Abstract
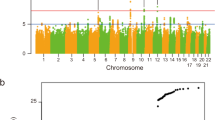
We identified a SNP in the DPP6 gene that is consistently strongly associated with susceptibility to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in different populations of European ancestry, with an overall P value of 5.04 × 10−8 in 1,767 cases and 1,916 healthy controls and with an odds ratio of 1.30 (95% confidence interval (CI) of 1.18–1.43). Our finding is the first report of a genome-wide significant association with sporadic ALS and may be a target for future functional studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rowland, L.P. & Shneider, N.A. N. Engl. J. Med. 344, 1688–1700 (2001).
Pasinelli, P. & Brown, R.H. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 7, 710–723 (2006).
Graham, A.J., Macdonald, A.M. & Hawkes, C.H. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 62, 562–569 (1997).
Greenway, M.J. et al. Nat. Genet. 38, 411–413 (2006).
Lambrechts, D. et al. Nat. Genet. 34, 383–394 (2003).
Sutedja, N.A. et al. Arch. Neurol. 64, 63–67 (2007).
Saeed, M. et al. Neurology 67, 771–776 (2006).
Veldink, J.H. et al. Neurology 65, 820–825 (2005).
Schymick, J.C. et al. Lancet Neurol. 6, 322–328 (2007).
Skol, A.D., Scott, L.J., Abecasis, G.R. & Boehnke, M. Nat. Genet. 38, 209–213 (2006).
Zaitlen, N., Kang, H.M., Eskin, E. & Halperin, E. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 80, 683–691 (2007).
Wada, K. et al. Mamm. Genome 4, 234–237 (1993).
Tachibana, T., Noguchi, K. & Ruda, M.A. Neurosci. Lett. 327, 133–137 (2002).
Dorus, S. et al. Cell 119, 1027–1040 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to the individuals and their families who participated in this project. This project has been generously supported by The Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO) and the “Prinses Beatrix Fonds” (L.H.vdB.). We would also like to thank H. Kersten and M. Kersten for their generous support (L.H.vdB.) as well as J.R. van Dijk and the Adessium foundation (L.H.vdB.), the US National Institutes of Health grants GM68875 and MH078075 (R.A.O.), the Kempe Foundation (P.M.A.), the Swedish Brain Research Foundation and Bertil Hållsten (P.M.A.), the Björklund Foundation for ALS Research (P.M.A.), the Interuniversity Attraction Pole Programme P6/43 (Belgian Science Policy Office) (W.R., L.V.D.B. and C.V.B.) and the E. von Behring Chair for Neuromuscular and Neurodegenerative Disorders (W.R.). C.V.B., W.R. and L.V.D.B. are supported by the Fund for Scientific Research Flanders (FWO-F), and K.S. holds a postdoctoral fellowship of the FWO-F. P.M.A. and A.B. are supported by the 'Swedish Brain Power Foundation'. This study used data from the SNP Database at the US National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke Human Genetics Resource Center DNA and Cell Line Repository (http://ccr.coriell.org/ninds/). The authors thank E. Strengman, P. Sodaar, H. Veldman, H. Yigittop, W. Scheveneels, A. D'hondt, P. Tilkin and A. Nilsson for assistance with genotyping and DNA preparation. We also thank F.G. Jennekens and G. Hille Ris Lambers for helping with the DNA sample collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.A.vE., P.W.J.vV., H.M.B. and L.F. contributed equally to this study. M.A.vE., P.W.J.vV., H.M.B. and R.vS. participated in the Illumina and TaqMan SNP genotyping and data analysis. M.A.vE., J.H.V. and L.F. were involved in the design of the study, handled genotype data and performed statistical analyses. M.A.vE., H.M.B., C.G.J.S., P.M.A., L.V.D.B., S.W.dJ., A.B., R.L., V.dJ., F.B., H.J.S., K.S., C.V.B., J.H.J.W., C.W. and W.R. were responsible for DNA collection and clinical characterization of affected individuals in the study. J.C.S. and B.J.T. obtained all DNA samples from the United States and performed genotyping experiments and analysis on these samples. M.A.vE. drafted the manuscript. R.A.O. and L.H.vdB. are lead investigators and contributed equally to this work. They designed and supervised the study and contributed in the writing of the manuscript. All authors participated in the critical revisions of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Methods, Supplementary Tables 1–5, Supplementary Figures 1–3 (PDF 885 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Es, M., van Vught, P., Blauw, H. et al. Genetic variation in DPP6 is associated with susceptibility to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Genet 40, 29–31 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2007.52
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2007.52
This article is cited by
-
Association between DPP6 gene rs10260404 polymorphism and increased risk of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (sALS): a meta-analysis
Neurological Sciences (2024)
-
Genetics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: seeking therapeutic targets in the era of gene therapy
Journal of Human Genetics (2023)
-
Loss of the fragile X syndrome protein FMRP results in misregulation of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
Nature Cell Biology (2021)
-
Activity-dependent isomerization of Kv4.2 by Pin1 regulates cognitive flexibility
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Monozygotic twins and triplets discordant for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis display differential methylation and gene expression
Scientific Reports (2019)