Abstract
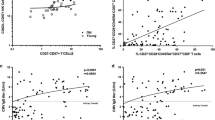
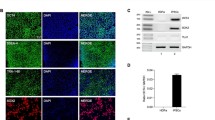
To test the hypothesis that CD4+ T lymphocytes accumulate in brains of end-stage acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients, we examined T-lymphocyte subsets in the CA1, CA3, and CA4 regions of the hippocampus of AIDS patients with (n = 10) and without (n = 11) human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis (HIVE) plus controls (n = 7). HIV p24 antigen was common in monocytic cells and rare in activated/memory CD45RO+ lymphocytes. Hippocampal activated/memory CD45RO+ T lymphocytes significantly increased (P < .001) in seven of the eight hippocampal subregions with hippocampal HIVE (1.14 ± 1.4 T cells/high-power field [hpf]), but AIDS hippocampus without HIVE were similar to controls (0.03 ± 0.07 T cells/hpf and 0.03 ± 0.09 T cells/hpf, respectively). CD45RO+ and CD3+ lymphocytes were similar in numbers and distribution, whereas CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes were weakly immunoreactive and less frequent. All four lymphocyte subtypes were present in perivascular spaces and microglial nodules of HIVE, and had direct contact with neurons. Monocytes, microglia, and multinucleated giant cells were immunoreactive for CD4 in AIDS cases with hippocampal HIVE but microglia in remaining AIDS cases and controls were CD4−. CD68+ macrophages significantly increased in hippocampus of HIVE patients (P < .05) and were predominately perivascular in the absence of local HIVE. These studies show that CD4+ T lymphocytes, as well as CD8+ T lymphocytes, participate in the local inflammatory response of HIVE in end-stage AIDS patients, and suggest that their recruitment requires local HIV infection. The perineuronal location of CD4+ cells provides the potential for lymphocyte-mediated neuronal injury or trans-receptor-mediated neuronal infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achim CL, Morey MK, Wiley CA (1991). Expression of major histocompatibility complex and HIV antigens within the brains of AIDS patients. AIDS 5: 535–541.
An SF, Groves M, Giometto B, Beckett AAJ, Scaravilli F (1999). Detection and localization of HIV-1 DNA and RNA in fixed adult AIDS brain by polymerase chain reaction-in situ technique. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 98: 481–487.
Bagasra O, Lavi E, Bobroski L, Khalili K, Pestaner JP, Tawadros R, Pomerantz RJ (1996). Cellular reservoirs of HIV-1 in the central nervous system of infected individuals: identification by the combination of in situ polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry. AIDS 10: 573–585.
Bauer J, Bradl M, Hickey WF, Forss-Petter S, Breitschopf H, Linington C, Wekerle H, Lassmann H (1998). T-cell apoptosis in inflammatory brain lesions: destruction of T cells does not depend on antigen recognition. Am J Pathol 153: 715–724.
Bell JE, Busuttil A, Ironside JW, Rebus S, Donaldson YK, Simmonds P, Peuthererm JF (1993). Human immunodeficiency virus and the brain: investigation of virus load and neuropathologic changes in pre-AIDS subjects. J Infect Dis 168: 818–824.
Bien CG, Bauer J, Deckwerth TI, Wiendl H, Deckert M, Wiestler OD, Schramm J, Elger CE, Lassman H (2002). Destruction of neurons by cytotoxic T cells: a new pathogenic mechanism in Rasmussen’s encephalitis. Ann Neurol 51: 311–318.
Budka H, Wiley CA, Kleihues P, Artigas J, Asbury AK, Cho E-S, Cornblath DR, Dal Canto MC, DeGirolami U, Dickson D, Epstein LG, Esiri MM, Giangaspero F, Gosztomi G, Gray F, Griffin JW, Henin D, Iwasaki Y, Janssen RS, Johnson RT, Lantos PL, Lyman WD, McArthur JC, Nagashima K, Peress N, Petito CK, Price RW, Rhodes RH, Rosenblum M, Said G, Scaravilli F, Sharer LR, Vinters HV (1991). HIV-associated disease of the nervous system: review of nomenclature and proposal for neuropathology-based terminology. Brain Pathol 1: 143–152.
Carson MJ, Reilly CR, Sutcliffe JG, Lo D (1999). Disproportionate recruitment of CD8+ T cell into the central nervous system by professional antigen-presenting cells. Cocaine opens the blood-brain barrier to HIV-1 invasion. Am J Pathol 154: 481–494.
Cserr HF, Harling-Berg CJ, Knopf PM (1991). Drainage of brain extracellular fluid into blood and deep cervical lymph and its immunological significance. Brain Pathol 2: 269–276.
Dhawan S, Weeks BS, Soderland C, Schnaper HW, Toro LA, Asthana SP, Hewlett IK, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Yamada SS, Yamada KM (1995). HIV-1 infection alters monocyte interactions with human microvascular endothelial cells. J Immunol 154: 422–432.
Falangola MF, Hanly A, Galvao-Castro B, Petito CK (1995). HIV infection of post-mortem human choroid plexus: a possible mechanism of viral entry into the CNS. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 54: 497–503.
Gan X, Zhang L, Berger O, Stins MF, Way D, Taub DD, Chang SL, Kim KS, House SD, Weinand M, Witte M, Graves MC, Fiala M (1999). Cocaine enhances brain endothelial adhesion molecules and leukocyte migration. Clin Immunol 91: 68–76.
Gendelman HE, Lipton SA, Tardieu M, Bukrinsky MI, Nottet HS (1994). The neuropathogenesis of HIV-1 infection. J Leuk Biol 56: 589–598.
Gold R, Schmeid M, Tontsch U, Hartung HP, Wekerle H, Toyka KV, Lassmann H (1996). Antigen presentation by astrocytes primes rat T lymphocytes for apoptotic cell death: A model for T-cell apoptosis in vivo. Brain 119: 651–659.
Gupta SK, Lysko PG, Pillarisetti K, Ohlstein E, Stadel JM (1998). Chemokine receptors in human endothelial cells. Functional expression of CXCR4 and its transcriptional regulation by inflammatory cytokines. J Biol Chem 273: 4282–4287.
Hesselgesser J, Taub D, Baskar P, Greenberg M, Hoxie J, Kolson DL, Horuk R (1998). Neuronal apoptosis induced by HIV-1 gp120 and the chemokine SDF-1 is mediated by the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Curr Biol 8: 595–598.
Hickey H, Hsu BL, Kimura H (1991). T-cell entry into the rat central nervous system. J Neurosci Res 28: 254–260.
Hurwitz AA, Berman JW, Lyman WD (1994). The role of the blood-brain barrier in HIV infection of the central nervous system. Adv Neuroimmunol 4: 249–256.
Janssen RS, Cornblath DR, Epstein LG, Foa RP, McArthur JC, Price RW (1991). Report of a working group of the AAN AIDS task force. Nomenclature and research case definitions for neurological manifestations of HIV-1 infection. Neurology 41: 778–785.
Katsetos CD, Fincke JE, Legido A, Lischner HW, de Chadarevian J-P, Kaye EM, Platsoucas CD, Oleszak EL (1999). Angiocentric CD3+ T cell infiltrates in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-associated central nervous system disease in children. Clin Diag Lab Immunol 6: 105–114.
Kennedy PGE, Gairns J (1992). Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigen expression in HIV encephalitis. Neuropathol Exp Neurobiol 18: 515–522.
Klein RS, Williams KC, Alvarez-Hernandez X, Westmoreland S, Force T, Lackner AA, Luster AD (1999). Chemokine receptor expression and signaling in macaque and human fetal neurons and astrocytes: implications for the neuropathogenesis of AIDS. J Immunol 163: 1636–1646.
Krajewski S, James HJ, Ross J, Blumberg BM, Epstein LG, Gendelman HE, Gummuluru S, Dewhurst S, Sharer LR, Reed JC, Gelbard HA (1997). Expression of pro- and anti-apoptosis gene products in brains from pediatric patients with HIV-1 encephalitis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 23: 242–253.
Lane JH, Sasseville VG, Smith MO, Vogel P, Pauley DR, Heyes MP, Lackner AA (1996). Neuroinvasion by simian immunodeficiency virus coincides with increased numbers of perivascular macrophages microglia and intrathecal immune activation. J NeuroVirol 2: 423–432.
Lavi E, Strizki JM, Ulrich AM, Zhang W, Fu L, Wang Q, O’Connor M, Hoxie JA, Gonzalez-Scarano F (1997). CCR-4 (Fusin), a co-receptor for HIV-1 is expressed in the human brain in a variety of cell types, including microglia and neurons. Am J Pathol 151: 1035–1042.
McCarthy M, He J, Wood C (1998). HIV-1 strain-associated variability in infection of primary neuroglia. J Neuro Virol 4: 80–89.
Nath A, Geiger JD (1998). Neurobiological aspects of HIV infections: neurotoxic mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol 54: 19–33.
Nath A, Harloper V, Furer M, Fowke K (1995). Infection of human fetal astrocytes with HIV-1: viral tropism and the role of cell to cell contact in viral transmission. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 54: 320–330.
Navia BA, Jordan BD, Price RW (1986). The AIDS dementia complex: I. Clinical features. Ann Neurol 19: 517–524.
Nottet HS, Persidsky Y, Sasseville VG, Nukuna AN, Bock P, Zhai QH, Sharer LR, McComb RD, Swindells S, Soderland C, Gendelman HE (1996). Mechanisms for the transendothelial migration of HIV-1-infected monocytes into brain. J Immunol 156: 1284–1295.
Nuovo GJ, Gallery F, MacConnell P, Braun A (1994). In situ detection of polymerase chain reaction-amplified HIV-1 nucleic acids and tumor necrosis factor mRNA in the central nervous system. Am J Pathol 144: 659–666.
O’Hagen A, Ghosh S, He J, Huang K, Chen Y, Yuan M, Osathanondh R, Gartner S, Shi B, Shaw G, Gabuzda D (1999). Apoptosis induced by infection of primary brain cultures with diverse human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates: evidence for a role of the envelope. J Virol 73: 897–906.
Okamoto Y, Yamashita J, Hasegawa M, Fujisawa H, Yamashima T, Hashimoto T, Nonomurat A, Matsumoto Y, Kida S (1999). Cervical lymph nodes play the role of regional lymph nodes in brain tumor immunity in rats. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 25: 113–122.
Petito CK, Roberts B, Cantando JD, Rabinstein A, Duncan R (2001). Hippocampal injury and alterations in neuronal chemokine co-receptor expression in patients with AIDS. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60: 377–385.
Petito CK, Roberts B, Duncan R (2000). Increased neuronal CXCR4 chemokine co-receptors and parenchymal CD4 T lymphocytes in hippocampus of AIDS patients. J NeuroVirol 6: 433.
Russell JH, Ley TJ (2002). Lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu Rev Immunol 20: 323–370.
Sasseville VG, Newman WA, Lackner AA, Smith MO, Lausen NCG, Beal D, Ringler DJ (1992). Elevated vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in AIDS encephalitis induced by simian immunodeficiency virus. Am J Pathol 141: 1021.
Seabrook TJ, Johnston M, Hay JB (1998). Cerebral spinal fluid lymphocytes are part of the normal recirculation lymphocyte pool. J Neuroimmunol 91: 100–107.
Seigneur M, Constans J, Blann A, Renard M, Pellegrin JL, Amiral J, Boisseau M, Conri C (1997). Soluble adhesion molecules and endothelial cell damage in HIV infected patients. Thromb Haemostasis 77: 646–649.
Sharer LR, Saito Y, Cunha AD, Ung P, Gelbard HA, Epstein L, Blumberg B (1996). In situ amplification and detection of HIV-1 DNA in fixed pediatric AIDS brain tissue. Hum Pathol 27: 614–617.
Snider WD, Simpson DM, Nielson S, Gold JWM, Metroka CE, Posner JB (1983). Neurological complications of acquired immune deficiency syndrome: analysis of 50 patients. Ann Neurol 14: 403–418.
Speck FR, Esser U, Penn ML, Eckstein DA, Pulliam L, Chan SY, Goldsmith MA (1999). A trans-receptor mechanism for infection of CD4-negative cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Curr Biol 9: 547–550.
Speth C, Joebstl B, Barcova M, Dierich MP (2000). HIV-1 envelope protein gp41 modulates expression of interleukin-10 and chemokine receptors on monocytes, astrocytes and neurons. AIDS 14: 629–636.
Svenningsson A, Anderson O, Edsbagge M, Stemme S (1995). Lymphocyte phenotype and subset distribution in normal cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuroimmunol 63: 39–46.
Takahashi K, Wesselingh SL, Griffin DE, McArthur JC, Johnson RT, Glass JD (1996). Localization of HIV-1 in human brain using polymerase chain reaction/in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry. Ann Neurol 39: 705–711.
Tornatore C, Nath A, Amemiya K, Major EO (1991). Persistent human immunodeficiency virus type I infection in human fetal glial cells reactivated by T-cell factors or by the cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 beta. J Virol 65: 6094–6100.
Torres-Muñoz J, Stockton P, Tacoronte N, Roberts B, Maronpot R, Petito CK (2001). Detection of HIV-1 gene sequences in hippocampal neurons isolated from postmortem AIDS brains by laser capture microdissection. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60: 885–892.
Tyor WR, Glass JD, Griffin JW, Becker PS, McArthur JC, Bezman L, Griffin DE (1992). Cytokine expression in the brain during the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol 31: 349–360.
van der Ende ME, Schutten M, Raschdorff B, Grossschupff G, Racz P, Osterhaus ADME, Tenner Racz K (1999). CD4 T cells remain the major source of HIV-1 during end stage disease. AIDS 13: 1015–1019.
van der Meer P, Ulrich AM, Gonzalez-Scarano F, Lavi E (2000). Immunohistochemical analysis of CCR2, CCR3, CCR5 and CXCR4 in the human brain: potential mechanisms for HIV dementia. Exp Mol Pathol 69: 192–201.
Volin MV, Joseph L, Shockley MS, Davie PF (1998). Chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression in endothelium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 242: 46–53.
Weidenheim KM, Epshteyn I, Lyman WD (1993). Immunocytochemical identification of T-cells in HIV-1 encephalitis: implications for pathogenesis of CNS disease. Mod Pathol 6: 167–174.
Wekerle H, Linington C, Lassmann H, Meyermann R (1986). Cellular immune reactivity within the CNS. Trends Neurosci 9: 271–277.
Wesselingh SL, Power C, Glass JD, Tyor WR, McArthur JC, Farber JM, Griffin JW, Griffin DE (1993). Intracerebral cytokine messenger RNA expression in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome dementia. Ann Neurol 33: 576–582.
Wisniewski HM, Lossinsky AS (1991). Structural and functional aspects of the interaction of inflammatory cells with the blood-brain barrier in experimental brain inflammation. Brain Pathol 1: 89–96.
Wong D, Prameya R, Dorovini-Zis K (1999). In vitro adhesion and migration of T lymphocytes across monolayers of human brain microvessel endothelial cells: regulation by ICAM-1, VCAM-1, E-selectin and PECAM-1. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58: 138–152.
Zhang L, Looney D, Taub D, Chang SL, Way D, Witte MH, Graves MC, Fiala M (1998). Cocaine opens the blood-brain barrier to HIV-1 invasion J NeuroVirol 4: 619–626.
Zheng J, Thylin MR, Ghorpade A, Xiong H, Persidsky Y, Cotter R, Niemann D, Che M, Zeng YC, Gelbard HA, Shepard RB, Swartz JM, Gendelman HE (1999). Intra-cellular CXCR4 signaling, neuronal apoptosis and neuropathogenic mechanisms of HIV-1-associated dementia. J Neuroimmunol 98: 185–200.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by grants from the National Institute of Health to CKP (R01 NS35331 and R01 NS39177).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petito, C.K., Adkins, B., McCarthy, M. et al. CD4+ and CD8+ cells accumulate in the brains of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients with human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis. Journal of NeuroVirology 9, 36–44 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280390173391
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280390173391