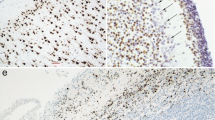
Summary
Two monoclonal antibodies, SC1 and SC2, were raisedin vitro against antigens from the stereocilia of guinea-pig hair cells. They both labelled stereociliary antigens that were not detected in any other cell within the cochlear duct or the vestibular epithelia. SC1 cross-reacted with the tectorial membrane in the cochlea and labelled both cochlear and vestibular hair cells from both the mouse and the rat. In the mouse the SC1 antigen was labelled from embryonic days 16–18, coincident with the development of the stereociliary bundles. SC1 cross-reacted with neuromuscular junctions from striated muscle and with basal keratinocytes in skin. SC2 did not cross-react cleanly with hair cells from the mouse or the rat but it cross-reacted with proximal tubules of the guinea-pig kidney. Both antibodies can be used as cellular markers within the guinea-pig cochlea and SC1 should be particularly useful for studies of hair cell differentiation in the mouse.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assad, J. A. &Corey, D. P. (1992) An active motor model for adaptation in vertebrate hair cells.Journal of Neuroscience 12, 3291–309.
Cotanche, D. A., Lee, K. H., Stone, J. S. &Picard, D. A. (1994) Hair cell regeneration in the bird cochlea following noise damage or ototoxic drug damage.Anatomy and Embryology 189, 1–18.
Engstrom, H. &Engstrom, B. (1978) Structure of hairs on cochlear sensory cells.Hearing Research 1, 49–66.
Flock, Å., Bretscher, A. &Weber, K. (1982) Immunohistochemical localisation of several cytoskeletal proteins in inner ear sensory and supporting cells.Hearing Research 6, 75–89.
Forge, A. (1995) Sensory cell regeneration and functional recovery: a review. InScientific Basis of Noise-induced Hearing Loss (edited byAxellson, A., Hamerink, R. P., Salvi, R. &Henderson, D.) pp. 3–22. New York: Theime Medical Publishers.
Forge, A., Li, L., Corwin, J. T. &Neville, G. (1993) Ultrastructural evidence for hair cell regeneration in the mammalian inner ear.Science 259, 1616–19.
Galfre, G., Howe, S. C., Milstein, C., Butcher, G. W. &Howard, J. C. (1977). Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines.Nature 266, 550–2.
Gillespie, P. G. &Hudspeth, A. J. (1991) High-purity isolation of bullfrog hair bundles and subcellular and topological localisation of constituent proteins.Journal of Cell Biology 112, 625–40.
Gillespie, P. G. &Hudspeth, A. J. (1993) Adenine nucleoside diphosphates block adaptation of mechanoelectrical transduction in hair cells.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 90, 2710–14.
Gillespie, P. G., Wagner, M. C. &Hudspeth, A. J. (1993) Identification of a 120 kd hair-bundle myosin located near stereociliary tips.Neuron 11, 581–94.
Goodyear, R. &Richardson, G. P. (1992) Distribution of the 275 kD hair-cell antigen and cell surface specialisations on auditory and vestibular hair bundles in the chicken inner ear.Journal of Comparative Neurology 325, 243–56.
Goodyear, R., Holley, M. C. &Richardson, G. P. (1995) Hair and supporting cell differentiation during development of the avian inner ear.Journal of Comparative Neurology 351, 81–93.
Hawkins, J. E. (1976) Drug ototoxicity. InHandbook of Sensory Physiology Vol 3 (edited byKedial, W. D. &Neff, W. D.) pp. 707–48. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Hirokawa, N. &Tilney, L. G. (1982) Interactions between actin filaments and between actin filaments and membranes in quick-frozen and deeply etched hair cells of the chick ear.Journal of Cell Biology 95, 249–61.
Holley, M. C. (1989) Purification of mammalian cochlear hair cells using small volume Percoll density gradients.Journal of Neuroscience Methods 27, 219–24.
Holley, M. C. (1992) A simplein vitro method for raising monoclonal antibodies to cochlear proteins.Tissue and Cell 24, 613–24.
Holley, M. C. &Richardson, G. P. (1994) Monoclonal antibodies specific for endoplasmic membranes of mammalian cochlear outer hair cells.Journal of Neurocytology 23, 87–96.
Kaloyanides, G. J. &Pastoriza-Munoz, E. (1980) Aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity.Kidney International 18, 571–82.
Kelley, M. W., Xu, X-M., Wagner, M. A., Warchol, M. E. &Corwin, J. T. (1993) The developing organ of Corti contains retinoic acid and forms supernumerary hair cells in response to exogenous retinoic acid in culture.Development 119, 1041–53.
Kelley, M. W., Talreja, D. R. &Corwin, J. T. (1995) Replacement of hair cells after laser microbeam irradiation in cultured organs of Corti from embryonic and neonatal mice.Journal of Neuroscience 15, 3013–26.
Killick, R., Malenczak, C. &Richardson, G. P. (1993) The protein composition of the avian tectorial membrane.Hearing Research 64, 21–38.
Kros, C. J., Rusch, A. &Richardson, G. P. (1992) Mechanoelectrical transducer currents in hair cells of the cultured neonatal mouse cochlea.Proceedings of the Royal Society B249, 185–93.
Lefebvre, P. P. Malgrange, B., Staecker, H., Moonen, G. &Van De Water, T. R. (1993) Retinoic acid stimulates regeneration of mammalian auditory hair cells.Science 260, 692–5.
Little, K. F. &Neugebauer, D.-C. (1985) Interconnections between the stereovilli of the fish inner ear. II. Systematic investigation of saccular hair bundles fromRutilus rutilus (Teleostei).Cell and Tissue Research 242, 427–32.
Metcalf, A. B., Chelliah, Y. &Hudspeth, A. J. (1994) Molecular cloning of a myosin Ibeta isozyme that may mediate adaptation by hair cells of the bullfrog's internal ear.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 91, 11821–5.
Monaghan, P. &Robertson, D. (1990) Freeze-substitution without aldehyde or osmium fixatives: ultrastructure and implication for immunocytochemistry.Journal of Microscopy 258, 355–63.
Munyer, P. D. &Schulte, B. A. (1993) Immunohistochemical localization of keratan sulfate and chondroitin 4- and 6-sulfate proteoglycans in subregions of the tectorial and basilar membranes.Hearing Research 79, 83–93.
Nagel, G., Neugebauer, D.-C., Schmidt, B. &Thurm, U. (1991) Structures transmitting stimulatory force to the sensory hairs of vestibular ampullae of fishes and frog.Cell and Tissue Research 265, 567–78.
Pickles, J. O., Comis, S. D. &Osborne, M. P. (1984) Cross-links between stereocilia in the guinea pig organ of Corti, and their possible role in sensory transduction.Hearing Research 15, 103–12.
Ptok, M., Nair, T. S., Altschuler, R. A., Schacht, J. &Carey, T. E. (1991) Monoclonal antibodies to inner ear antigens: II. Antigens expressed in sensory cell stereocilia.Hearing Research,57, 79–90.
Richardson, G. P., Russell, I. J., Duance, V. C. &Bailey, A. J. (1987) Polypeptide composition of the mammalian tectorial membrane.Hearing Research 25, 45–60.
Richardson, G. P., Bartolami, S. &Russell, I. J. (1990). Identification of a 275-kD protein associated with the apical surfaces of sensory hair cells in the avian inner ear.Journal of Cell Biology 110, 1055–66.
Russell, I. J. &Richardson, G. P. (1987). The morphology and physiology of hair cells in organotypic cultures of the mouse cochlea.Hearing Research,31, 9–24.
Rybak, L. P. (1986) Drug ototoxicity.Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 26, 79–99.
Shepherd, G. M. G. &Corey, D. P. (1994) The extent of adaptation in bullfrog saccular hair cells.Journal of Neuroscience 14, 6217–29.
Shepherd, G. M. G., Barres, B. A. &Corey, D. P. (1989) ‘Bundle-blot’ purification and initial protein characterisation of hair cell stereocilia.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 86, 4873–7.
Slepecky, N. &Chamberlain, S. C. (1985) Immunoelectron microscopic and immunofluorescent localisation of cytoskeletal and muscle-like contractile proteins in inner ear sensory hair cells.Hearing Research 20, 245–60.
Slepecky, N. B., Savage, J. E., Cefaratti, L. K. &Yoo, T. J. (1992) Electron-microscopic localisation of type II, IX and V collagen in the organ of Corti of the gerbil.Cell & Tissue Research 267, 413–18.
Solc, C. F., Derfler, B. H., Duyk, G. M. &Corey, D. P. (1994) Molecular cloning of myosins from the bullfrog saccular macula: a candidate for the hair cell adaptation motor.Auditory Neuroscience 1, 63–75.
Tilney, L. G., Derosier, D. J. &Mulroy, M. J. (1980) The organisation of actin filaments in the stereocilia of cochlear hair cells.Journal of Cell Biology 86, 244–59.
Tokuyasu, K. T. (1980) Immunocytochemistry of ultrathin frozen sections.Histochemical Journal 12, 381–403.
Tsue, T. T., Oesterle, E. C. &Rubel, E. W. (1994) Hair cell regeneration in the inner ear.Otolaryngology-Headand Neck Surgery 111, 281–301.
Turner, C. E. &Burridge, K. (1991) Transmembrane molecular assemblies in cell-extracellular matrix interaction.Current Opinions in Cell Biology 5, 849–53.
Walker, R. G., Hudspeth, A. J. &Gillespie, P. G. (1993) Calmodulin and calmodulin-binding proteins in hair bundles.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 90, 2807–11.
Warchol, M. E., Lambert, P. R., Goldstein, B. J., Forge, A. &Corwin, J. T. (1993) Regenerative proliferation in inner ear sensory epithelia from adult guinea pigs and humans.Science 259, 1619–22.
Wataya, H., Handa, K., Hozawa, K., Takasaka, T., Cunningham, D., Rubel, E. W. &Hakomori, S. (1994) A characteristic protein highly expressed in guinea pig inner ear, defined by monoclonal antibody WH-1.Hearing Research 72, 254–62.
Zajic, G., Nair, T. S., Ptok, M., Van Waes, C., Altschuler, R. A., Schacht, J. &Carey, T. S. (1991) Monoclonal antibodies to inner ear antigens: I. Antigens expressed by supporting cells of the guinea pig cochlea.Hearing Research,52, 59–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holley, M.C., Nishida, Y. Monoclonal antibody markers for early development of the stereociliary bundles of mammalian hair cells. J Neurocytol 24, 853–864 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01179984
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01179984