Abstract
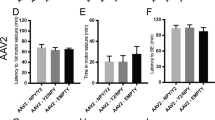
Seizure disorders present an attractive gene therapy target, particularly because viral vectors such as adeno-associated virus (AAV) and lentivirus can stably transduce neurons1,2,3. When we targeted the N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) excitatory amino acid receptor with an AAV-delivered antisense oligonucleotide, however, the promoter determined whether focal seizure sensitivity was significantly attenuated or facilitated4. One potential means to circumvent this liability would be to express an inhibitory neuroactive peptide and constitutively secrete the peptide from the transduced cell. The neuropeptide galanin can modulate seizure activity in vivo5,6, and the laminar protein fibronectin is usually secreted through a constitutive pathway7,8. Initially, inclusion of the fibronectin secretory signal sequence (FIB)9 in an AAV vector caused significant gene product secretion in vitro. More importantly, the combination of this secretory signal with the coding sequence for the active galanin peptide significantly attenuated in vivo focal seizure sensitivity, even with different promoters, and prevented kainic acid–induced hilar cell death. Thus, neuroactive peptide expression and local secretion provides a new gene therapy platform for the treatment of neurological disorders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Kaplitt, M.G. et al. Long term gene expression and phenotypic correction using adeno-associated virus vectors in the mammalian brain. Nat. Genet. 8,148–154 (1994).
McCown, T.J. et al. Differential and persistent expression patterns of CNS gene transfer by an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector. Brain Res. 713, 99–107 (1996).
Naldini, L. et al. Efficient transfer, integration and sustained long-term expression of the transgene in adult rat brains injected with a lentiviral vector. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 11382–11388 (1996).
Haberman, R.P. et al. Therapeutic liabilities of in vivo viral vector tropism: adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors, NMDAR 1 antisense and focal seizure sensitivity. Mol. Ther. 6, 495–500 (2002).
Mazarati, A.M. et al. Galanin modulation of seizures and seizure modulation of hippocampal galanin in animal models of status epilepticus. J. Neurosci. 18, 10070–10077 (1998).
Bartfai, T., Hokfelt, T. & Langel, U. Galanin—a neuroendocrine peptide. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 7, 229–274 (1993).
Hynes, R.O. Fibronectins. (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1990).
Kelly, R.B. Pathways of protein secretion in eukaryotes. Science 230, 25–32 (1985).
Schwarzbauer, J.E., Patel, R.S., Fonda, D. & Hynes, R.O. Multiple sites of alternative splicing of the rat fibronectin gene transcript. EMBO J. 6, 2573–2580 (1987).
Crawley, J.N. Galanin-acetylcholine interactions: relevance to memory and Alzheimer's disease. Life Sci. 58, 2185–2199 (1996).
Haberman, R.P., McCown, T.J. & Samulski, R.J. Inducible long-term gene expression in brain with adeno-associated virus gene transfer. Gene Ther. 5, 1604–1611 (1998).
McCown, T.J., Greenwood, R.S., Frye, G.D. & Breese, G.R. Electrically elicited seizures from the inferior colliculus: a potential site for the genesis of epilepsy? Exp. Neurol. 86, 527–542 (1984).
McCown, T.J., Duncan, G.E. & Breese, G.R. Neuroanatomical characterization of inferior collicular seizure genesis: 2-deoxyglucose and stimulation mapping. Brain Res. 567, 25–32 (1991).
Burazin, T.C.D., Larm, J.A., Ryan, M.C. & Gundlach, A.L. Galanin-R1 and -R2 receptor mRNA expression during the development of rat brain suggests differential subtype involvement in synaptic transmission and plasticity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 12, 2901–2917 (2000).
Baron, U. & Bujard, H. Tet repressor-based system for regulated gene expression in eukaryotic cells: principles and advances. Meth. Enzymol. 327, 401–421 (2000).
Nadler, J.V. Kainic acid as a tool for the study of temporal lobe epilepsy. Life Sci. 29, 2031–2042 (1981).
Buckmaster, P.S. & Dudek, F.E. Neuron loss, granule cell axon reorganization, and functional changes in the dentate gyrus of epileptic kainite-treated rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 385, 385–404 (1997).
Sarang, S.S. et al. Discovery of molecular mechanisms of neuroprotection using cell-based bioassays and oligonucleotide arrays. Physiol. Genomics 11, 45–52 (2002).
Ben-Ari,Y. Galanin and gilbenclamide modulate the anoxic release of glutamate in rat CA3 hippocampal neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1, 62–68 (1990).
Huber, H. et al. Grafts of adenosine-releasing cells suppress seizures in kindling epilepsy. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 7611–7616 (2001).
Haberman, R.P., McCown, T.J. & Samulski, R.J. Novel transcriptional regulatory signals in the adeno-associated virus terminal repeat A/D junction element. J. Virol. 74, 8732–8739 (2000).
Xiao, X., Li, J. & Samulski, R.J. Production of high-titer recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors in the absence of helper adenovirus. J. Virol. 72, 2224–2232 (1998).
Zeng, G. Sticky-end PCR: a new method for subcloning. Biotechniques 25, 206–208 (1998).
Paxinos, G. & Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates (Academic Press, San Diego, 1988).
Racine, R.J. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 32, 281–294 (1972).
Criswell, H.E. et al. Action of zolpidem on responses to GABA in relation to mRNAs for GABAA alpha receptor subunits within single cells: evidence for multiple functional GABAA isoreceptors on individual neurons. Neuropharmacology 36, 1641–1652 (1998).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the UNC Virus Vector Core for production of the recombinant AAV viruses and H.E. Criswell for his invaluable electrophysiological advice. This work was supported by National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke grant NS 35633 to T.J.M.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haberman, R., Samulski, R. & McCown, T. Attenuation of seizures and neuronal death by adeno-associated virus vector galanin expression and secretion. Nat Med 9, 1076–1080 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm901
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm901
This article is cited by
-
The current and emerging therapeutic approaches in drug-resistant epilepsy management
Acta Neurologica Belgica (2019)
-
A Molecular Approach to Epilepsy Management: from Current Therapeutic Methods to Preconditioning Efforts
Molecular Neurobiology (2015)
-
Gene therapy in epilepsy—is it time for clinical trials?
Nature Reviews Neurology (2014)
-
Progress in gene therapy for neurological disorders
Nature Reviews Neurology (2013)
-
HIV Tat Domain Improves Cross-correction of Human Galactocerebrosidase in a Gene- and Flanking Sequence-dependent Manner
Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids (2013)