Abstract
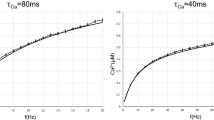
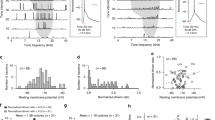
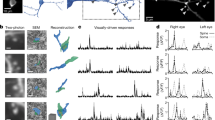
Sound features are blended together en route to the central nervous system before being discriminated for further processing by the cortical synaptic network. The mechanisms underlying this synaptic processing, however, are largely unexplored. Intracortical processing of the auditory signal was investigated by simultaneously recording from pairs of connected principal neurons in layer II/III in slices from A1 auditory cortex. Physiological patterns of stimulation in the presynaptic cell revealed two populations of postsynaptic events that differed in mean amplitude, failure rate, kinetics and short-term plasticity. In contrast, transmission between layer II/III pyramidal neurons in barrel cortex were uniformly of large amplitude and high success (release) probability (Pr). These unique features of auditory cortical transmission may provide two distinct mechanisms for discerning and separating transient from stationary features of the auditory signal at an early stage of cortical processing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rouiller, E., de Ribaupierre, Y., Toros-Morel, A. & de Ribaupierre, F. Neural coding of repetitive clicks in the medial geniculate body of the cat. Hear. Res. 5, 81–100 (1981).
Phillips, D. P. & Kelly, J. B. Coding of tone-pulse amplitude by single neurons in auditory cortex of albino rat. Hear. Res. 37, 269–280 (1989).
Clarey, J. C., Barone, P. & Imig, T. J. in The Mammalian Auditory Pathway: Neurophysiology (eds. Popper, A. N. & Fay, R. R.) 232–334 (Springer, New York, 1992).
Winer, J. A. The pyramidal neurons in layer III of cat primary auditory cortex (AI). J. Comp. Neurol. 229, 476–496 (1984).
Winer, J. A. Structure of layer II in cat primary auditory cortex (AI). J. Comp. Neurol. 238, 10–37 (1985).
Metherate, R. & Aramakis, V. B. Intrinsic electrophysiology of neurons in thalamorecipient layers of developing rat auditory cortex. Dev. Brain Res. 115, 131–44 (1999).
Clarke, S., de Ribaupierre, F., Rouiller, E. M. & de Ribaupierre, Y. Several neuronal and axonal types form long intrinsic connections in the cat primary auditory cortical field (AI). Anat. Embryol. (Berl.) 188, 117–138 (1993).
Shen, J. X., Xu, Z. M. & Yao, Y. D. Evidence for columnar organization in the auditory cortex of the mouse. Hear. Res. 137, 174–177 (1999).
Blaschke, M. et al. A single amino-acid determines the subunit-specific spider toxin block of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionate kainate receptor channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 6528–6528 (1993).
Brackley, P. T., Bell, D. R., Choi, D. K., Nakanishi, K. & Usherwood, P. N. Selective antagonism of native and cloned kainate and NMDA receptors by polyamine-containing toxins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 266, 1573–1580 (1993).
Herlitze, S. et al. Argiotoxin detects molecular differences in AMPA receptor channels. Neuron 10, 1131–1140 (1993).
Washburn, M. S. & Dingledine, R. Block of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors by polyamines and polyamine toxins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 278, 669–678 (1996).
Toth, K., & McBain, C. J. Afferent specific innervation of two distinct AMPA receptor subtypes on single hippocampal interneurons. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 572–578 (1998).
Dingledine, R., Borges, K., Bowie, D. & Traynelis, S. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 51, 7–61 (1999).
Markram, H., Lubke, J., Frotscher, M., Roth, A. & Sakmann, B. Physiology and anatomy of synaptic connections between thick tufted pyramidal neurones in the developing rat neocortex. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 500, 409–440 (1997).
Faber, D. & Korn, H. Applicability of the coefficient of variation method for analyzing synaptic plasticity. Biophys. J. 60, 1288–1291 (1991).
DeCharms, R. C., Blake, D. T. & Merzenich, M. M. Optimizing sound features for cortical neurons. Science 280, 1439–1443 (1998).
DeCharms, R. C. & Zador, A. Neural representation and the cortical code. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 23, 613–647 (2000).
Kilgard, M. P. & Merzenich, M. M. Plasticity of temporal information processing in the primary auditory cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 727–731 (1998).
Zucker, R. S. Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 12, 13–31 (1989).
Zucker, R. S. Calcium- and activity-dependent synaptic plasticity. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 9, 305–313 (1999).
Debanne, D., Guerineau, N. C., Gahwiler, B. H. & Thompson, S. M. Paired pulse facilitation and depression at unitary synapses in rat hippocampus: quantal fluctuation affects subsequent release. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 491, 163–176 (1996).
Feldman, D. E. Timing-based LTP and LTD at vertical inputs to Layer II/III pyramidal cells in rat barrel cortex. Neuron 27, 45–56 (2000).
Schreiner, C. E., Read, H. L. & Sutter, M. L. Modular organization of frequency integration in primary auditory cortex. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 23, 501–529 (2000).
Abbott, L. F., Varela, J. A., Sen, K. & Nelson, S. B. Synaptic depression and control of cortical gain. Science 275, 220–224 (1997).
Giraud, A. et al. Representation of the temporal envelope sounds in the human brain. J. Neurophysiol. 22, 1588–1598 (2000).
Kaas, J. & Hackett, T. 'What' and 'where' processing in the auditory cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 1045–1047 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Feldman for his assistance in preparing Barrel cortex slices and C. Trouth for cell reconstruction and camera lucida drawings of neurons. This work was supported by an Intramural Research award to C.McB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atzori, M., Lei, S., Evans, D. et al. Differential synaptic processing separates stationary from transient inputs to the auditory cortex. Nat Neurosci 4, 1230–1237 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn760
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn760
This article is cited by
-
Stimulus dependent transformations between synaptic and spiking receptive fields in auditory cortex
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Norepinephrine Homogeneously Inhibits α-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate- (AMPAR-) Mediated Currents in All Layers of the Temporal Cortex of the Rat
Neurochemical Research (2009)
-
The dual-pathway model of auditory signal processing
Neuroscience Bulletin (2008)
-
Excitatory signal flow and connectivity in a cortical column: focus on barrel cortex
Brain Structure and Function (2007)