Abstract
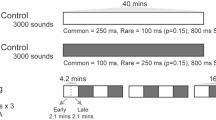
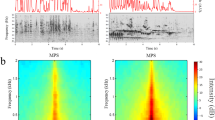
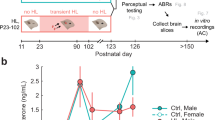
This study demonstrates that the adult form of 'tonotopic maps' of sound frequency in the rat primary auditory cortex (A1) arises from parallel developmental processes involving two cortical zones: the progressive differentiation and refinement of selectively tone-responsive receptive fields within an initially broadly-tuned posterior zone, and the progressive loss of tone-evoked, short-latency response over an initially large, very broadly tuned anterior zone. The formation of tonotopic maps in A1 was specifically influenced by a rat pup's early acoustic environments. Exposure to pulsed tones resulted in accelerated emergence and an expansion of A1 representations of those specific tone frequencies, as well as a deteriorated tonotopicity and broader-than-normal receptive fields. Thus, auditory experiences during early postnatal development are important in shaping the functional development of auditory cortical representations of specific acoustic environments.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Romand, R. Modification of tonotopic representation in the auditory system during development. Prog. Neurobiol. 51, 1–17 (1997).
Rauschecker, J. P. Auditory cortical plasticity: a comparison with other sensory systems. Trends Neurosci. 22, 74–80 (1999).
Clopton, B. M. & Winfield, J. A. Effect of early exposure to patterned sound on unit activity in rat inferior colliculus. J. Neurophysiol. 39, 1081–1089 (1976).
Sanes, D. H. & Constantine-Paton, M. Altered activity patterns during development reduce neural tuning. Science 16, 1183–1185 (1983).
Gao, E. & Suga, N. Experience-dependent corticofugal adjustment of midbrain frequency map in bat auditory system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 12663–12670 (1998).
Brugge, J. F., Reale, R. A. & Wilson, C. E. Sensitivity of auditory cortical neurons of kittens to monaural and binaural high frequency sound. Hear. Res. 34, 127–140 (1988).
Eggermont, J. J. Maturational aspects of periodicity coding in cat primary auditory cortex. Hear. Res. 57, 45–56 (1991).
Heil, P. & Scheich, H. Spatial representation of frequency-modulated signals in the tonotopically organized auditory cortex analogue of the chick. J. Comp. Neurol. 322, 548–565 (1992).
Katz, L. C. & Shatz, C. J. Synaptic activity and the construction of cortical circuits. Science 274, 1133–1138 (1996).
Fox, K. The role of excitatory amino acid transmission in development and plasticity of SI barrel cortex. Prog. Brain Res. 108, 219–234 (1996).
Buonomano, D. V. & Merzenich, M. M. Cortical plasticity: from synapses to maps. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 21, 149–186 (1998).
Weinberger, N. M. Dynamic regulation of receptive fields and maps in the adult sensory cortex. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 18, 129 (1995).
Stanton, S. G. & Harrison, R. V. Abnormal cochleotopic organization in the auditory cortex of cats reared in a frequency augmented environment. Audit. Neurosci. 2, 97–107 (1996).
Rajan, R., Irvine, D. R., Wise, L. Z. & Heil, P. Effect of unilateral partial cochlear lesions in adult cats on the representation of lesioned and unlesioned cochleas in primary auditory cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 338, 17–49 (1993).
Harrison, R. V., Stanton, S. G., Ibrahim, D., Nagasawa, A. & Mount, R. J. Neonatal cochlear hearing loss results in developmental abnormalities of the central auditory pathways. Acta. Otolaryngol. 113, 296–302 (1993).
Ahissar, E. et al. Dependence of cortical plasticity on correlated activity of single neurons and on behavioral context. Science 257, 1412–1415 (1992).
Recanzone, G. H., Schreiner, C. E. & Merzenich, M. M. Plasticity in the frequency representation of primary auditory cortex following discrimination training in adult owl monkeys. J. Neurosci. 13, 87–103 (1993).
Kilgard, M. P. & Merzenich, M. M. Cortical map reorganization enabled by nucleus basalis activity. Science 279, 1714–1718 (1998).
Pantev, C. et al. Increased auditory cortical representation in musicians. Nature 392, 811–814 (1998).
Gao, E. & Suga, N. Experience-dependent plasticity in the auditory cortex and the inferior colliculus of bats: role of the corticofugal system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 8081–8086 (2000).
Frost, D. O. Sensory processing by novel, experimentally induced cross-modal circuits. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 608, 92–112 (1990).
Sharma, J., Angelucci, A. & Sur, M. Induction of visual orientation modules in auditory cortex. Nature 404, 841–847 (2000).
von Melchner, L., Pallas, S. L. & Sur, M. Visual behaviour mediated by retinal projections directed to the auditory pathway. Nature 404, 871–876 (2000).
Kuhl, P. K., Williams, K. A., Lacerda, F., Stevens, K. N. & Lindblom, B. Linguistic experience alters phonetic perception in infants by 6 months of age. Science 255, 606–608 (1992).
Tallal, P. et al. Language comprehension in language-learning impaired children improved with acoustically modified speech. Science 271, 81–84 (1996).
Doupe, A. J. & Kuhl, P. K. Birdsong and human speech: common themes and mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 22, 567–631 (1999).
Kelly, J. B. & Sally, S. L. Organization of auditory cortex in the albino rat: sound frequency. J. Neurophysiol. 59, 1627–1638 (1988).
Kilgard, M. P. & Merzenich, M. M. Distributed representation of spectral and temporal information in rat primary auditory cortex. Hear. Res. 134, 16–28 (1999).
Friauf, E. Tonotopic order in the adult and developing auditory system of the rat as shown by c-fos immunohistochemistry. Eur. J. Neurosci. 4, 798–808 (1992).
Blatchley, B. J., Cooper, W. A. & Coleman, J. R. Development of auditory brainstem response to tone pip stimuli in the rat. Brain Res. 429, 75–84 (1987).
Eggermont, J. J. Differential maturation rates for response parameters in cat primary auditory cortex. Audit. Neurosci. 2, 309–327 (1996).
Horikawa, J., Ito, S., Hosokawa, Y., Homma, T. & Murata, K. Tonotopic representation in the rat auditory cortex. Proc. Japan Acad. 64B, 260–263 (1988).
Zilles, K. in The Cerebral Cortex of the Rat (eds. Kolb, B. & Tees, R. C.) 77–112 (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1990).
Puel, J. L. & Uziel, A. Correlative development of cochlear action potential sensitivity, latency, and frequency selectivity. Brain Res. 15, 179–88 (1987).
Sanes, D. H. & Constantine-Paton, M. The sharpening of frequency tuning curves requires patterned activity during development in the mouse, Mus musculus. J. Neurosci. 5, 1152–1166 (1985).
Poon, P. W. & Chen, X. Postnatal exposure to tones alters the tuning characteristics of inferior collicular neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 585, 391–394 (1992).
King, A. J., Hutchings, M. E., Moore, D. R. & Blakemore, C. Developmental plasticity in the visual and auditory representations in the mammalian superior colliculus. Nature 332, 73–76 (1988).
Knudsen, E. I. Capacity for plasticity in the adult owl auditory system expanded by juvenile experience. Science 279, 1531–1533 (1998).
Condon, C. D. & Weinberger, N. M. Habituation produces frequency-specific plasticity of receptive fields in the auditory cortex. Behav. Neurosci. 105, 416–430 (1991).
Weliky, M. & Katz, L. C. Disruption of orientation tuning in visual cortex by artificially correlated neuronal activity. Nature 386, 680–685 (1997).
Schmidt, J. T. & Buzzard, M. Activity-driven sharpening of the retinotectal projection in goldfish: development under stroboscopic illumination prevents sharpening. J. Neurobiol. 24, 384–399 (1993).
Feldman, D. E., Nicoll, R. A. & Malenka, R. C. Synaptic plasticity at thalamocortical synapses in developing rat somatosensory cortex: LTP, LTD, and silent synapses. J. Neurobiol. 41, 92–101 (1999).
Zhang, L. I., Tao, H. W. & Poo, M. Visual input induces long-term potentiation of developing retinotectal synapses. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 708–715 (2000).
Zheng, C., Feinstein, P., Bozza, T., Rodriguez, I. & Mombaerts, P. Peripheral olfactory projections are differentially affected in mice deficient in a cyclic nucleotide-gated channel subunit. Neuron 26, 81–91 (2000).
Lin, D. M. et al. Formation of precise connections in the olfactory bulb occurs in the absence of odorant-evoked neuronal activity. Neuron 26, 69–80 (2000).
Crair, M. C., Gillespie, D. C. & Stryker, M. P. The role of visual experience in the development of columns in cat visual cortex. Science 279, 566–570 (1998).
Crowley, J. C. & Katz, L. C. Early development of ocular dominance columns. Science 290, 1321–1324 (2000).
Penn, A. A., Riquelme, P. A., Feller, M. B. & Shatz, C. J. Competition in retinogeniculate patterning driven by spontaneous activity. Science 279, 2108–2112 (1998).
Penn, A. A. & Shatz, C. J. Brain waves and brain wiring: the role of endogenous and sensory-driven neural activity in development. Pediatr. Res. 45, 447–458 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Blake, T. Moallem, H. Tao and M. Poo for discussion. This work was supported by NIH grants NS-10414 and NS-34835 and by grants from the Sandler and MIND Foundations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Bao, S. & Merzenich, M. Persistent and specific influences of early acoustic environments on primary auditory cortex. Nat Neurosci 4, 1123–1130 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn745
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn745
This article is cited by
-
Juvenile depletion of microglia reduces orientation but not high spatial frequency selectivity in mouse V1
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
A cross-species assay demonstrates that reward responsiveness is enduringly impacted by adverse, unpredictable early-life experiences
Neuropsychopharmacology (2022)
-
Bone conducted responses in the neonatal rat auditory cortex
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
On the relationship between maps and domains in inferotemporal cortex
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2021)
-
Development of Auditory Cortex Circuits
Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology (2021)