8: 447.
Tuzcu EM, Kapadia SR, Tutar E, Ziada KM, Hobbs RE, McCarthy PM et al. High prevalence of coronary atherosclerosis in asymptomatic teenagers and young adults: evidence from intravascular ultrasound. Circulation 2001; 103: 2705–2710.
Powell ND, Sloan EK, Bailey MT, Arevalo JM, Miller GE, Chen E et al. Social stress up-regulates inflammatory gene expression in the leukocyte transcriptome via beta-adrenergic induction of myelopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 16574–16579.
Wohleb ES, Powell ND, Godbout JP, Sheridan JF . Stress-induced recruitment of bone marrow-derived monocytes to the brain promotes anxiety-like behavior. J Neurosci 2013; 33: 13820–13833.
Ressler KJ, Mayberg HS . Targeting abnormal neural circuits in mood and anxiety disorders: from the laboratory to the clinic. Nat Neurosci 2007; 10: 1116–1124.
Shin LM, Liberzon I . The neurocircuitry of fear, stress, and anxiety disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010; 35: 169–191.
Ataka K, Asakawa A, Nagaishi K, Kaimoto K, Sawada A, Hayakawa Y et al. Bone marrow-derived microglia infiltrate into the paraventricular nucleus of chronic psychological stress-loaded mice. PLoS ONE 2013; 8: e81744.
Brevet M, Kojima H, Asakawa A, Atsuchi K, Ushikai M, Ataka K et al. Chronic foot-shock stress potentiates the influx of bone marrow-derived microglia into hippocampus. J Neurosci Res 2010; 88: 1890–1897.
Wohleb ES, Hanke ML, Corona AW, Powell ND, Stiner LM, Bailey MT et al. β-Adrenergic receptor antagonism prevents anxiety-like behavior and microglial reactivity induced by repeated social defeat. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 6277–6288.
Wohleb ES, Patterson JM, Sharma V, Quan N, Godbout JP, Sheridan JF . Knockdown of interleukin-1 receptor type-1 on endothelial cells attenuated stress-induced neuroinflammation and prevented anxiety-like behavior. J Neurosci 2014; 34: 2583–2591.
Iwata M, Ota KT, Li XY, Sakaue F, Li N, Dutheil S et al. Psychological Stress Activates the Inflammasome via Release of Adenosine Triphosphate and Stimulation of the Purinergic Type 2X7 Receptor. Biol Psychiatry 2015; 80: 12–22.
Kreisel T, Frank MG, Licht T, Reshef R, Ben-Menachem-Zidon O, Baratta MV et al. Dynamic microglial alterations underlie stress-induced depressive-like behavior and suppressed neurogenesis. Mol Psychiatry 2014; 19: 699–709.
McKim DB, Patterson JM, Wohleb ES, Jarrett BL, Reader BF, Godbout JP et al. Sympathetic Release of Splenic Monocytes Promotes Recurring Anxiety Following Repeated Social Defeat. Biol Psychiatry 2015; 79: 803–813.
Ramirez K, Niraula A, Sheridan JF . GABAergic modulation with classical benzodiazepines prevent stress-induced neuro-immune dysregulation and behavioral alterations. Brain Behav Immun 2016; 51: 154–168.
Ferrarese C, Appollonio I, Bianchi G, Frigo M, Marzorati C, Pecora N et al. Benzodiazepine receptors and diazepam binding inhibitor: a possible link between stress, anxiety and the immune system. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1993; 18: 3–22.
Henry CJ, Huang Y, Wynne A, Hanke M, Himler J, Bailey MT et al. Minocycline attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation, sickness behavior, and anhedonia. J Neuroinflammation 2008; 5: 15.
McKim DB, Niraula A, Tarr AJ, Wohleb ES, Sheridan JF . Neuroinflammatory dynamics underlie memory impairments after repeated social defeat. 2016; 36: 2590–2604.
Dagher NN, Najafi AR, Kayala KM, Elmore MR, White TE, Medeiros R et al. Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor inhibition prevents microglial plaque association and improves cognition in 3xTg-AD mice. J Neuroinflammation 2015; 12: 139.
Capotondo A, Milazzo R, Politi LS, Quattrini A, Palini A, Plati T et al. Brain conditioning is instrumental for successful microglia reconstitution following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 15018–15023.
Maier SF . Bi-directional immune-brain communication: Implications for understanding stress, pain, and cognition. Brain Behav Immun 2003; 17: 69–85.
An Y, Chen Q, Quan N . Interleukin-1 exerts distinct actions on different cell types of the brain in vitro. J Inflamm Res 2011; 2011: 11–20.
Liu X, Yamashita T, Chen Q, Belevych N, McKim DB, Tarr AJ et al. Interleukin 1 type 1 receptor restore: a genetic mouse model for studying interleukin 1 receptor-mediated effects in specific cell types. J Neurosci 2015; 35: 2860–2870.
Quan N . In-depth conversation: spectrum and kinetics of neuroimmune afferent pathways. Brain Behav Immun 2014; 40: 1–8.
Sawicki C, McKim D, Wohleb E, Jarrett B, Reader B, Norden D et al. Social defeat promotes a reactive endothelium in a brain region-dependent manner with increased expression of key adhesion molecules, selectins and chemokines associated with the recruitment of myeloid cells to the brain. Neuroscience 2014; 302: 151–164.
Nourshargh S, Alon R . Leukocyte migration into inflamed tissues. Immunity 2014; 41: 694–707.
Hodes GE, Pfau ML, Leboeuf M, Golden SA, Christoffel DJ, Bregman D et al. Individual differences in the peripheral immune system promote resilience versus susceptibility to social stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111: 16136–16141.
Elmore MR, Najafi AR, Koike MA, Dagher NN, Spangenberg EE, Rice RA et al. Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor signaling is necessary for microglia viability, unmasking a microglia progenitor cell in the adult brain. Neuron 2014; 82: 380–397.
Chitu V, Nacu V, Charles JF, Henne WM, McMahon HT, Nandi S et al. PSTPIP2 deficiency in mice causes osteopenia and increased differentiation of multipotent myeloid precursors into osteoclasts. Blood 2012; 120: 3126–3135.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Institute of Health (NIMH) grants R01-MH-093473 and R01-MH093472 to JFS. DBM, MDW, CMS and BLJ were supported by NIDCR Training Grant T32-DE014320. DBM was supported by F31-MH-109234. Authors thank Brian West at Plexxikon for the use of PLX5622. We thank The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center's (OSUCCC) Analytical Cytometry and Nucleic Acid Shared Resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McKim, D., Weber, M., Niraula, A. et al. Microglial recruitment of IL-1β-producing monocytes to brain endothelium causes stress-induced anxiety. Mol Psychiatry 23, 1421–1431 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2017.64
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2017.64
This article is cited by
-
Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced macrophages of individuals with autism spectrum disorder adversely affect neuronal dendrites through the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines
Molecular Autism (2024)
-
Enhanced fear memory after social defeat in mice is dependent on interleukin-1 receptor signaling in glutamatergic neurons
Molecular Psychiatry (2024)
-
Distinguishing features of depression in dementia from primary psychiatric disease
Discover Mental Health (2024)
-
α7 Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: a key receptor in the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway exerting an antidepressant effect
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2023)
-
Noteworthy perspectives on microglia in neuropsychiatric disorders
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2023)