Abstract
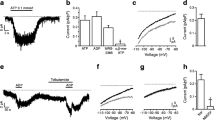
The influence of the antidiabetic sulphonylurea tolbutamide on K+ channels of mouse pancreatic β-cells was investigated using different configurations of the patch clamp technique. The dominant channel in resting cells is a K+ channel with a single-channel conductance of 60 pS that is inhibited by intracellular ATP or, in intact cells, by stimulation with glucose. In isolated patches of β-cells membrane, this channel was blocked by tolbutamide (0.1 mM) when applied to either the intracellular or extracellular side of the membrane. The dose-dependence of the tolbutamide-induced block was obtained from whole-cell experiments and revealed that 50% inhibition was attained at approximately 7 μM. In cell-attached patches low concentrations of glucose augmented the action of tolbutamide. Thus, the simultaneous presence of 5 mM glucose and 0.1 mM tolbutamide abolished channel activity and induced action potentials. These were not produced when either of these substances was added alone at these concentrations. The inhibitory action of tolbutamide or glucose on the K+ channel was counteracted by the hyperglycaemic sulphonamide diazoxide (0.4 mM). Tolbutamide (1 mM) did not affect Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. It is concluded that the hypo- and hyperglycaemic properties of tolbutamide and diazoxide reflect their ability to induce the closure or opening, respectively, of ATP-regulated K+ channels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamsson H, Berggren PO, Rorsman P (1985) Direct measurements of increased free cytoplasmic Ca2+ in mouse pancreatic β-cells following stimulation by hypoglycemic sulfonylureas. FEBS Lett 190:21–24
Ashcroft FM, Harrison DE, Ashcroft SJH (1984) Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic β-cells. Nature: 312:446–448
Atwater I, Ribalet B, Rojas E (1978) Cyclic changes in potential and resistance of the β-cell membrane induced by glucose in islets of Langerhans from mouse. J Physiol 278:117–139
Atwater I, Rosario L, Rojas E (1983) Properties of Ca-activated K+-channel in pancreatic β-cells. Cell Calcium 4:451–461
Cook DL, Hales N (1984) Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature 311:271–273
Cook DL, Ikeuchi M, Fujimoto WY (1984) Lowering of pHi inhibits Ca2+-activated K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature 311:269–271
Deleers M, Malaisse W (1984) Binding of hypoglycaemic sulphonylureas to an artificial phospholipid bilayer. Diabetologia 26:55–59
Findlay I, Dunne MJ, Petersen OH (1985a) High-conductance K+ channel in pancreatic islet cells can be activated and inactivated by internal calcium. J Membr Biol 83:169–175
Findlay I, Dunne MJ, Petersen OH (1985b) ATP-sensitive inward rectifier and voltage- and calcium-activated K+ channels in cultured pancreatic islet cells. J Membr Biol 88:165–172
Frerichs H, Gerber R, Creutzfeldt W (1966) Insulinsekretion in vitro. Hemmung der glucoseinduzierten Insulinabgabe durch Diazoxide. Diabetologia 2:269–276
Geisen K, Hitzel V, Ökomonopoulos R, Pünter J, Weyer R, Summ HD (1985) Inhibition of3H-glibenclamide binding to sulfonylurea receptors by oral antidiabetics. Arzneimittelforsch/Drug Res 35:707–712
Gillis K, Falke L, Misler S (1986) An ATP-sensitive K+ channel in inside-out membrane patches from pancreatic B-cells. Biophys J 49:163a
Gylfe E, Hellman B (1982) Lack of ionophoretic activity of hypoglycemic sulfonylureas in excitable cells and isolated secretory granules. Mol Pharmacol 22:715–720
Gylfe E, Hellman B, Sehlin J, Täljedal IB (1984) Interaction of sulfonylurea with the pancreatic B-cell. Experientia 40:1126–1134
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recordings from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Häussler A, Pechtold F (1971) Die Analytik der Sulfonylharnstoffe. In: Maske H (ed) Oral wirksame Antidiabetika. Handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol XXIX, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 251–290
Hellman B, Täljedal IB (1975) Effects of sulfonylurea derivatives on pancreatic β-cells. In: Hasselblatt, A, v Bruchhausen F (eds) Insulin II. Handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol XXXII, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 175–194
Henquin JC (1980) Tobutamide stimulation and inhibition of insulin release: studies of the underlying ionic mechanisms in isolated rat islets. Diabetologia 18:151–160
Henquin JC, Meissner HP (1982) Opposite effects of tolbutamide and diazoxide of86Rb+ fluxes and membrane potential in pancreatic β-cells. Biochem Pharmacol 31:1407–1415
Henquin JC, Charles S, Nenquin M, Mathot F, Tamagawa T (1982) Diazoxide and D600 inhibition of insulin release. Distinct mechanisms explain the specificity for different stimuli. Diabetes 31:776–783
Kakei M, Noma A, Shibasaki T (1985) Properties of adenosinetriphosphate-regulated potassium channels in guinea-pig ventricular cells. J Physiol 363:441–462
Malaisse WJ, Herchuelz A (1982) Nutritional regulation of K+ conductance: An unsettled aspect of pancreatic B cell physiology. In: Litwack G (ed) Biochemical actions of hormones, vol IX, Ch 3. Academic Press, New York, pp 107–122.
Malaisse, WJ, Hutton JC, Kawazu S, Herchuelz A, Valverde I, Sener A (1979) The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XXXV. The links between metabolic and cationic events. Diabetologia 16:331–341
Martell AE, Smith RM (1974) Critical stability constants, vol 1, Amino acids, vol 2, Amines Plenum Press, New York
Matthews EK, Shotton PA (1984) Efflux of86Rb+ from rat and mouse pancreatic islets: the role of membrane depolarization. Br J Pharmacol 83:831–839
Noma A, Shibasaki T (1985) Membrane current through adenosine-triphosphate-regulated potassium channels in guinea-pig ventricular cells. J Physiol 363:463–480
Pruitt AW, Dayton PG, Patterson JH (1973) Disposition of diazoxide in children. Clin Pharmacol Ther 14:73–82
Rorsman P, Trube G (1985) Glucose dependent K+-channels in pancreatic β-cells are regulated by intracellular ATP. Pflügers Arch 405:305–309
Rorsman P, Trube G (1986) Calcium and delayed potassium currents in mouse pancreatic β-cells under voltage clamp conditions. J Physiol 374:531–550
Sakmann B, Neher E (1984) Patch clamp techniques for studying ionic channels in excitable membranes. Ann Rev Physiol 46:455–472
Sturgess NC, Ashford MLJ, Cook DL, Hales CN (1985) The sulphonylurea receptor may be an ATP-sensitive potassium channel. Lancet 8453:474–475
Trube G, Hescheler J (1984) Inward-rectifying channels in isolated patches of the heart cell membrane: ATP-dependence and comparison with cell-attached patches. Pflügers Arch 401:178–184
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trube, G., Rorsman, P. & Ohno-Shosaku, T. Opposite effects of tolbutamide and diazoxide on the ATP-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic β-cells. Pflugers Arch. 407, 493–499 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00657506
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00657506