Abstract
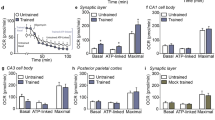
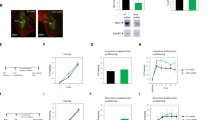
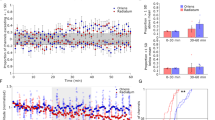
Induction and expression of long-term potentiation (LTP) in area CA1 of the hippocampus require the coordinated regulation of several cellular processes. We found that LTP in area CA1 was associated with an N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor–dependent increase in glutamate uptake. The increase in glutamate uptake was inhibited by either removal of Na+ or addition of d,l-threo-β-hydroxyaspartate. Dihydrokainate (DHK), a specific inhibitor of the glial glutamate transporter GLT-1, did not block the increase in glutamate uptake. LTP was also associated with a translocation of the EAAC1 glutamate transporter from the cytosol to the plasma membrane. Contextual fear conditioning increased the maximum rate (Vmax) of glutamate uptake and membrane expression of EAAC1 in area CA1. These results indicate that regulation of glutamate uptake may be important for maintaining the level of synaptic strength during long-term changes in synaptic efficacy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Diamond, J. S. & Jahr, C. E. Transporters buffer synaptically released glutamate on a submillisecond time scale. J. Neurosci. 17, 4672–4687 (1997).
Grewer, C., Watzke, N., Wiessner, M. & Rauen, T. Glutamate translocation of the neuronal glutamate transporter EAAC1 occurs within milliseconds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 9706–9711 (2000).
Mennerick, S. & Zorumski, C. F. Glial contributions to excitatory neurotransmission in cultured hippocampal cells. Nature 368, 59–62 (1994).
Tong, G. & Jahr, C. E. Block of glutamate transporters potentiates postsynaptic excitation. Neuron 13, 1195–1203 (1994).
Tanaka, K. et al. Epilepsy and exacerbation of brain injury in mice lacking the glutamate transporter GLT-1. Science 276, 1699–1702 (1997).
Overstreet, L. S., Kinney, G. A., Liu, Y. B., Billups, D. & Slater, N. T. Glutamate transporters contribute to the time course of synaptic transmission in cerebellar granule cells. J. Neurosci. 19, 9663–9673 (1999).
Turecek, R. & Trussell, L. O. Control of synaptic depression by glutamate transporters. J. Neurosci. 20, 2054–2063 (2000).
Brasnjo, G. & Otis, T. S. Neuronal glutamate transporters control activation of postsynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptors and influence cerebellar long-term depression. Neuron 31, 607–616 (2001).
Danbolt, N. C. Glutamate uptake. Prog. Neurobiol. 65, 1–105 (2001).
Harris, K. M. & Stevens, J. K. Dendritic spines of CA 1 pyramidal cells in the rat hippocampus: serial electron microscopy with reference to their biophysical characteristics. J. Neurosci. 9, 2982–2997 (1989).
Sorra, K. E. & Harris, K. M. Occurrence and three-dimensional structure of multiple synapses between individual radiatum axons and their target pyramidal cells in hippocampal area CA1. J. Neurosci. 13, 3736–3748 (1993).
Lehre, K. P. & Danbolt, N. C. The number of glutamate transporter subtype molecules at glutamatergic synapses: chemical and stereological quantification in young adult rat brain. J. Neurosci. 18, 8751–8757 (1998).
Rothstein, J. D. et al. Knockout of glutamate transporters reveals a major role for astroglial transport in excitotoxicity and clearance of glutamate. Neuron 16, 675–686 (1996).
Rothstein, J. D. et al. Localization of neuronal and glial glutamate transporters. Neuron 13, 713–725 (1994).
He, Y., Janssen, W. G., Rothstein, J. D. & Morrison, J. H. Differential synaptic localization of the glutamate transporter EAAC1 and glutamate receptor subunit GluR2 in the rat hippocampus. J. Comp. Neurol. 418, 255–269 (2000).
Arriza, J. L. et al. Functional comparisons of three glutamate transporter subtypes cloned from human motor cortex. J. Neurosci. 14, 5559–5569 (1994).
Torp, R., Hoover, F., Danbolt, N. C., Storm-Mathisen, J. & Ottersen, O. P. Differential distribution of the glutamate transporters GLT1 and rEAAC1 in rat cerebral cortex and thalamus: an in situ hybridization analysis. Anat. Embryol. (Berl.) 195, 317–326 (1997).
Gundersen, V., Danbolt, N. C., Ottersen, O. P. & Storm-Mathisen, J. Demonstration of glutamate/aspartate uptake activity in nerve endings by use of antibodies recognizing exogenous d-aspartate. Neuroscience 57, 97–111 (1993).
Bergles, D. E. & Jahr, C. E. Glial contribution to glutamate uptake at Schaffer collateral-commissural synapses in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 18, 7709–7716 (1998).
Ng, K. T. et al. Complex roles of glutamate in the Gibbs-Ng model of one-trial aversive learning in the new-born chick. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 21, 45–54 (1997).
Levenson, J. et al. Long-term regulation of neuronal high-affinity glutamate and glutamine uptake in Aplysia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 12858–12863 (2000).
Maleszka, R., Helliwell, P. & Kucharski, R. Pharmacological interference with glutamate re-uptake impairs long-term memory in the honeybee, Apis mellifera. Behav. Brain Res. 115, 49–53 (2000).
Harris, E. W., Ganong, A. H. & Cotman, C. W. Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus involves activation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. Brain Res. 323, 132–137 (1984).
Frey, U., Krug, M., Reymann, K. G. & Matthies, H. Anisomycin, an inhibitor of protein synthesis, blocks late phases of LTP phenomena in the hippocampal CA1 region in vitro. Brain Res. 452, 57–65 (1988).
Kang, H. & Schuman, E. M. A requirement for local protein synthesis in neurotrophin-induced hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Science 273, 1402–1406 (1996).
Malenka, R. C., Ayoub, G. S. & Nicoll, R. A. Phorbol esters enhance transmitter release in rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 403, 198–203 (1987).
Malinow, R., Schulman, H. & Tsien, R. W. Inhibition of postsynaptic PKC or CaMKII blocks induction but not expression of LTP. Science 245, 862–866 (1989).
Dowd, L. A. & Robinson, M. B. Rapid stimulation of EAAC1-mediated Na+-dependent L-glutamate transport activity in C6 glioma cells by phorbol ester. J. Neurochem. 67, 508–516 (1996).
Furuta, A., Martin, L. J., Lin, C. L., Dykes-Hoberg, M. & Rothstein, J. D. Cellular and synaptic localization of the neuronal glutamate transporters excitatory amino acid transporter 3 and 4. Neuroscience 81, 1031–1042 (1997).
Davis, K. E. et al. Multiple signaling pathways regulate cell surface expression and activity of the excitatory amino acid carrier 1 subtype of Glu transporter in C6 glioma. J. Neurosci. 18, 2475–2485 (1998).
Atkins, C. M., Selcher, J. C., Petraitis, J. J., Trzaskos, J. M. & Sweatt, J. D. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 602–609 (1998).
Impey, S. et al. Stimulation of cAMP response element (CRE)-mediated transcription during contextual learning. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 595–601 (1998).
Huerta, P. T., Sun, L. D., Wilson, M. A. & Tonegawa, S. Formation of temporal memory requires NMDA receptors within CA1 pyramidal neurons. Neuron 25, 473–480 (2000).
Rampon, C. et al. Enrichment induces structural changes and recovery from nonspatial memory deficits in CA1 NMDAR1-knockout mice. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 238–244 (2000).
Aggleton, J. P., Vann, S. D., Oswald, C. J. & Good, M. Identifying cortical inputs to the rat hippocampus that subserve allocentric spatial processes: a simple problem with a complex answer. Hippocampus 10, 466–474 (2000).
Casado, M. et al. Phosphorylation and modulation of brain glutamate transporters by protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 27313–27317 (1993).
Jackson, M. et al. Modulation of the neuronal glutamate transporter EAAT4 by two interacting proteins. Nature 410, 89–93 (2001).
Lin, C. I. et al. Modulation of the neuronal glutamate transporter EAAC1 by the interacting protein GTRAP3-18. Nature 410, 84–88 (2001).
Diamond, J. S., Bergles, D. E. & Jahr, C. E. Glutamate release monitored with astrocyte transporter currents during LTP. Neuron 21, 425–433 (1998).
Luscher, C., Malenka, R. C. & Nicoll, R. A. Monitoring glutamate release during LTP with glial transporter currents. Neuron 21, 435–441 (1998).
Asztely, F., Erdemli, G. & Kullmann, D. M. Extrasynaptic glutamate spillover in the hippocampus: dependence on temperature and the role of active glutamate uptake. Neuron 18, 281–293 (1997).
Min, M. Y., Rusakov, D. A. & Kullmann, D. M. Activation of AMPA, kainate, and metabotropic receptors at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses: role of glutamate diffusion. Neuron 21, 561–570 (1998).
Rusakov, D. A. & Kullmann, D. M. Extrasynaptic glutamate diffusion in the hippocampus: ultrastructural constraints, uptake, and receptor activation. J. Neurosci. 18, 3158–3170 (1998).
Abdul-Ghani, A. S. et al. Anti-epileptogenic and anticonvulsant activity of l-2-amino-4- phosphonobutyrate, a presynaptic glutamate receptor agonist. Brain Res. 755, 202–212 (1997).
Cochilla, A. J. & Alford, S. Metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated control of neurotransmitter release. Neuron 20, 1007–1016 (1998).
Dube, G. R. & Marshall, K. C. Activity-dependent activation of presynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptors in locus coeruleus. J. Neurophysiol. 83, 1141–1149 (2000).
Otis, T. S., Wu, Y. C. & Trussell, L. O. Delayed clearance of transmitter and the role of glutamate transporters at synapses with multiple release sites. J. Neurosci. 16, 1634–1644 (1996).
Ferkany, J. & Coyle, J. T. Heterogeneity of sodium-dependent excitatory amino acid uptake mechanisms in rat brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 16, 491–503 (1986).
Acknowledgements
We thank J.H. Byrne, D. Baxter and E. Antzoulatos for discussions and critical reviews. This work was supported by NIH grants MH48147 (to J.D.S.), NS28462 (to A.E.) and NS42156 (to A.E.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levenson, J., Weeber, E., Selcher, J. et al. Long-term potentiation and contextual fear conditioning increase neuronal glutamate uptake. Nat Neurosci 5, 155–161 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn791
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn791
This article is cited by
-
The Effect of Ulinastatin to the Learning and Memory in Zebrafish
NeuroMolecular Medicine (2021)
-
Neurotransmitter changes after traumatic brain injury: an update for new treatment strategies
Molecular Psychiatry (2019)
-
The role of glutamate transporters in the pathophysiology of neuropsychiatric disorders
npj Schizophrenia (2017)
-
Doxepin and imipramine but not fluoxetine reduce the activity of the rat glutamate transporter EAAT3 expressed in Xenopus oocytes
BMC Anesthesiology (2015)
-
Limbic but not non-limbic kindling impairs conditioned fear and promotes plasticity of NPY and its Y2 receptor
Brain Structure and Function (2015)