Abstract
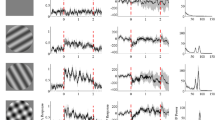
LGN Y-cells in 3 anaesthetized (N2O/O2) and paralyzed rhesus monkeys were investigated with stimuli, intensity modulated by gaussian white noise, and with moving and counterphase modulated spatial sine wave gratings. The results support the model, postulated on the base of electrophysiological recordings in the retina of cat and mudpuppy, which consists of a linear centre and surround mechanism whose responses are modified in a frequency-selective multiplicative way by a nonlinear mechanism in the receptive field. This nonlinear mechanism is also held responsible for the second-order harmonic responses, which are the defining characteristic of Y-cells. The temporal and spatial characteristics of these mechanisms were determined. The responses obtained with the GWN stimulation and with modulated spatial sine wave gratings both indicate that the optimal temporal frequency of the linear mechanisms is near 7 Hz at 70 td and near 5 Hz for the nonlinear mechanism. The optimal spatial frequency for the linear mechanism is between 0.5–2 cycles/deg and between 6–12 cycles/deg for the nonlinear mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barlow, H.B., Derrington, A.M., Harris, L.R., Lennie, P.: The effects of remote retinal stimulation on the responses of cat retinal ganglion cells. J. Physiol. (London) 269, 177–194 (1977)
De Monasterio, F.M.: Properties of concentrically organized X and Y ganglion cells of macaque retina. J. Neurophysiol. 41, 1394–1417 (1978a)
De Monasterio, F.M.: Center and surround mechanisms of opponent-color X and Y ganglion cells of the retina of macaques. J. Neurophysiol. 41, 1418–1434 (1978b)
Derrington, A.M., Lennie, P., Wright, M.J.: The mechanism of peripherally evoked responses in retinal ganglion cells. J. Physiol. (London) 289, 299–310 (1979)
De Valois, R.L., Snodderly, D.M., Yund, E.W., Hepler, N.K.: Responses of macaque lateral geniculate cells to luminance and color figures. Sens. Processes 1, 244–259 (1977)
Dreher, B., Fukada, Y., Rodieck, R.W.: Identification, classification and anatomical segregation of cells with X-like and Y-like properties in the lateral geniculate nucleus of old-world primates. J. Physiol. (London) 258, 433–452 (1976)
Enroth-Cugell, C., Robson, J.G.: The contrast sensitivity of retinal ganglion cells of the cat. J. Physiol. (London) 187, 517–552 (1966)
Enroth-Cugell, C., Lennie, P.: The control of retinal ganglion cell discharge by receptive field surrounds. J. Physiol. (London) 247, 551–578 (1975)
Gielen, C.C.A.M.: Spatio-temporal and chromatic properties of visual neurones in the rhesus monkey geniculate nucleus. Thesis: University of Nijmegen (1980)
Hochstein, S., Sharpley, R.M.: Quantitative analysis of retinal ganglion cell classifications. J. Physiol. (London) 262, 237–264 (1976a)
Hochstein, S., Shapley, R.M.: Linear and nonlinear spatial subunits in Y cat retinal ganglion cells. J. Physiol. (London) 262, 265–284 (1976b)
Jakiela, H.G.: The effect of retinal image motion on the responsiveness of retinal ganglion cells in the cat. Thesis: University of Illinois, USA (1978)
Kratz, K.E., Webb, S.V., Sherman, S.M.: Electrophysiological classification of X-and Y-cells in the cat's lateral geniculate nucleus. Vision Res. 18, 489–492 (1978)
Krüger, J., Fischer, B.: Strong periphery effect in cat retinal ganglion cells. Excitatory responses in on-and off-centre neurones to single grid displacements. Exp. Brain Res. 18, 316–318 (1973)
Lee, Y.W., Schetzen, M.: Measurement of the Wiener kernels of a nonlinear system by cross-correlation. J. Int. Control 2, 237–254 (1965)
Lehmkuhle, S., Kratz, K.E., Mangel, S.C., Sherman, S.M.: Spatial and temporal sensitivity of X-and Y-cells in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus in the cat. J. Neurophysiol. 43, 520–541 (1980)
Maffei, L., Cervetto, L., Fiorentini, A.: Transfer characteristics of excitation and inhibition in cat retinal ganglion cells. J. Neurophysiol. 23, 276–284 (1970)
Marmarelis, P.Z., Naka, K.-I.: Identification of multi-input biological systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed Eng. 21, 88–101 (1974)
Marmarelis, P.Z., Marmarelis, V.Z.: Analysis of physiological systems. New York: Plenum Press 1978
Ratliff, F., Knight, B.W., Toyoda, J.-I., Hartline, H.K.: Enhancement of flicker by lateral inhibition. Science 158, 392–393 (1967)
Shapley, R.M., Hochstein, S.: Visual spatial summation in two classes of geniculate cells. Nature 256, 411–413 (1975)
Shapley, R.M., Victor, J.D.: The effect of contrast on the transfer properties of cat retinal ganglion cells. J. Physiol. (London) 285, 275–298 (1978)
Shapley, R.M., Victor, J.D.: Nonlinear spatial summation and the contrast gain control of cat retinal ganglion cells. J. Physiol. (London) 290, 141–161 (1979)
So, Y.T., Shapley, R.M.: Spatial properties of X and Y cells in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat and conduction velocities of their inputs. Exp. Brain Res. 36, 533–550 (1979)
Swerup, C.: On the choice of noise for the analysis of the peripheral auditory system. Biol. Cybern. 29, 97–104 (1978)
Thibos, L.N., Werblin, F.S.: The response properties of the steady antagonistic surround in the mudpuppy retina. J. Physiol. (London) 278, 79–99 (1978a)
Thibos, L.N., Werblin, F.S.: The properties of surround antagonism elicited by spinning windmill patterns in the mudpuppy retina. J. Physiol. (London) 278, 101–116 (1978b)
Victor, J.D., Shapley, R.M.: Receptive field mechanisms of cat X and Y retinal ganglion cells. J. Gen. Physiol. 74, 275–298 (1979a)
Victor, J.D., Shapley, R.M.: The nonlinear pathway of Y ganglion cells in the cat retina. J. Gen. Physiol. 74, 671–689 (1979b)
Victor, J., Shapley, R.: A method of nonlinear analysis in the frequency domain. Biophys. J. 29, 459–484 (1980)
Werblin, F.S.: Lateral interactions at inner plexiform layer of vertebrate retina: antagonistic responses to change. Science 175, 1008–1010 (1972)
Werblin, F.S.: Regenerative amacrine cell depolarisation and formation of on-off ganglion cell response. J. Physiol. (London) 264, 767–785 (1977)
Wiesel, T.N., Hubel, D.H.: Spatial and chromatic interactions in the lateral geniculate body of the rhesus monkey. J. Neurophysiol. 29, 1115–1156 (1966)
Wunk, D.F., Werblin, F.S.: Synaptic inputs to the ganglion cells in the tiger salamander retina. J. Gen. Physiol. 73, 265–286 (1979)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gielen, C.C.A.M., van Gisbergen, J.A.M. & Vendrik, A.J.H. Characterization of spatial and temporal properties of monkey LGN Y-cells. Biol. Cybern. 40, 157–170 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00453366
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00453366