Abstract
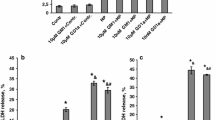
This study demonstrates modulation by GM1 ganglioside of prostaglandin E1 (PGE1)-induced cAMP formation in Neuro-2a neuroblastoma cells. Pretreatment of the cells with neuraminidase, an enzyme that increases cell surface GM1, resulted in significant elevation of PGE1-induced cAMP formation, as did preincubation of the cells with nmolar concentrations of GM1. Pretreatment with brain ganglioside mixture lacking GM1 had no effect. Cholera toxin B subunit, a specific GM1-binding ligand, inhibited adenylyl cyclase. When the concentration of exogenous GM1 in which the cells were preincubated was increased from nmolar to μmolar levels there was a dose-responsive fall off in cAMP elevation, attributed to progressive inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by increasing GM1. These results are interpreted as indicating modulation of this PGE1 receptor in Neuro-2a cells by plasma membrane-localized GM1 in a structure-specific manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PGE1:
-
prostaglandin E1
- Ctx B:
-
B subunit of cholera toxin
- BBG:
-
bovine brain ganglioside mixture
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- IBMX:
-
3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine
- N'ase:
-
neuraminidase
- D-PBS:
-
Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline
References
Yu RK, Saito M (1989) InNeurobiology of Glycoconjugates (Margolis RU, Margolis RK eds) pp. 1–42. New York: Plenum Press.
Ohashi Y, Gage DA, Sweeley CC (1991) InTechniques in Diagnostic Human Biochemical Genetics (Hommes FA ed) pp. 239–65, New York: Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Mullin BR, Fishman PH, Lee G, Aloj SmM, Ledley FD, Winand RJ, Kohn LD, Brady RO (1976)Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73: 842–46.
Lee G, Aloj SM, Brady RO, Kohn LD (1976)Biochem Biophys Res Commun 73: 370–77.
Lee G, Aloj SM, Kohn LD (1977)Biochem Biophys Res Commun 77: 434–41.
Hakomori S-i (1993)Biochem Soc Trans 21: 583–95.
Hakomori S-i, Igarashi Y (1993)Adv Lip Res 25: 147–62.
Hakomori S-i (1990)J Biol Chem 265: 18713–16.
Bremer EG, Hakomori S-i (1984) InGanglioside Structure, Function, and Biomedical Potential (Ledeen RW, Yu RK, Rapport MM, Suzuki K, eds) pp. 381–94. NY: Plenum Press.
Bremer EG, Schlessinger J, Hakomori S-i (1986)J Biol Chem 261: 2434–40.
Bremer EG, Hakomori S-i, Bowen-Pope DF, Raines E, Ross R (1984)J Biol Chem 259: 6818–25.
Brocklyn JV, Bremer EG, Yates AJ (1993)J Neurochem 61: 371–74.
Nojiri H, Strored M, Hakomori S-i (1991)J Biol Chem 266: 4531–37.
Shen KF, Crain SM, Ledeen RW (1991).Brain Res 559: 130–38.
Skrivanek JA, Livermore GH (1981)Trans Am Soc Neurochem 12: 236.
Wu G, Fan SF, Lu ZH, Ledeen RW, Crain SM (1995)J Neurosci Res:42: 493–503.
Wu G, Lu ZH, Ledeen RW (1991)Develop Brain Res 61: 217–28.
Wu G, Ledeen RW (1991).J. Neurochem 56: 95–104.
Fishman PH (1982)J Membr Biol 69: 85–97.
Wu G, Ledeen RW (1994)Prog Brain Res 101: 101–12.
Saqr HE, Pearl DK, Yates AJ (1993)J Neurochem 61: 395–411.
Ledeen RW, Wu G (1992)Trends Glycosci Glycotech 4: 174–87.
Saito M, Frielle T, Benovic J, Ledeen RW (1995)Biochim Biophys Acta:1267: 1–5.
Shen KF, Crain SM (1990)Brain Res 531: 1–7.
Wu G, Lu Z, Ledeen RW (1995)J Neurochem 64: S104.
Berry-Kravis E, Dawson G (1985)J Neurochem 45: 1739–47.
Wolfe LS, Coceani F (1979)Ann Rev Physiol 41: 669–84.
Coleman RA, Smith WL, Naumiya S (1994)Am Soc Pharmacol Exp Ther 46: 205–29.
An S, Yang J, Goetzl EJ (1993)Biochem Biophys Commun 197: 263–70.
Honda A, Sugimoto Y, Namba T, Watabe A, Ire A, Negishi M, Narumiya S, Ichikawa A (1993)J Biol Chem 268: 7759–62.
Sando T, Usui T, Tanaka I, Mori K, Sasaki Y, Fukuda Y, Nambra T, Sugimoto A, Ichikawa A, Narumiya S, Nakao K (1994)Biochem Biophys Commun 200: 1329–33.
Ammer H, Schulz R (1993)Mol Pharmacol 43: 556–63.
Dacremont G, De Baets M, Kaufman JM, Elewaut A, Vermeulen A (1984)Biochim Biophys Acta 770: 142–47.
Partington CR, Daly JW (1979)Mol Pharmacol 15: 484–91.
Iyengar R (1993)FASEB J 7: 768–75.
Kielczynski W, Harrison L, Leedman P (1991)Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 1991–95.
Mullin BR, Fishman PH, Lee G, Aloj SM, Ledley FD, Winand RJ, Kohn LD, Brady RO (1976)Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73: 842–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, G., Lu, ZH. & Ledeen, R.W. GM1 ganglioside modulates prostaglandin E1 stimulated adenylyl cyclase in neuro-2A cells. Glycoconjugate J 13, 235–239 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00731498
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00731498