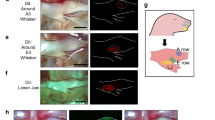
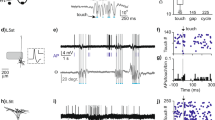
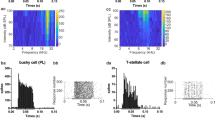
Abstract
To investigate synaptic events underlying sensory perception, we made whole-cell membrane potential recordings of barrel cortex neurons in awake mice while recording whisker-related behavior. During quiet periods, we recorded slow, large-amplitude membrane potential changes, which switched during whisking to small, fast fluctuations that were correlated with whisker position. Robust subthreshold responses were evoked by passive whisker stimulation during quiet behavior and by active whisker contact with an object.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Margrie, T.W., Brecht, M. & Sakmann, B. Pflugers Arch. 444, 491–498 (2002).
Petersen, C.C., Hahn, T.T., Mehta, M., Grinvald, A. & Sakmann, B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 13638–13643 (2003).
Cowan, R.L. & Wilson, C.J. J. Neurophysiol. 71, 17–32 (1994).
Timofeev, I., Grenier, F. & Steriade, M. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 1924–1929 (2001).
Fee, M.S., Mitra, P.P. & Kleinfeld, D. J. Neurophysiol. 78, 1144–1149 (1997).
Szwed, M., Bagdasarian, K. & Ahissar, E. Neuron 40, 621–630 (2003).
Mehta, S.B. & Kleinfeld, D. Neuron 41, 181–184 (2004).
Fanselow, E.E. & Nicolelis, M.A. J. Neurosci. 19, 7603–7616 (1999).
Castro-Alamancos, M.A. & Oldford, E. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 541, 319–331 (2002).
Hentschke, H., Haiss, F. & Schwarz, C. Cereb. Cortex published online 12 October 2005 (doi:10.1093/cercor/bhj056).
Wilent, W.B. & Contreras, D. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1364–1370 (2005).
Chung, S., Li, X. & Nelson, S.B. Neuron 34, 437–446 (2002).
Arabzadeh, E., Zorzin, E. & Diamond, M.E. PLoS Biol. 3, E17 (2005).
Jones, L.M., Depireux, D.A., Simons, D.J. & Keller, A. Science 304, 1986–1989 (2004).
Krupa, D.J., Wiest, M.C., Shuler, M.G., Laubach, M. & Nicolelis, M.A. Science 304, 1989–1992 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank R. Rödel (Max Planck Institute, Heidelberg, Germany) and C. Nicolas (Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland) for electronic design and construction of the magnetic whisker stimulators; E. Ahissar and M. Diamond for help and advice with whisker filming; and I. Ferezou, J.F.A. Poulet and A. Borgdorff for discussion and critical reading of the manuscript. The authors are grateful to the Swiss National Science Foundation and the Leenaards Foundation for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
EEG recordings from head-fixed mice (PDF 942 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Membrane potential dynamics during behavior (PDF 1093 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Measuring neuronal input resistance (PDF 644 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Comparison of quiet (Q) and whisking (W) behaviour (PDF 80 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Neurons selected for analysis (PDF 73 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crochet, S., Petersen, C. Correlating whisker behavior with membrane potential in barrel cortex of awake mice. Nat Neurosci 9, 608–610 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1690
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1690
This article is cited by
-
Endogenous cannabinoids in the piriform cortex tune olfactory perception
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Ongoing movement controls sensory integration in the dorsolateral striatum
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Abnormal patterns of sleep and waking behaviors are accompanied by neocortical oscillation disturbances in an Ank3 mouse model of epilepsy-bipolar disorder comorbidity
Translational Psychiatry (2023)
-
Heterogeneity of voltage gated sodium current density between neurons decorrelates spiking and suppresses network synchronization in Scn1b null mouse models
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Norepinephrine links astrocytic activity to regulation of cortical state
Nature Neuroscience (2023)