Abstract
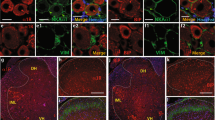
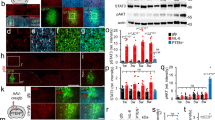
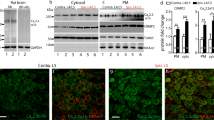
We examined the role of spinal tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα) in neuropathic pain of peripheral nerve origin. Two weeks after selective L5 spinal nerve ligation (SNL), rats exhibiting mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia showed a marked increase in full-length membrane-associated TNFα (mTNFα) in the dorsal horn of spinal cord, in the absence of detectable soluble TNFα peptide. Local release of the soluble p55 TNF receptor, achieved by herpes simplex virus vector-based gene transfer to dorsal root ganglion, resulted in a reduction of mTNFα and concomitant reductions in interleukin-1β and phosphorylated p38 MAP kinase. Subcutaneous inoculation of soluble p55 TNF receptor expressing HSV vector into the plantar surface of the hind foot ipsilateral to the ligation 1 week before SNL delayed the development of both mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia; subcutaneous inoculation into the hind foot ipsilateral to the ligation 1 week after SNL resulted in a statistically significant reduction in mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia that was apparent 1 week after inoculation. These results suggest a novel ‘reverse signaling’ through glial mTNFα, which may be exploited to downregulate the neuroimmune reaction in spinal cord to reduce chronic neuropathic pain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
McDermott AM, Toelle TR, Rowbotham DJ, Schaefer CP, Dukes EM . The burden of neuropathic pain: results from a cross-sectional survey. Eur J Pain 2006; 10: 127–135.
Wolfe GI, Trivedi JR . Painful peripheral neuropathy and its nonsurgical treatment. Muscle Nerve 2004; 30: 3–19.
DeLeo JA, Yezierski RP . The role of neuroinflammation and neuroimmune activation in persistent pain. Pain 2001; 90: 1–6.
Watkins LR, Milligan ED, Maier SF . Spinal cord glia: new players in pain. Pain 2001; 93: 201–205.
DeLeo JA, Tanga FY, Tawfik VL . Neuroimmune activation and neuroinflammation in chronic pain and opioid tolerance/hyperalgesia. Neuroscientist 2004; 10: 40–52.
Wieseler-Frank J, Maier SF, Watkins LR . Glial activation and pathological pain. Neurochem Int 2004; 45: 389–395.
Ohtori S, Takahashi K, Moriya H, Myers RR . TNF-alpha and TNF-alpha receptor type 1 upregulation in glia and neurons after peripheral nerve injury: studies in murine DRG and spinal cord. Spine 2004; 29: 1082–1088.
Sommer C, Schmidt C, George A . Hyperalgesia in experimental neuropathy is dependent on the TNF receptor 1. Exp Neurol 1998; 151: 138–142.
Schafers M, Svensson CI, Sommer C, Sorkin LS . Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces mechanical allodynia after spinal nerve ligation by activation of p38 MAPK in primary sensory neurons. J Neurosci 2003; 23: 2517–2521.
Svensson CI, Schafers M, Jones TL, Powell H, Sorkin LS . Spinal blockade of TNF blocks spinal nerve ligation-induced increases in spinal P-p38. Neurosci Lett 2005; 379: 209–213.
Hehlgans T, Pfeffer K . The intriguing biology of the tumour necrosis factor/tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily: players, rules and the games. Immunology 2005; 115: 1–20.
Mullberg J, Althoff K, Jostock T, Rose-John S . The importance of shedding of membrane proteins for cytokine biology. Eur Cytokine Netw 2000; 11: 27–38.
Fang C, Shi B, Pei YY, Hong MH, Wu J, Chen HZ . In vivo tumor targeting of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-loaded stealth nanoparticles: Effect of MePEG molecular weight and particle size. Eur J Pharm Sci 2006; 27: 27–36.
Barnes PJ, Karin M . Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med 1997; 336: 1066–1071.
Karin M, Liu Z, Zandi E . AP-1 function and regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1997; 9: 240–246.
Eissner G, Kirchner S, Lindner H, Kolch W, Janosch P, Grell M et al. Reverse signaling through transmembrane TNF confers resistance to lipopolysaccharide in human monocytes and macrophages. J Immunol 2000; 164: 6193–6198.
Eissner G, Kolch W, Scheurich P . Ligands working as receptors: reverse signaling by members of the TNF superfamily enhance the plasticity of the immune system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2004; 15: 353–366.
Peng X, Zhou Z, Glorioso JC, Fink DJ, Mata M . Tumor necrosis factor alpha contributes to below-level neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. Ann Neurol 2006; 59: 843–851.
Sheen K, Chung JM . Signs of neuropathic pain depend on signals from injured nerve fibers in a rat model. Brain Res 1993; 610: 62–68.
Hao S, Mata M, Wolfe D, Glorioso JC, Fink DJ . Gene transfer of glutamic acid decarboxylase reduces neuropathic pain. Ann Neurol 2005; 57: 914–918.
Hao S, Mata M, Goins W, Glorioso JC, Fink DJ . Transgene-mediated enkephalin release enhances the effect of morphine and evades tolerance to produce a sustained antiallodynic effect. Pain 2003; 102: 135–142.
Catheline G, Le Guen S, Besson JM . Intravenous morphine does not modify dorsal horn touch-evoked allodynia in the mononeuropathic rat: a Fos study. Pain 2001; 92: 389–398.
Ma W, Quirion R . Partial sciatic nerve ligation induces increase in the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) in astrocytes in the lumbar spinal dorsal horn and the gracile nucleus. Pain 2002; 99: 175–184.
Jin SX, Zhuang ZY, Woolf CJ, Ji RR . p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase is activated after a spinal nerve ligation in spinal cord microglia and dorsal root ganglion neurons and contributes to the generation of neuropathic pain. J Neurosci 2003; 23: 4017–4022.
Sweitzer S, Martin D, DeLeo JA . Intrathecal interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in combination with soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor exhibits an anti-allodynic action in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 2001; 103: 529–539.
Wolf G, Gabay E, Tal M, Yirmiya R, Shavit Y . Genetic impairment of interleukin-1 signaling attenuates neuropathic pain, autotomy, and spontaneous ectopic neuronal activity, following nerve injury in mice. Pain 2006; 120: 315–324.
Hao S, Mata M, Glorioso JC, Fink DJ . HSV-mediated expression of interleukin-4 in dorsal root ganglion neurons reduces neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 2006; 2: 6.
Winkelstein BA, Rutkowski MD, Sweitzer SM, Pahl JL, DeLeo JA . Nerve injury proximal or distal to the DRG induces similar spinal glial activation and selective cytokine expression but differential behavioral responses to pharmacologic treatment. J Comp Neurol 2001; 439: 127–139.
Raghavendra V, Tanga F, DeLeo JA . Inhibition of microglial activation attenuates the development but not existing hypersensitivity in a rat model of neuropathy. J Pharmacol Exp Therapy 2003; 306: 624–630.
Ledeboer A, Sloane EM, Milligan ED, Frank MG, Mahony JH, Maier SF et al. Minocycline attenuates mechanical allodynia and proinflammatory cytokine expression in rat models of pain facilitation. Pain 2005; 115: 71–83.
Nicol GD, Lopshire JC, Pafford CM . Tumor necrosis factor enhances the capsaicin sensitivity of rat sensory neurons. J Neurosci 1997; 17: 975–982.
Sorkin LS, Xiao WH, Wagner R, Myers RR . Tumour necrosis factor-alpha induces ectopic activity in nociceptive primary afferent fibres. Neuroscience 1997; 81: 255–262.
DeLeo JA, Rutkowski MD, Stalder AK, Campbell IL . Transgenic expression of TNF by astrocytes increases mechanical allodynia in a mouse neuropathy model. Neuroreport 2000; 11: 599–602.
Schafers M, Lee DH, Brors D, Yaksh TL, Sorkin LS . Increased sensitivity of injured and adjacent uninjured rat primary sensory neurons to exogenous tumor necrosis factor-alpha after spinal nerve ligation. J Neurosci 2003; 23: 3028–3038.
Sommer C, Lindenlaub T, Teuteberg P, Schafers M, Hartung T, Toyka KV . Anti-TNF-neutralizing antibodies reduce pain-related behavior in two different mouse models of painful mononeuropathy. Brain Res 2001; 913: 86–89.
Kirchner S, Holler E, Haffner S, Andreesen R, Eissner G . Effect of different tumor necrosis factor (TNF) reactive agents on reverse signaling of membrane integrated TNF in monocytes. Cytokine 2004; 28: 67–74.
Waetzig GH, Rosenstiel P, Arlt A, Till A, Brautigam K, Schafer H et al. Soluble tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-1 induces apoptosis via reverse TNF signaling and autocrine transforming growth factor-beta1. FASEB J 2005; 19: 91–93.
Solomon KA, Pesti N, Wu G, Newton RC . Cutting edge: a dominant negative form of TNF-alpha converting enzyme inhibits proTNF and TNFRII secretion. J Immunol 1999; 163: 4105–4108.
Oligino T, Ghivizzani S, Wolfe D, Lechman E, Krisky D, Mi Z et al. Intra-articular delivery of a herpes simplex virus IL-1Ra gene vector reduces inflammation in a rabbit model of arthritis. Gene Therapy 1999; 6: 1713–1720.
Kim SH, Chung JM . An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain 1992; 50: 355–363.
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL . Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 1994; 53: 55–63.
Dixon WJ . Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 1980; 20: 441–462.
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C, Joris J . A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 1988; 32: 77–88.
Ji RR, Baba H, Brenner GJ, Woolf CJ . Nociceptive-specific activation of ERK in spinal neurons contributes to pain hypersensitivity. Nat Neurosci 1999; 2: 1114–1119.
Hao S, Mata M, Wolfe D, Huang S, Glorioso J, Fink DJ . HSV-mediated gene transfer of the glial cell derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) provides an anti-allodynic effect in neuropathic pain. Mol Ther 2003; 8: 367–375.
Hao S, Takahata O, Mamiya K, Iwasaki H . Sevoflurane suppresses noxious stimulus-evoked expression of Fos-like immunoreactivity in the rat spinal cord via activation of endogenous opioid systems. Life Sci 2002; 71: 571–580.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Department of Veterans Affairs to Drs Mata and Fink. We gratefully acknowledge the assistance of Shue Liu in histology and Mr Vikram Thakur in propagation of the vectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, S., Mata, M., Glorioso, J. et al. Gene transfer to interfere with TNFα signaling in neuropathic pain. Gene Ther 14, 1010–1016 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302950
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302950
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bone mesenchymal stem cells attenuate radicular pain by inhibiting microglial activation in a rat noncompressive disk herniation model
Cell and Tissue Research (2018)
-
Current Gene Therapy using Viral Vectors for Chronic Pain
Molecular Pain (2015)
-
Analgesia for Neuropathic Pain by Dorsal Root Ganglion Transplantation of Genetically Engineered Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Initial Results
Molecular Pain (2015)
-
The Red Nucleus TNF-α Participates in the Initiation and Maintenance of Neuropathic Pain Through Different Signaling Pathways
Neurochemical Research (2015)
-
IL-10 Mediated by Herpes Simplex Virus Vector Reduces Neuropathic Pain Induced by HIV gp120 Combined with ddC in Rats
Molecular Pain (2014)