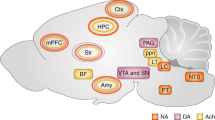
Abstract
How sensory information is transformed by learning into adaptive behaviors is a fundamental question in neuroscience. Studies of auditory fear conditioning have revealed much about the formation and expression of emotional memories and have provided important insights into this question. Classical work focused on the amygdala as a central structure for fear conditioning. Recent advances, however, have identified new circuits and neural coding strategies mediating fear learning and the expression of fear behaviors. One area of research has identified key brain regions and neuronal coding mechanisms that regulate the formation, specificity and strength of fear memories. Other work has discovered critical circuits and neuronal dynamics by which fear memories are expressed through a medial prefrontal cortex pathway and coordinated activity across interconnected brain regions. Here we review these recent advances alongside prior work to provide a working model of the extended circuits and neuronal coding mechanisms mediating fear learning and memory.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
LeDoux, J.E. Emotion circuits in the brain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 23, 155–184 (2000).
Davis, M. & Whalen, P.J. The amygdala: vigilance and emotion. Mol. Psychiatry 6, 13–34 (2001).
Maren, S. & Quirk, G.J. Neuronal signaling of fear memory. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 5, 844–852 (2004).
Fanselow, M.S. & Poulos, A.M. The neuroscience of mammalian associative learning. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 56, 207–234 (2005).
Duvarci, S. & Pare, D. Amygdala microcircuits controlling learned fear. Neuron 82, 966–980 (2014).
Pape, H.C. & Pare, D. Plastic synaptic networks of the amygdala for the acquisition, expression, and extinction of conditioned fear. Physiol. Rev. 90, 419–463 (2010).
Morrison, S.E. & Salzman, C.D. Re-valuing the amygdala. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 20, 221–230 (2010).
LeDoux, J.E. Coming to terms with fear. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 2871–2878 (2014).
Ehrlich, I. et al. Amygdala inhibitory circuits and the control of fear memory. Neuron 62, 757–771 (2009).
Sah, P., Faber, E.S., Lopez De Armentia, M. & Power, J. The amygdaloid complex: anatomy and physiology. Physiol. Rev. 83, 803–834 (2003).
Bienvenu, T.C., Busti, D., Magill, P.J., Ferraguti, F. & Capogna, M. Cell type–specific recruitment of amygdala interneurons to hippocampal theta rhythm and noxious stimuli in vivo. Neuron 74, 1059–1074 (2012).
McDonald, A.J., Mascagni, F., Mania, I. & Rainnie, D.G. Evidence for a perisomatic innervation of parvalbumin-containing interneurons by individual pyramidal cells in the basolateral amygdala. Brain Res. 1035, 32–40 (2005).
Romanski, L.M., Clugnet, M.C., Bordi, F. & LeDoux, J.E. Somatosensory and auditory convergence in the lateral nucleus of the amygdala. Behav. Neurosci. 107, 444–450 (1993).
Johansen, J.P., Tarpley, J.W., LeDoux, J.E. & Blair, H.T. Neural substrates for expectation-modulated fear learning in the amygdala and periaqueductal gray. Nat. Neurosci. 13, 979–986 (2010).
Uwano, T., Nishijo, H., Ono, T. & Tamura, R. Neuronal responsiveness to various sensory stimuli and associative learning in the rat amygdala. Neuroscience 68, 339–361 (1995).
Johansen, J.P., Cain, C.K., Ostroff, L.E. & LeDoux, J.E. Molecular mechanisms of fear learning and memory. Cell 147, 509–524 (2011).
Quirk, G.J., Repa, C. & LeDoux, J.E. Fear conditioning enhances short-latency auditory responses of lateral amygdala neurons: parallel recordings in the freely behaving rat. Neuron 15, 1029–1039 (1995).
Repa, J.C. et al. Two different lateral amygdala cell populations contribute to the initiation and storage of memory. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 724–731 (2001).
Goosens, K.A., Hobin, J.A. & Maren, S. Auditory-evoked spike firing in the lateral amygdala and Pavlovian fear conditioning: mnemonic code or fear bias? Neuron 40, 1013–1022 (2003).
Pitkänen, A., Savander, V. & LeDoux, J.E. Organization of intra-amygdaloid circuitries in the rat: an emerging framework for understanding functions of the amygdala. Trends Neurosci. 20, 517–523 (1997).
Herry, C. et al. Switching on and off fear by distinct neuronal circuits. Nature 454, 600–606 (2008).
Amano, T., Duvarci, S., Popa, D. & Pare, D. The fear circuit revisited: contributions of the basal amygdala nuclei to conditioned fear. J. Neurosci. 31, 15481–15489 (2011).
Wilensky, A.E., Schafe, G.E., Kristensen, M.P. & LeDoux, J.E. Rethinking the fear circuit: the central nucleus of the amygdala is required for the acquisition, consolidation and expression of Pavlovian fear conditioning. J. Neurosci. 26, 12387–12396 (2006).
Zimmerman, J.M., Rabinak, C.A., McLachlan, I.G. & Maren, S. The central nucleus of the amygdala is essential for acquiring and expressing conditional fear after overtraining. Learn. Mem. 14, 634–644 (2007).
Goosens, K.A. & Maren, S. Pretraining NMDA receptor blockade in the basolateral complex, but not the central nucleus, of the amygdala prevents savings of conditional fear. Behav. Neurosci. 117, 738–750 (2003).
Watabe, A.M. et al. Synaptic potentiation in the nociceptive amygdala following fear learning in mice. Mol. Brain 6, 11 (2013).
Li, H. et al. Experience-dependent modification of a central amygdala fear circuit. Nat. Neurosci. 16, 332–339 (2013).
Romanski, L.M. & LeDoux, J.E. Equipotentiality of thalamo-amygdala and thalamo-cortico-amygdala circuits in auditory fear conditioning. J. Neurosci. 12, 4501–4509 (1992).
Kholodar-Smith, D.B., Allen, T.A. & Brown, T.H. Fear conditioning to discontinuous auditory cues requires perirhinal cortical function. Behav. Neurosci. 122, 1178–1185 (2008).
Boatman, J.A. & Kim, J.J. A thalamo-cortico-amygdala pathway mediates auditory fear conditioning in the intact brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 24, 894–900 (2006).
Campeau, S. & Davis, M. Involvement of subcortical and cortical afferents to the lateral nucleus of the amygdala in fear conditioning measured with fear-potentiated startle in rats trained concurrently with auditory and visual conditioned stimuli. J. Neurosci. 15, 2312–2327 (1995).
Sacco, T. & Sacchetti, B. Role of secondary sensory cortices in emotional memory storage and retrieval in rats. Science 329, 649–656 (2010).
Letzkus, J.J. et al. A disinhibitory microcircuit for associative fear learning in the auditory cortex. Nature 480, 331–335 (2011).
Weinberger, N.M. Associative representational plasticity in the auditory cortex: a synthesis of two disciplines. Learn. Mem. 14, 1–16 (2007).
Weinberger, N.M. The medial geniculate, not the amygdala, as the root of auditory fear conditioning. Hear. Res. 274, 61–74 (2011).
Johansen, J.P., Wolff, S.B., Luthi, A. & LeDoux, J.E. Controlling the elements: an optogenetic approach to understanding the neural circuits of fear. Biol. Psychiatry 71, 1053–1060 (2012).
Aitkin, L.M. Medial geniculate body of the cat: responses to tonal stimuli of neurons in medial division. J. Neurophysiol. 36, 275–283 (1973).
Linke, R. & Schwegler, H. Convergent and complementary projections of the caudal paralaminar thalamic nuclei to rat temporal and insular cortex. Cereb. Cortex 10, 753–771 (2000).
Calford, M.B. & Webster, W.R. Auditory representation within principal division of cat medial geniculate body: an electrophysiology study. J. Neurophysiol. 45, 1013–1028 (1981).
Ryugo, D.K. & Weinberger, N.M. Differential plasticity of morphologically distinct neuron populations in the medical geniculate body of the cat during classical conditioning. Behav. Biol. 22, 275–301 (1978).
Maren, S., Yap, S.A. & Goosens, K.A. The amygdala is essential for the development of neuronal plasticity in the medial geniculate nucleus during auditory fear conditioning in rats. J. Neurosci. 21, RC135 (2001).
Han, J.H. et al. Increasing CREB in the auditory thalamus enhances memory and generalization of auditory conditioned fear. Learn. Mem. 15, 443–453 (2008).
Parsons, R.G., Riedner, B.A., Gafford, G.M. & Helmstetter, F.J. The formation of auditory fear memory requires the synthesis of protein and mRNA in the auditory thalamus. Neuroscience 141, 1163–1170 (2006).
Antunes, R. & Moita, M.A. Discriminative auditory fear learning requires both tuned and nontuned auditory pathways to the amygdala. J. Neurosci. 30, 9782–9787 (2010).
Schafe, G.E., Doyere, V. & LeDoux, J.E. Tracking the fear engram: the lateral amygdala is an essential locus of fear memory storage. J. Neurosci. 25, 10010–10014 (2005).
Tye, K.M. & Deisseroth, K. Optogenetic investigation of neural circuits underlying brain disease in animal models. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 13, 251–266 (2012).
Johansen, J.P. & Fields, H.L. Glutamatergic activation of anterior cingulate cortex produces an aversive teaching signal. Nat. Neurosci. 7, 398–403 (2004).
Shi, C. & Davis, M. Pain pathways involved in fear conditioning measured with fear-potentiated startle: lesion studies. J. Neurosci. 19, 420–430 (1999).
Brunzell, D.H. & Kim, J.J. Fear conditioning to tone, but not to context, is attenuated by lesions of the insular cortex and posterior extension of the intralaminar complex in rats. Behav. Neurosci. 115, 365–375 (2001).
Lanuza, E., Nader, K. & Ledoux, J.E. Unconditioned stimulus pathways to the amygdala: effects of posterior thalamic and cortical lesions on fear conditioning. Neuroscience 125, 305–315 (2004).
Gross, C.T. & Canteras, N.S. The many paths to fear. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 13, 651–658 (2012).
Di Scala, G., Mana, M.J., Jacobs, W.J. & Phillips, A.G. Evidence of Pavlovian conditioned fear following electrical stimulation of the periaqueductal grey in the rat. Physiol. Behav. 40, 55–63 (1987).
Kim, E.J. et al. Dorsal periaqueductal gray-amygdala pathway conveys both innate and learned fear responses in rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 14795–14800 (2013).
Johansen, J.P. et al. Optical activation of lateral amygdala pyramidal cells instructs associative fear learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 12692–12697 (2010).
Wolff, S.B. et al. Amygdala interneuron subtypes control fear learning through disinhibition. Nature 509, 453–458 (2014).
Johansen, J.P. et al. Hebbian and neuromodulatory mechanisms interact to trigger associative memory formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA (in the press).
Bajic, D. & Proudfit, H.K. Projections of neurons in the periaqueductal gray to pontine and medullary catecholamine cell groups involved in the modulation of nociception. J. Comp. Neurol. 405, 359–379 (1999).
Watabe-Uchida, M., Zhu, L., Ogawa, S.K., Vamanrao, A. & Uchida, N. Whole-brain mapping of direct inputs to midbrain dopamine neurons. Neuron 74, 858–873 (2012).
McNally, G.P., Johansen, J.P. & Blair, H.T. Placing prediction into the fear circuit. Trends Neurosci. 34, 283–292 (2011).
Tang, J. et al. Pavlovian fear memory induced by activation in the anterior cingulate cortex. Mol. Pain 1, 6 (2005).
Schultz, W., Dayan, P. & Montague, P.R. A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 275, 1593–1599 (1997).
Schultz, W. Updating dopamine reward signals. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 23, 229–238 (2013).
Young, S.L. & Fanselow, M.S. Associative regulation of Pavlovian fear conditioning: unconditional stimulus intensity, incentive shifts, and latent inhibition. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process. 18, 400–413 (1992).
Rescorla, R.A. & Wagner, A.R. A theory of pavlovian conditioning: variations in the effectiveness of reinforcement and nonreinforcement. in Classical Conditioning II: Current Research and Theory (eds. Black, A.H. & Prokasy, W.F.) (Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York, 1972).
Sutton, R.S. & Barto, A.G. Toward a modern theory of adaptive networks: expectation and prediction. Psychol. Rev. 88, 135–170 (1981).
Pearce, J.M. & Hall, G. A model for Pavlovian learning: variations in the effectiveness of conditioned but not of unconditioned stimuli. Psychol. Rev. 87, 532–552 (1980).
Belova, M.A., Paton, J.J., Morrison, S.E. & Salzman, C.D. Expectation modulates neural responses to pleasant and aversive stimuli in primate amygdala. Neuron 55, 970–984 (2007).
Klavir, O., Genud-Gabai, R. & Paz, R. Functional connectivity between amygdala and cingulate cortex for adaptive aversive learning. Neuron 80, 1290–1300 (2013).
McHugh, S.B. et al. Aversive prediction error signals in the amygdala. J. Neurosci. 34, 9024–9033 (2014).
Schoenbaum, G., Chiba, A.A. & Gallagher, M. Neural encoding in orbitofrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala during olfactory discrimination learning. J. Neurosci. 19, 1876–1884 (1999).
Shabel, S.J., Schairer, W., Donahue, R.J., Powell, V. & Janak, P.H. Similar neural activity during fear and disgust in the rat basolateral amygdala. PLoS ONE 6, e27797 (2011).
Roesch, M.R., Calu, D.J., Esber, G.R. & Schoenbaum, G. Neural correlates of variations in event processing during learning in basolateral amygdala. J. Neurosci. 30, 2464–2471 (2010).
Tye, K.M., Cone, J.J., Schairer, W.W. & Janak, P.H. Amygdala neural encoding of the absence of reward during extinction. J. Neurosci. 30, 116–125 (2010).
Roy, M. et al. Representation of aversive prediction errors in the human periaqueductal gray. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 1607–1612 (2014).
Bolles, R.C. & Fanselow, M.S. A perceptual-defensive-recuperative model of fear and pain. Behav. Brain Sci. 3, 291–323 (1980).
McNally, G.P. & Cole, S. Opioid receptors in the midbrain periaqueductal gray regulate prediction errors during pavlovian fear conditioning. Behav. Neurosci. 120, 313–323 (2006).
Helmstetter, F.J. & Tershner, S.A. Lesions of the periaqueductal gray and rostral ventromedial medulla disrupt antinociceptive but not cardiovascular aversive conditional responses. J. Neurosci. 14, 7099–7108 (1994).
Fanselow, M.S. Pavlovian conditioning, negative feedback and blocking: mechanisms that regulate association formation. Neuron 20, 625–627 (1998).
Furlong, T.M., Cole, S., Hamlin, A.S. & McNally, G.P. The role of prefrontal cortex in predictive fear learning. Behav. Neurosci. 124, 574–586 (2010).
Johansen, J.P., Hamanaka, H., Diaz-Mataix, L. & LeDoux, J.E. Hebbian and neuromodulatory mechanisms act synergistically to instruct associative memory formation. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 914.15 (2010).
Lima, S.Q., Hromadka, T., Znamenskiy, P. & Zador, A.M. PINP: a new method of tagging neuronal populations for identification during in vivo electrophysiological recording. PLoS ONE 4, e6099 (2009).
Courtin, J. et al. Prefrontal parvalbumin interneurons shape neuronal activity to drive fear expression. Nature 505, 92–96 (2014).
Senn, V. et al. Long-range connectivity defines behavioral specificity of amygdala neurons. Neuron 81, 428–437 (2014).
Pezze, M.A. & Feldon, J. Mesolimbic dopaminergic pathways in fear conditioning. Prog. Neurobiol. 74, 301–320 (2004).
Sara, S.J. The locus coeruleus and noradrenergic modulation of cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10, 211–223 (2009).
Bissière, S., Humeau, Y. & Luthi, A. Dopamine gates LTP induction in lateral amygdala by suppressing feedforward inhibition. Nat. Neurosci. 6, 587–592 (2003).
Grace, A.A. & Rosenkranz, J.A. Regulation of conditioned responses of basolateral amygdala neurons. Physiol. Behav. 77, 489–493 (2002).
Tully, K., Li, Y., Tsvetkov, E. & Bolshakov, V.Y. Norepinephrine enables the induction of associative long-term potentiation at thalamo-amygdala synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 14146–14150 (2007).
Heidbreder, C.A. & Groenewegen, H.J. The medial prefrontal cortex in the rat: evidence for a dorso-ventral distinction based upon functional and anatomical characteristics. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 27, 555–579 (2003).
LeDoux, J.E., Iwata, J., Cicchetti, P. & Reis, D.J. Different projections of the central amygdaloid nucleus mediate autonomic and behavioral correlates of conditioned fear. J. Neurosci. 8, 2517–2529 (1988).
Petrovich, G.D. & Swanson, L.W. Projections from the lateral part of the central amygdalar nucleus to the postulated fear conditioning circuit. Brain Res. 763, 247–254 (1997).
Ciocchi, S. et al. Encoding of conditioned fear in central amygdala inhibitory circuits. Nature 468, 277–282 (2010).
Haubensak, W. et al. Genetic dissection of an amygdala microcircuit that gates conditioned fear. Nature 468, 270–276 (2010).
Viviani, D. et al. Oxytocin selectively gates fear responses through distinct outputs from the central amygdala. Science 333, 104–107 (2011).
Penzo, M.A., Robert, V. & Li, B. Fear conditioning potentiates synaptic transmission onto long-range projection neurons in the lateral subdivision of central amygdala. J. Neurosci. 34, 2432–2437 (2014).
Quirk, G.J., Likhtik, E., Pelletier, J.G. & Pare, D. Stimulation of medial prefrontal cortex decreases the responsiveness of central amygdala output neurons. J. Neurosci. 23, 8800–8807 (2003).
Sotres-Bayon, F., Sierra-Mercado, D., Pardilla-Delgado, E. & Quirk, G.J. Gating of fear in prelimbic cortex by hippocampal and amygdala inputs. Neuron 76, 804–812 (2012).
Pi, H.J. et al. Cortical interneurons that specialize in disinhibitory control. Nature 503, 521–524 (2013).
Klavir, O., Genud-Gabai, R. & Paz, R. Low-frequency stimulation depresses the primate anterior-cingulate-cortex and prevents spontaneous recovery of aversive memories. J. Neurosci. 32, 8589–8597 (2012).
Maroun, M., Kavushansky, A., Holmes, A., Wellman, C. & Motanis, H. Enhanced extinction of aversive memories by high-frequency stimulation of the rat infralimbic cortex. PLoS ONE 7, e35853 (2012).
Likhtik, E., Pelletier, J.G., Paz, R. & Pare, D. Prefrontal control of the amygdala. J. Neurosci. 25, 7429–7437 (2005).
Livneh, U. & Paz, R. Amygdala-prefrontal synchronization underlies resistance to extinction of aversive memories. Neuron 75, 133–142 (2012).
Burgos-Robles, A., Vidal-Gonzalez, I. & Quirk, G.J. Sustained conditioned responses in prelimbic prefrontal neurons are correlated with fear expression and extinction failure. J. Neurosci. 29, 8474–8482 (2009).
Corcoran, K.A. & Quirk, G.J. Activity in prelimbic cortex is necessary for the expression of learned, but not innate, fears. J. Neurosci. 27, 840–844 (2007).
Buzsáki, G. & Draguhn, A. Neuronal oscillations in cortical networks. Science 304, 1926–1929 (2004).
Markram, H., Lubke, J., Frotscher, M. & Sakmann, B. Regulation of synaptic efficacy by coincidence of postsynaptic APs and EPSPs. Science 275, 213–215 (1997).
Kayser, C., Montemurro, M.A., Logothetis, N.K. & Panzeri, S. Spike-phase coding boosts and stabilizes information carried by spatial and temporal spike patterns. Neuron 61, 597–608 (2009).
Likhtik, E., Stujenske, J.M., Topiwala, M.A., Harris, A.Z. & Gordon, J.A. Prefrontal entrainment of amygdala activity signals safety in learned fear and innate anxiety. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 106–113 (2014).
Huxter, J., Burgess, N. & O'Keefe, J. Independent rate and temporal coding in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Nature 425, 828–832 (2003).
Huxter, J.R., Senior, T.J., Allen, K. & Csicsvari, J. Theta phase-specific codes for two-dimensional position, trajectory and heading in the hippocampus. Nat. Neurosci. 11, 587–594 (2008).
Benchenane, K. et al. Coherent theta oscillations and reorganization of spike timing in the hippocampal- prefrontal network upon learning. Neuron 66, 921–936 (2010).
Pastalkova, E., Itskov, V., Amarasingham, A. & Buzsaki, G. Internally generated cell assembly sequences in the rat hippocampus. Science 321, 1322–1327 (2008).
Adhikari, A., Topiwala, M.A. & Gordon, J.A. Single units in the medial prefrontal cortex with anxiety-related firing patterns are preferentially influenced by ventral hippocampal activity. Neuron 71, 898–910 (2011).
Popa, D., Duvarci, S., Popescu, A.T., Lena, C. & Pare, D. Coherent amygdalocortical theta promotes fear memory consolidation during paradoxical sleep. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 6516–6519 (2010).
Ascoli, G.A. et al. Petilla terminology: nomenclature of features of GABAergic interneurons of the cerebral cortex. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 557–568 (2008).
Lovett-Barron, M. et al. Regulation of neuronal input transformations by tunable dendritic inhibition. Nat. Neurosci. 15, 423–430 (2012).
Massi, L. et al. Temporal dynamics of parvalbumin-expressing axo-axonic and basket cells in the rat medial prefrontal cortex in vivo. J. Neurosci. 32, 16496–16502 (2012).
Baeg, E.H. et al. Fast spiking and regular spiking neural correlates of fear conditioning in the medial prefrontal cortex of the rat. Cereb. Cortex 11, 441–451 (2001).
Carlén, M. et al. A critical role for NMDA receptors in parvalbumin interneurons for gamma rhythm induction and behavior. Mol. Psychiatry 17, 537–548 (2012).
Acknowledgements
We thank T.C. Bienvenu, R.R. Rozeske and J. Ormond for helpful comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by grants to C.H. from the French National Research Agency (ANR-2010-BLAN-1442-01; ANR-10-EQPX-08 OPTOPATH; LABEX BRAIN ANR 10-LABX-43), the European Research Council under the European Union's Seventh Framework Program (FP7/2007-2013)/ERC grant agreement no. 281168, the Conseil Regional d'Aquitaine, and by grants to J.P.J. from MEXT (Brain Mapping by Integrated Neurotechnologies for Disease Studies (Brain/MINDS)), Strategic Research Program for Brain Sciences (11041047) and Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (25710003, 25116531).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herry, C., Johansen, J. Encoding of fear learning and memory in distributed neuronal circuits. Nat Neurosci 17, 1644–1654 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3869
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3869
This article is cited by
-
Plasticity of neuronal dynamics in the lateral habenula for cue-punishment associative learning
Molecular Psychiatry (2023)
-
Nigrostriatal dopamine modulates the striatal-amygdala pathway in auditory fear conditioning
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Plastic and stimulus-specific coding of salient events in the central amygdala
Nature (2023)
-
Activity-dependent organization of prefrontal hub-networks for associative learning and signal transformation
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Ventromedial prefrontal neurons represent self-states shaped by vicarious fear in male mice
Nature Communications (2023)