Abstract
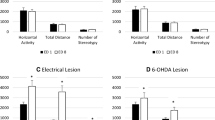
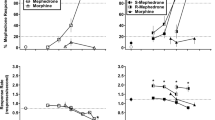
Mice that received five daily injection of methylphenidate HCl, 10–75 mg/kg, showed an increased running response to methylphenidate, cocaine, and amphetamine. Sensitization to methylphenidate persisted for at least 50 days. Repeated IP injections of methylphenidate into mice with unilateral striatal lesions increased ipsilateral turning in response to methylphenidate, but decreased contralateral turning after apomorphine. The climbing response to apomorphine in intact, methylphenidate-sensitized mice was also decreased. There was no change in either basal or dopamine-stimulated adenyl cyclase activity in the striata of sensitized mice, but there was a 36% increase in the specific binding of haloperidol. The rate of turnover of striatal dopamine was increased in sensitized mice. These results suggest that pretreatment with methylphenidate may alter the sensitivity of presynaptic dopamine receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Algeri S, Brunello N, Vantini G (1980) Different adaptive responses by rat striatal dopamine synthetic and receptor mechanisms after repeated treatment with d-amphetamine, methylphenidate and nomifensine. Pharmacol Res Commun 12:675–681
Babbini M, Gaiardi M, Bartoletti M (1979) Dose-time mobility effects of morphine and methadone in naive or morphinized rats. Pharmacol Res Commun 11:809–816
Breese GR, Taylor TD (1970) Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine on brain nor-epinephrine and dopamine: Evidence for selective degeneration of catecholamine neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 174:413–420
Burt DR, Enna SJ, Creese I, Snyder SH (1975) Dopamine receptor binding in the corpus striatum of mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:4655–4659
Clement-Cormier YC, Parrish RG, Petzold GL, Kebabian JW, Greengard P (1975) Characterization of a dopamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in the rat caudate nucleus. J Neurochem 25:143–149
Costa E, Neff NH (1970) Estimation of turnover rates to study the metabolic regulation of the steady-state level of neuronal amines. In: Lajtha A (ed) Handbook of neurochemistry, vol 4. Plenum Press, New York, pp 45–90
Creese I, Sibley DR, Leff S, Hamblin M (1981) Dopamine receptors: Subtypes, localization and regulation. Fed Proc 40:147–152
Denkla MB, Bemporad JR, Mackay MC (1976) Tics following methylphenidate administration. A report of 20 cases. JAMA 235:1349–1351
Epstein PN, Altschuler HL (1979) Altered response to apomorphine and haloperidol after 9 days of cocaine injections. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 10:189–193
Ferris RM, Tang FLM, Maxwell RA (1972) A comparison of the capacities of isomers of amphetamine, deoxypipadrol and methylphenidate to inhibit the uptake of tritiated catecholamines into rat cerebral cortex slices, synaptosomal preparations of rat cerebral cortex, hypothalamus and striatum and into adrenergic nerves of rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 181:407–416
Golden GS (1974) Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome following methylphenidate administration. Dev Med Child Neurol 16:76–68
Goldstein A (1964) Biostatistics. The MacMillan Co., New York
Herve D, Tassin JP, Barthelemy C, Blanc G, Lavielle S, Glowinski J (1979) Difference in the reactivity of the mesocortical dopaminergic neurons to stress in the BALB/c and C57B1/6 mice. Life Sci 25:1659–1664
Howlett DR, Nahorski SR (1979) Acute and chronic amphetamine treatments modulate striatal dopamine receptor binding sites. Brain Res 161:173–178
Kebabian JW, Calne DB (1979) Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature 277:93–96
Keller R, Oke A, Mefford T, Adams R (1976) Liquid chromatographic analysis of catecholamines. Routine assay for regional mapping. Life Sci 19:995–1004
Kilbey MM, Ellinwood EH (1977) Reverse tolerance to stimulant-induced abnormal behavior. Life Sci 20:1063–1076
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lust WD, Dye E, Deaton AV, Passoneau J (1976) A modified cyclic AMP binding assay. Anal Biochem 72:8–15
Martres MP, Costentin J, Baudry M, Marcais H, Protais P, Schwartz JC (1977) Long-term changes in the sensitivity of pre- and postsynaptic receptors in mouse striatum evidenced by behavioral and biochemical studies. Brain Res 136:319–339
Mishra RK, Wong YW, Varmuza SL, Tuff L (1978) Chemical lesion and drug-induced supersensitivity and subsensitivity of caudate dopamine receptors. Life Sci 23:443–446
Moyer TP, Jiang NS (1978) Optimized isocratic conditions for the analysis of catecholamines by high-performance reversed phase paired-ion chromatography with amperometric detection. J Chromatogr 153:365–372
Muller P, Seeman P (1979) Presynaptic subsensitivity as a possible basis for sensitization by long-term dopamine mimetics. Eur J Pharmacol 55:149–157
Post RM, Rose H (1976) Increasing effects of repetitive cocaine administration in rats. Nature 260:731–732
Protais P, Constentin J, Schwartz JC (1976) Climbing behavior induced by apomorphine in mice: A simple test for the study of dopamine receptors in the striatum. Psychopharmacology 50:1–6
Schwartz JC, Constentin J, Martres MP, Protais P, Baudry M (1978) Modulation of receptor mechanism in the CNS: Hyper- and hyposensitivity to catecholamines. Neuropharmacology 17:665–685
Segal DS (1975) Behavioral and neurochemical correlates of repeated d-amphetamine administration. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 13:247–262
Short PH, Shuster L (1976) Changes in brain nor-epinephrine associated with sensitization to d-amphetamine. Psychopharmacology 48:59–67
Shuster L, Webster GW, Yu G (1975) Increased running response to morphine in morphine-treated mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 192:64–72
Shuster L, Yu G, Bates A (1977) Sensitization to cocaine stimulation in mice. Psychopharmacology 52:185–190
Sidman RL, Angevine B (1971) Atlas of the mouse brain and spinal cord. Harvard University Press, Boston
Tarsy D, Baldessarini RJ (1974) Behavioral supersensitivity to apomorphine following chronic treatment with drugs which interfere with the synaptic function of catecholamines. Neuropharmacology 13:927–940
Ungerstedt U (1971) Postsynaptic supersensitivity after 6-hydroxydopamine-induced degeneration of the nigro-striatal dopamine system. Acta Physiol Scand [Suppl] 367:1–69
von Voigtlander PF, Moore KE (1973) Turning behavior of mice with unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesions in the striatum: Effect of apomorphine, l-dopa, amantadine, amphetamine and other psychomotor stimulants. Neuropharmacology 12:451–462
Wilcox RE, Smith RV, Anderson TA, Riffee WH (1980) Apomorphine-induced stereotypic cage climbing in mice as a model for studying changes in dopamine receptor sensitivity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 12:29–33
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shuster, L., Hudson, J., Anton, M. et al. Sensitization of mice to methylphenidate. Psychopharmacology 77, 31–36 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00436096
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00436096